spring-cloud-pipelines is no longer actively maintained by VMware, Inc.
Migration
This project is deprecated. It was migrated to: Cloud Pipelines. You can read more about it here.
Spring Cloud Pipelines
Spring, Spring Boot, and Spring Cloud are tools that let developers speed up the time of creating new business features. It is common knowledge, however, that the feature is only valuable if it is in production. That is why companies spend a lot of time and resources on building their own deployment pipelines.
This project tries to solve the following problems:
-
Creation of a common deployment pipeline.
-
Propagation of good testing and deployment practices.
-
Reducing the time required to deploy a feature to production.
A common way of running, configuring, and deploying applications lowers support costs and time needed by new developers to blend in when they change projects.
Introduction
This section describes the rationale behind the opinionated pipeline. We go through each deployment step and describe it in detail.
|
Important
|
You do not need to use all the pieces of Spring Cloud Pipelines. You can (and should) gradually migrate your applications to use those pieces of Spring Cloud Pipelines that you think best suit your needs. |
Five-second Introduction
Spring Cloud Pipelines provides scripts, configuration, and convention for automated deployment pipeline creation for Jenkins and Concourse with Cloud Foundry or Kubernetes. We support JVM languages, PHP, and NodeJS. Since SC-Pipelines uses bash scripts, you can use it with whatever automation server you have.
Five-minute Introduction
Spring Cloud Pipelines comes with bash scripts (available under common/src/main/bash)
that represent the logic of all steps in our opinionated deployment pipeline.
Since we believe in convention over configuration, for the supported framework and
languages, we assume that the projects follow certain conventions of task naming,
profile setting, and so on. That way, if you create a new application,
your application can follow those conventions and the deployment pipeline works.
Since no one pipeline can serve the purposes of all
teams in a company, we believe that minor deployment pipeline tweaking should take place.
That is why we allow the usage of that sc-pipelines.yml descriptor, which allows for
provide some customization.
From the pipeline visualization perspective, we have prepared templates for Concourse and Jenkins (through the Jenkins Job DSL and Jenkinsfile). That means you can reuse them immediately to visualize a deployment pipeline. If you use some other tool for continuous delivery, you can set the visualization yourself and reference the bash scripts for each step. In other words, Spring Cloud Pipelines can be reused with any continuous delivery tool.
How to Use It
This repository can be treated as a template for your pipeline. We provide some opinionated implementation that you can alter to suit your needs. To use it, we recommend downloading the Spring Cloud Pipelines repository as a zip file, unzipping it in a directory, initializing a Git project in that directory, and then modifying the project to suit your needs. The following bash script shows how to do so:
$ # pass the branch (e.g. master) or a particular tag (e.g. v1.0.0.RELEASE)
$ SC_PIPELINES_RELEASE=...
$ curl -LOk https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines/archive/${SC_PIPELINES_RELEASE}.zip
$ unzip ${SC_PIPELINES_RELEASE}.zip
$ cd spring-cloud-pipelines-${SC_PIPELINES_RELEASE}
$ git init
$ # modify the pipelines to suit your needs
$ git add .
$ git commit -m "Initial commit"
$ git remote add origin ${YOUR_REPOSITORY_URL}
$ git push origin masterTo keep your repository aligned with the changes in the upstream repository, you can also
clone the repository. To not have many merge conflicts, we recommend using the custom
folder hooks to override functions.
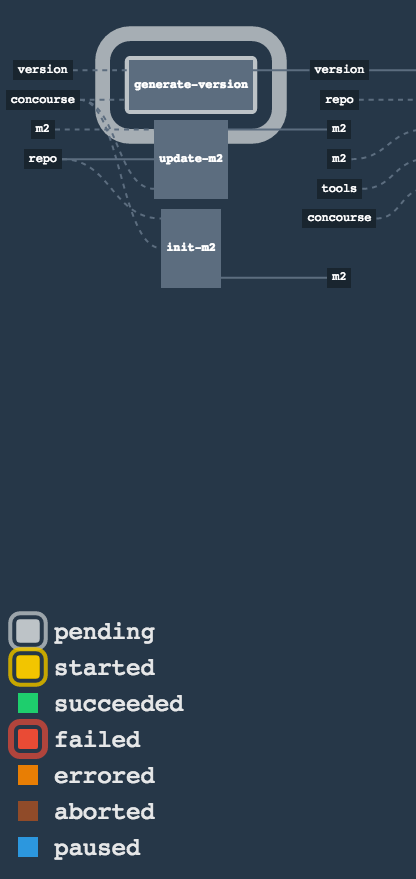
How It Works
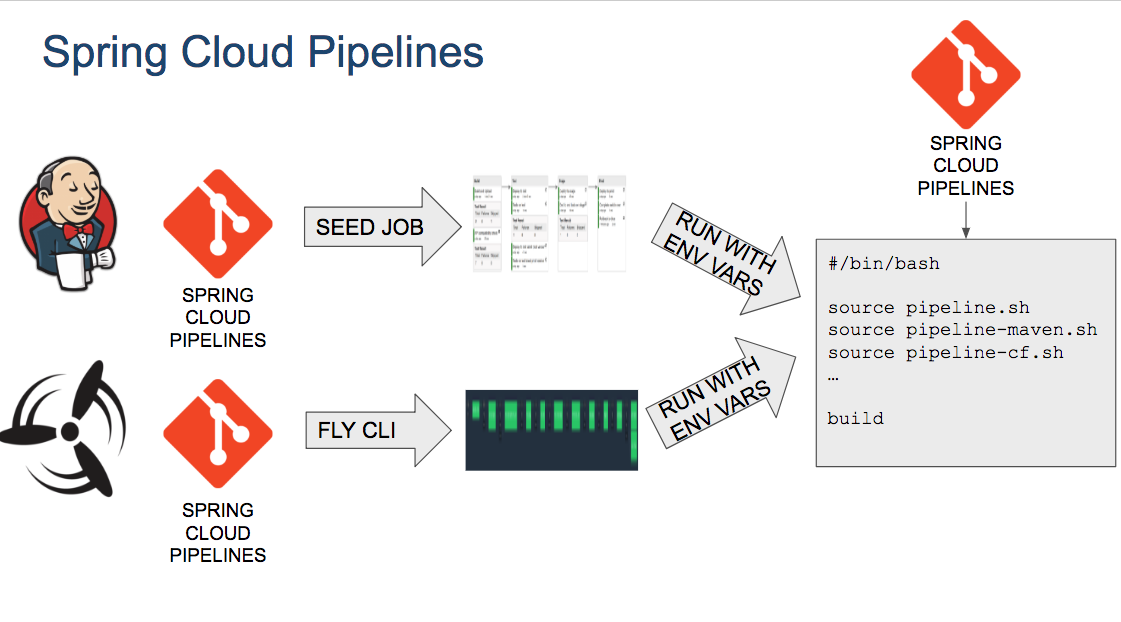
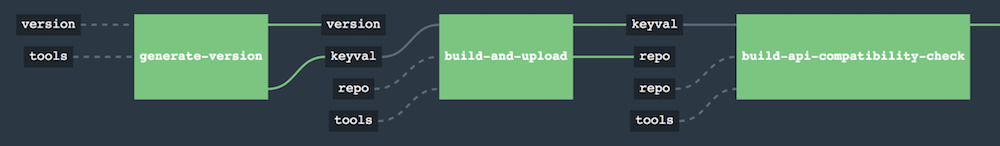
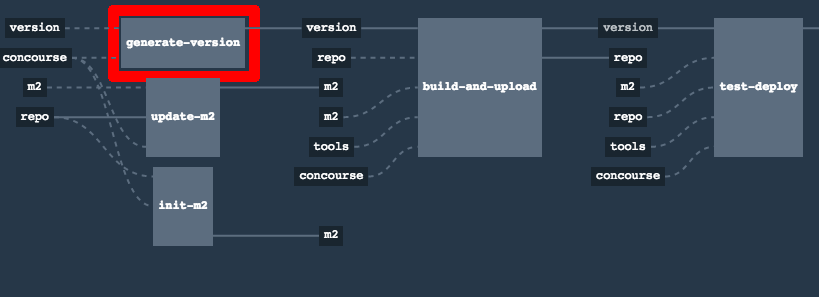
As the following image shows, Spring Cloud Pipelines contains logic to generate a pipeline and the runtime to execute pipeline steps.
Once a pipeline is created (for example, by using the Jenkins Job DSL or from a Concourse
templated pipeline), when the jobs are ran, they clone or download Spring Cloud Pipelines
code to run each step. Those steps run functions that are
defined in the commons module of Spring Cloud Pipelines.
Spring Cloud Pipelines performs steps to guess what kind of a project your repository is (for example, JVM or PHP) and what framework it uses (Maven or Gradle), and it can deploy your application to a cloud (Cloud Foundry or Kubernetes). You can read about how it works by reading the How the Scripts Work section.
All of that happens automatically if your application follows the conventions. You can read about them in the Project Opinions section.
Supported Languages
Currently, we support the following languages:
-
JVM
-
Maven wrapper-based project
-
Gradle wrapper-based project
-
-
PHP
-
Composer-based project
-
-
NPM
Centralized Pipeline Creation
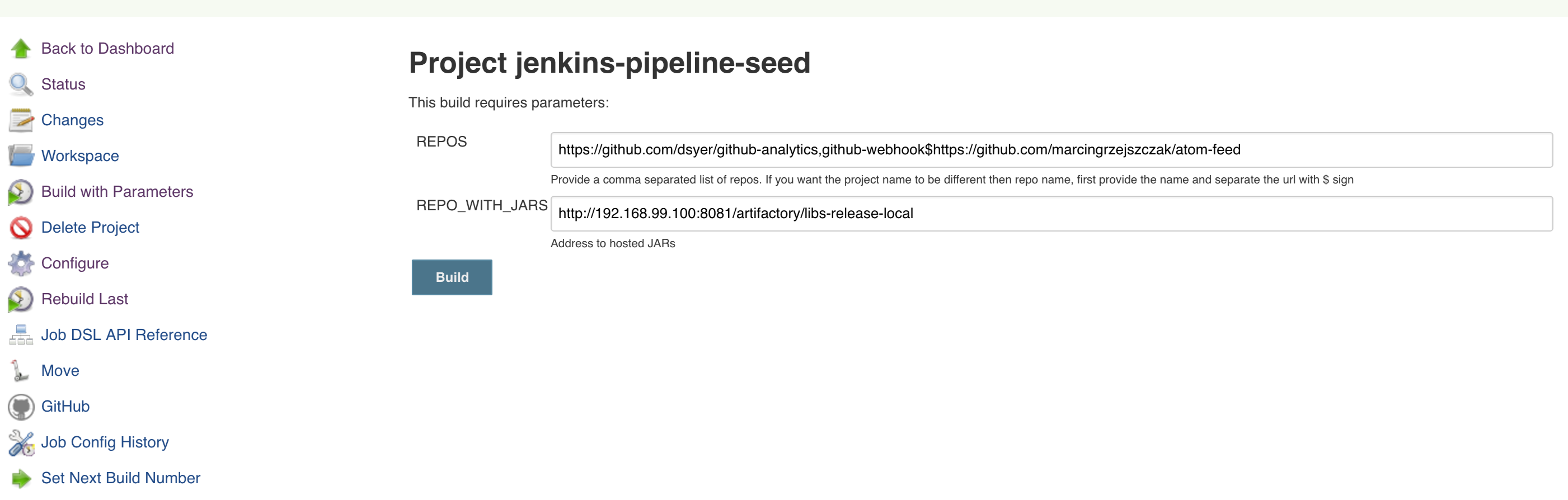
You can use Spring Cloud Pipelines to generate pipelines for all the projects in your system. You can scan all your repositories (for example, you can call the Stash or Github API to retrieve the list of repositories) and then:
-
For Jenkins, call the seed job and pass the
REPOSparameter, which contains the list of repositories. -
For Concourse, call
flyand set the pipeline for every repository.
|
Tip
|
We recommend using Spring Cloud Pipelines this way. |
A Pipeline for Each Repository
You can use Spring Cloud Pipelines in such a way that each project contains its own pipeline definition in its code. Spring Cloud Pipelines clones the code with the pipeline definitions (the bash scripts), so the only piece of logic that needs to be in your application’s repository is the pipeline definition.
For Jenkins, you need to either set up the Jenkinsfile
or the jobs by using the Jenkins Job DSL plugin in your repo.
Then, in Jenkins, whenever you set up a new pipeline for a repository,
you can reference the pipeline definition in that repo.
For Concourse, each project contains its own pipeline steps,
and it is up to the project to set up the pipeline.
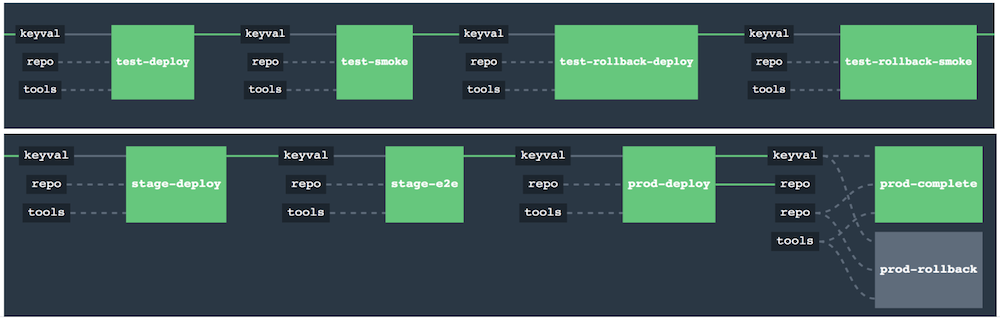
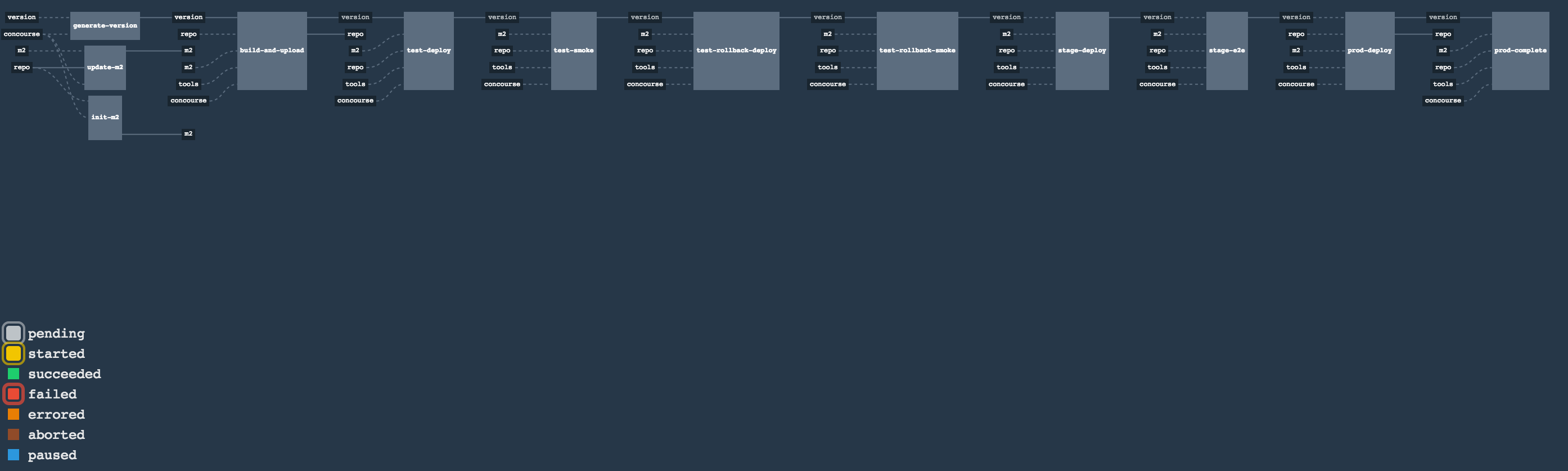
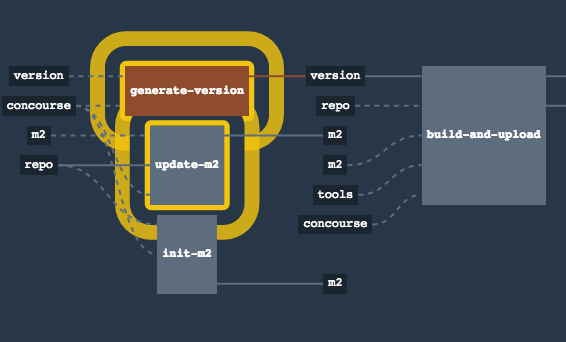
The Flow
The following images show the flow of the opinionated pipeline:
We first describe the overall concept behind the flow and then split it into pieces and describe each piece independently.
===Vocabulary
This section defines some common vocabulary. We describe four typical environments in terms of running the pipeline.
Environments
We typically encounter the following environments:
-
build environment is a machine where the building of the application takes place. It is a continuous integration or continuous delivery tool worker.
-
test is an environment where you can deploy an application to test it. It does not resemble production, because we cannot be sure of its state (which application is deployed there and in which version). It can be used by multiple teams at the same time.
-
stage is an environment that does resemble production. Most likely, applications are deployed there in versions that correspond to those deployed to production. Typically, staging databases hold (often obfuscated) production data. Most often, this environment is a single environment shared between many teams. In other words, in order to run some performance and user acceptance tests, you have to block and wait until the environment is free.
-
prod is the production environment where we want our tested applications to be deployed for our customers.
Tests
We typically encounter the following kinds of tests:
-
Unit tests: Tests that run on the application during the build phase. No integrations with databases or HTTP server stubs or other resources take place. Generally speaking, your application should have plenty of these tests to provide fast feedback about whether your features work.
-
Integration tests: Tests that run on the built application during the build phase. Integrations with in-memory databases and HTTP server stubs take place. According to the test pyramid, in most cases, you should not have many of these kind of tests.
-
Smoke tests: Tests that run on a deployed application. The concept of these tests is to check that the crucial parts of your application are working properly. If you have 100 features in your application but you gain the most money from five features, you could write smoke tests for those five features. We are talking about smoke tests of an application, not of the whole system. In our understanding inside the opinionated pipeline, these tests are executed against an application that is surrounded with stubs.
-
End-to-end tests: Tests that run on a system composed of multiple applications. These tests ensure that the tested feature works when the whole system is set up. Due to the fact that it takes a lot of time, effort, and resources to maintain such an environment and that these tests are often unreliable (due to many different moving pieces, such as network, database, and others), you should have a handful of those tests. They should be only for critical parts of your business. Since only production is the key verifier of whether your feature works, some companies do not even want to have these tests and move directly to deployment to production. When your system contains KPI monitoring and alerting, you can quickly react when your deployed application does not behave properly.
-
Performance testing: Tests run on an application or set of applications to check if your system can handle a big load. In the case of our opinionated pipeline, these tests can run either on test (against a stubbed environment) or on staging (against the whole system).
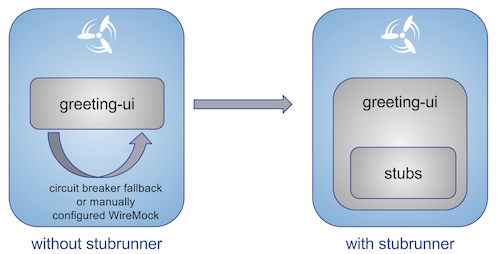
Testing against Stubs
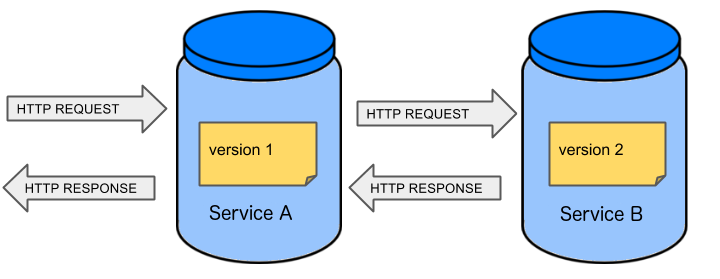
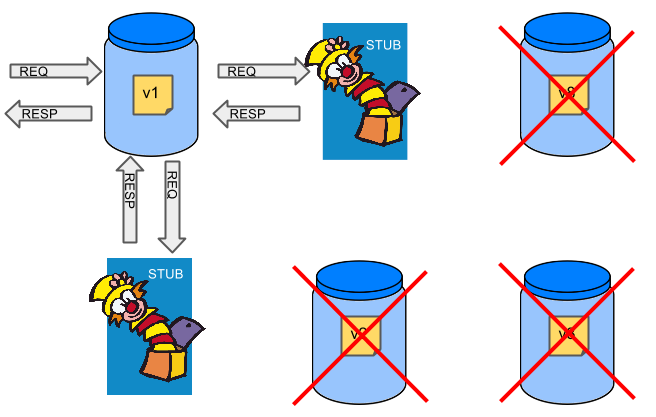
Before we go into the details of the flow, consider the example described by the following image:
When you have only a handful of applications, end-to-end testing is beneficial. From the operations perspective, it is maintainable for a finite number of deployed instances. From the developers perspective, it is nice to verify the whole flow in the system for a feature.
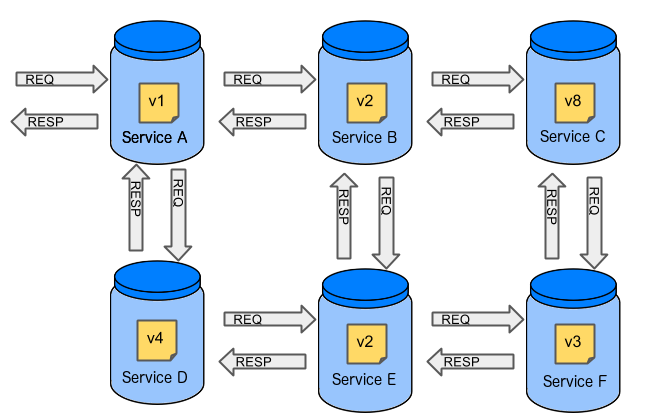
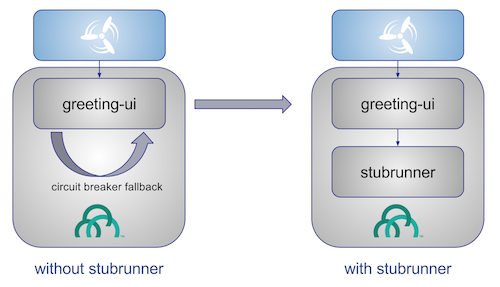
In the case of microservices, the scale starts to be a problem, as the following image shows:
The following questions arise:
-
Should I queue deployments of microservices on one testing environment or should I have an environment per microservice?
-
If I queue deployments, people have to wait for hours to have their tests run. That can be a problem
-
-
To remove that issue, I can have an environment for each microservice.
-
Who will pay the bills? (Imagine 100 microservices, each having each own environment).
-
Who will support each of those environments?
-
Should we spawn a new environment each time we execute a new pipeline and then wrap it up or should we have them up and running for the whole day?
-
-
In which versions should I deploy the dependent microservices - development or production versions?
-
If I have development versions, I can test my application against a feature that is not yet on production. That can lead to exceptions in production.
-
If I test against production versions, I can never test against a feature under development anytime before deployment to production.
-
One of the possibilities of tackling these problems is to not do end-to-end tests.
The following image shows one solution to the problem, in the form of stubbed dependencies:
If we stub out all the dependencies of our application, most of the problems presented earlier disappear. There is no need to start and setup the infrastructure required by the dependent microservices. That way, the testing setup looks like the following image:
Such an approach to testing and deployment gives the following benefits (thanks to the usage of Spring Cloud Contract):
-
No need to deploy dependent services.
-
The stubs used for the tests run on a deployed microservice are the same as those used during integration tests.
-
Those stubs have been tested against the application that produces them (see Spring Cloud Contract for more information).
-
We do not have many slow tests running on a deployed application, so the pipeline gets executed much faster.
-
We do not have to queue deployments. We test in isolation so that pipelines do not interfere with each other.
-
We do not have to spawn virtual machines each time for deployment purposes.
However, this approach brings the following challenges:
-
No end-to-end tests before production. You do not have full certainty that a feature is working.
-
The first time the applications interact in a real way is on production.
As with every solution, it has its benefits and drawbacks. The opinionated pipeline lets you configure whether you want to follow this flow or not.
General View
The general view behind this deployment pipeline is to:
-
Test the application in isolation.
-
Test the backwards compatibility of the application, in order to roll it back if necessary.
-
Allow testing of the packaged application in a deployed environment.
-
Allow user acceptance tests and performance tests in a deployed environment.
-
Allow deployment to production.
The pipeline could have been split to more steps, but it seems that all of the aforementioned actions fit nicely in our opinionated proposal.
Pipeline Descriptor
Each application can contain a file (called sc-pipelines.yml) with the following structure:
language_type: jvm
pipeline:
# used for multi module projects
main_module: things/thing
# used for multi projects
project_names:
- monoRepoA
- monoRepoB
# should deploy to stage automatically and run e2e tests
auto_stage: true
# should deploy to production automatically
auto_prod: true
# should the api compatibility check be there
api_compatibility_step: true
# should the test rollback step be there
rollback_step: true
# should the stage step be there
stage_step: true
# should the test step (including rollback) be there
test_step: true
lowercaseEnvironmentName1:
# used by spinnaker
deployment_strategy: HIGHlANDER
# list of services to be deployed
services:
- type: service1Type
name: service1Name
coordinates: value
- type: service2Type
name: service2Name
key: value
lowercaseEnvironmentName2:
# used by spinnaker
deployment_strategy: HIGHlANDER
# list of services to be deployed
services:
- type: service3Type
name: service3Name
coordinates: value
- type: service4Type
name: service4Name
key: valueIf you have a multi-module project, you should point to the folder that contains the
module that produces the fat jar. In the preceding example, that module
would be present under the things/thing folder. If you have a single module project,
you need not create this section.
For a given environment, we declare a list of infrastructure services that we want to have deployed. Services have:
-
type(examples:eureka,mysql,rabbitmq, andstubrunner): This value gets then applied to thedeployServiceBash function -
[KUBERNETES]: For
mysql, you can pass the database name in thedatabaseproperty. -
name: The name of the service to get deployed. -
coordinates: The coordinates that let you fetch the binary of the service. It can be a Maven coordinate (groupid:artifactid:version), a docker image (organization/nameOfImage), and so on. -
Arbitrary key value pairs, which let you customize the services as you wish.
Pipeline Descriptor for Cloud Foundry
When deploying to Cloud Foundry you can provide services of the following types:
-
type: broker-
broker: The name of the CF broker -
plan: The name of the plan -
params: Additional parameters are converted to JSON -
useExisting: Whether to use an existing one or create a new one (defaults tofalse)
-
-
type: app-
coordinates: The Maven coordinates of the stub runner jar -
manifestPath: The path to the manifest for the stub runner jar
-
-
type: cups-
params: Additional parameters are converted to JSON
-
-
type: cupsSyslog-
url: The URL to the syslog drain
-
-
type: cupsRoute-
url: The URL to the route service
-
-
type: stubrunner-
coordinates: The Maven coordinates of the stub runner jar -
manifestPath: The path to the manifest for the stub runner jar
-
The following example shows the contents of a YAML file that defines the preceding values:
# This file describes which services are required by this application
# in order for the smoke tests on the TEST environment and end to end tests
# on the STAGE environment to pass
# lowercase name of the environment
test:
# list of required services
services:
- name: config-server
type: broker
broker: p-config-server
plan: standard
params:
git:
uri: https://github.com/ciberkleid/app-config
useExisting: true
- name: cloud-bus
type: broker
broker: cloudamqp
plan: lemur
useExisting: true
- name: service-registry
type: broker
broker: p-service-registry
plan: standard
useExisting: true
- name: circuit-breaker-dashboard
type: broker
broker: p-circuit-breaker-dashboard
plan: standard
useExisting: true
- name: stubrunner
type: stubrunner
coordinates: io.pivotal:cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot:0.0.1.M1
manifestPath: sc-pipelines/manifest-stubrunner.yml
stage:
services:
- name: config-server
type: broker
broker: p-config-server
plan: standard
params:
git:
uri: https://github.com/ciberkleid/app-config
- name: cloud-bus
type: broker
broker: cloudamqp
plan: lemur
- name: service-registry
type: broker
broker: p-service-registry
plan: standard
- name: circuit-breaker-dashboard
type: broker
broker: p-circuit-breaker-dashboard
plan: standardAnother CF specific property is artifact_type. Its value can be either binary or source.
Certain languages (such as Java) require a binary to be uploaded, but others (such as PHP)
require you to push the sources. The default value is binary.
Project Setup
Spring Cloud Pipelines supports three main types of project setup:
-
Single Project -
Multi Module -
Multi Project(also known as mono repo)
A Single Project is a project that contains a single module that gets
built and packaged into a single, executable artifact.
A Multi Module project is a project that contains multiple modules.
After building all modules, one gets packaged into a single, executable artifact.
You have to point to that module in your pipeline descriptor.
A Multi Project is a project that contains multiple projects. Each of those
projects can in turn be a Single Project or a Multi Module project. Spring
Cloud Pipelines assume that, if a PROJECT_NAME environment
variable corresponds to a folder with the same name in the root of the
repository, this is the project it should build. For example, for
PROJECT_NAME=something, if there’s a folder named something, then Spring Cloud Pipelines
treats the something directory as the root of the something project.
How the Scripts Work
This section describes how the scripts and jobs correspond to each other.
If you need to see detailed documentation of the bash scripts, go to the
code repository and read common/src/main/bash/README.adoc.
Build and Deployment
The following text image (created via textart.io) shows a high-level overview:
+---------+ +-----------+ +-----------+ +-------+ +---------------+
| script | | language | | framework | | paas | | customization |
+---------+ +-----------+ +-----------+ +-------+ +---------------+
| | | | |
| What is your language? | | | |
|-------------------------------->| | | |
| | | | |
| I'm written in X language | | | |
|<--------------------------------| | | |
| | | | |
| | What framework do you use? | | |
| |--------------------------------->| | |
| | | | |
| | I use Y framework | | |
|<-------------------------------------------------------------------| | |
| | | | |
| I know that you use Z PAAS? | | | |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------->| |
| | | | |
| | Here are all Z-related deployment functions | |
|<-------------------------------------------------------------------------------| |
| | | | |
| Anything custom to override in bash? | | |
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->|
| | | | |
| | | Not this time... |
|<---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| | | | |
| Ok, run the script | | | |
|------------------- | | | |
| | | | | |
|<------------------ | | | |
| | | | |Before we run the script, we need to answer a few questions related to your repository:
-
What is your language (for example,
jvm,php, or something else)? -
what framework do you use (for example,
mavenorgradle)? -
what PAAS do you use (for example,
cfork8s)?
The following sequence diagram (created via textart.io) describes how the sourcing of bash scripts takes place:
+---------+ +-----------+ +-------------+ +-----------+ +-----------+ +-------+ +---------+
| script | | pipeline | | projectType | | language | | framework | | paas | | custom |
+---------+ +-----------+ +-------------+ +-----------+ +-----------+ +-------+ +---------+
| | | | | | |
| [source pipeline.sh] | | | | | |
|--------------------------------------------------->| | | | | |
| | ------------------------------\ | | | | |
| |-| loading functions, env vars | | | | | |
| | |-----------------------------| | | | | |
| -----------------------------------------\ | | | | | |
| | hopefully all functions get overridden |-| | | | | |
| | otherwise nothing will work | | | | | | |
| |----------------------------------------| | | | | | |
| | Source the [projectType/pipeline-projectType.sh] | | | | |
| |-------------------------------------------------------->| | | | |
| | -------------------------------\ | | | | |
| | | What do we have here...? |-| | | | |
| | | A [mvnw] file, | | | | | |
| | | it has to be a [jvm] project | | | | | |
| | |------------------------------| | Source [pipeline-jvm.sh] | | | |
| | |------------------------------->| | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | Maven or Gradle? | | |
| | | |----------------------->| | |
| | | | | ----------------------------------------\ | |
| | | | |-| There's a [mvnw] file? | | |
| | | | | | So the [PROJECT_TYPE] must be [maven] | | |
| | | | | |---------------------------------------| | |
| | | | It's a Maven project | | |
| |<------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | |
| | | | | | |
| | The [PAAS_TYPE] is [cf] so I'll source [pipeline-cf.sh] | | | | |
| |---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->| |
| | | | | | -------------------------------\ |
| | | | | |-| Loading all | |
| | | | | | | deployment-related functions | |
| -------------------------------\ | | | | | |------------------------------| |
| | Ok, we know that it's Maven |-| | | | | |
| | and should be deployed to CF | | | | | | |
| |------------------------------| | | | | | |
| | Try to source [custom/build_and_upload.sh] | | | | |
| |------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------>|
| | | | | | | ----------------------------\
| | | | | | |-| No such file so |
| | | | | | | | nothing custom to be done |
| ---------------------------------------------\ | | | | | | |---------------------------|
|-| All build related functions | | | | | | |
| | overridden by language / framework scripts | | | | | | |
| -------------------------------\-------------| | | | | | |
|-| All deploy related functions | | | | | | |
| | overridden by paas scripts | | | | | | |
| |------------------------------| | | | | | |
| run [build] function | | | | | |
|--------------------- | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
|<-------------------- | | | | | |
| | | | | | |The process works as follows:
-
A script (for example,
build_and_upload.sh) is called. -
It sources the
pipeline.shscript that contains all the essential function “interfaces” and environment variables. -
pipeline.shneeds information about the project type. It sourcesprojectType/pipeline-projectType.sh. -
projectType/pipeline-projectType.shcontains logic to determine the language.-
Verify whether a repository contains files that correspond to the given languages (for example,
mvnworcomposer.json). -
Verify whether a concrete framework that we support (for example,
mavenorgradle) is present.
-
-
Once we know what the project type is, we can deal with PAAS. Depending on the value of the
PAAS_TYPEenvironment variable, we can source proper PAAS functions (for example,pipeline-cf.shfor Cloud Foundry). -
Determine whether we can do some further customization.
-
Search for a file called
${sc-pipelines-root}/common/src/main/bash/custom/build_and_upload.shto override any functions you want.
-
-
Run the
buildfunction frombuild_and_upload.sh
Project Crawler
In Jenkins, you can generate the deployment pipelines by passing an environment variable with a comma-separated list of repositories. This, however, does not scale. We would like to automatically fetch a list of all repositories from a given organization and team.
To do so, we use the Project Crawler library, which can:
-
Fetch all projects for a given organization.
-
Fetch contents of a file for a given repository.
The following diagram depicts this situation:
+---------+ +-------+ +-------------+ +---------+
| Jenkins | | Seed | | SCPipelines | | Github |
+---------+ +-------+ +-------------+ +---------+
| | | |
| Copy the seed job from the repo | | |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->| |
| | | |
| Run seed job to generate Spinnaker pipelines and jobs | | |
|---------------------------------------------------------->| | |
| | | |
| | Crawl org [foo] and fetch all repositories | |
| |--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->|
| | | |
| | In org [foo] there [a,b,c] repos |
| |<---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| | | |
| | For each repo fetch pipeline descriptor | |
| |--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->|
| | | |
| | There you go. [a] wants no [test] env, [b] no [stage] env, [c] wants all envs |
| |<---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| | | |
| | Build pipelines. For [a] without [test], for [b] without [stage]. All for [c] | |
| |------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |
| | | | |
| |<----------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
| ----------------------------\ | | |
| | By having descriptors, |-| | |
| | we can tune the pipelines | | | |
| | as the app wanted it to. | | | |
| |---------------------------| | Build jobs / pipelines for [a,b,c] repos | |
| |----------------------------------------- | |
| | | | |
| |<---------------------------------------- | |
| | | |Thanks to the Project Crawler, you can run the seed job, and ,automatically, all the new repositories are picked and pipelines are created for them. Project Crawler supports repositories stored at Github, Gitlab, and Bitbucket. You can also register your own implementation. See the Project Crawler repository for more information.
How Scripts Work with Spinnaker
With Spinnaker, the deployment pipeline is inside of Spinnaker. No longer do we treat Jenkins or Concourse as a tool that does deployments. In Jenkins, we create only the CI jobs (that is, build and test) and prepare the JSON definitions of Spinnaker pipelines.
The following diagram shows how Jenkins, the seed job for Spinnaker, and Spinnaker cooperate:
+---------+ +-------+ +-------------+ +---------+ +-----------+
| Jenkins | | Seed | | SCPipelines | | Github | | Spinnaker |
+---------+ +-------+ +-------------+ +---------+ +-----------+
| | | | |
| Copy the seed job from the repo | | | |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->| | |
| | | | |
| Run seed job to generate Spinnaker pipelines and jobs | | | |
|---------------------------------------------------------->| | | |
| | | | |
| | Crawl org [foo] and fetch all repositories | | |
| |---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->| |
| | | | |
| | | In org [foo] there [a,b,c] repos | |
| |<----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| |
| | | | |
| | For each repo fetch pipeline descriptor | | |
| |---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->| |
| | | | |
| | There you go. [a] wants no [test], [b] no [stage], [c] wants all | |
| |<----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| |
| | | | |
| | Build pipelines. For [a] without [test], for [b] without [stage]. All for [c] | | |
| |------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | |
| | | | | |
| |<----------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | |
| ----------------------------\ | | | |
| | By having descriptors, |-| | | |
| | we can tune the pipelines | | | | |
| | as the app wanted it to. | | | | |
| |---------------------------| | Build CI jobs for [a,b,c] repos | | |
| |-------------------------------- | | |
| | | | | |
| |<------------------------------- | | |
| | | | |
| | Build Spinnaker pipelines JSON definitions | | |
| |------------------------------------------- | | |
| | | | | |
| |<------------------------------------------ | | |
| | | | |
| Seed job done | | | |
|<----------------------------------------------------------| | | |
| | | | |
| Upload JSON pipelines to Spinnaker | | | |
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->|
| | | | |
| | | | | The pipelines for [a,b,c] successfully created
| | | | |-----------------------------------------------
| | | | | |
| | | | |<----------------------------------------------
| | | | |
| | Waiting for [spinnaker-a-build] build to start & complete |
|<-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| | | | |
| New commit! Running a build [spinnaker-a-build] | | | |
|------------------------------------------------ | | | |
| | | | | |
|<----------------------------------------------- | | | |
| | | | |
| Run the [build_and_upload.sh] script | | | |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->| | |
| | | --------------------------------\ | |
| | |-| Proceed with all the sourcing | | |
| | | | depending on language etc. | | |
| | | |-------------------------------| | |
| | Build completed! | | |
|<-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | |
| | | | |
| [spinnaker-a-build] started and completed | | | |
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->|
| | | | | ------------------------------------\
| | | | |-| Running the rest of the pipeline! |
| | | | | |-----------------------------------|
| | | | |
| | | | | Pipeline for [a] in progress. Deploy [a] to test env
| | | | |-----------------------------------------------------
| | | | | |
| | | | |<----------------------------------------------------
| | | | |
| | Calling [spinnaker-a-test-on-test] to run test on test |
|<-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| | | | |
| [spinnaker-a-test-on-test] started and completed | | | |
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->|
| | | | |
| | | | | ... we continue like this throughout the pipeline ...
| | | | |------------------------------------------------------
| | | | | |
| | | | |<-----------------------------------------------------
| | | | |
| | | | | ... and the pipeline is done
| | | | |-----------------------------
| | | | | |
| | | | |<----------------------------
| | | | |Deployment & languages compatibility matrix
In the following table we present which language is supported by which deployment mechanism.
| Language | CF | K8S | Ansible |
|---|---|---|---|
JVM with Gradle |
|||
JVM with Maven |
|||
PHP with Composer |
|||
NodeJS with NPM |
|||
Dotnet core |
|
Tip
|
For K8S, a deployment unit is a docker image so any language and framework can be used. |
Opinionated Implementation
This section describes a full flow of the demo applications.
|
Important
|
Your applications need not have the same dependencies (such as Eureka) as this demo.
|
For demo purposes, we provide Docker Compose setup with Artifactory, Concourse, and Jenkins tools. Regardless of the CD application, for the pipeline to pass, you need one of the following:
-
A Cloud Foundry instance (for example, Pivotal Web Services or PCF Dev).
-
A Kubernetes cluster (for example, Minikube).
-
The infrastructure applications deployed to the JAR hosting application (for the demo, we provide Artifactory).
-
Eurekafor Service Discovery. -
Stub Runner Bootfor running Spring Cloud Contract stubs.
|
Tip
|
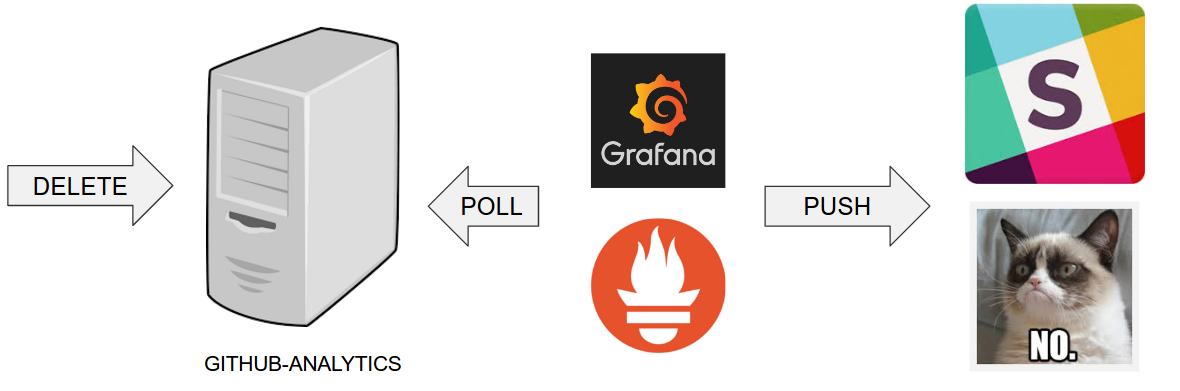
In the demos, we show you how to first build the github-webhook project. That is because
the github-analytics needs the stubs of github-webhook to pass the tests. We also use
references to the github-analytics project, since it contains more interesting pieces as far as testing
is concerned.
|
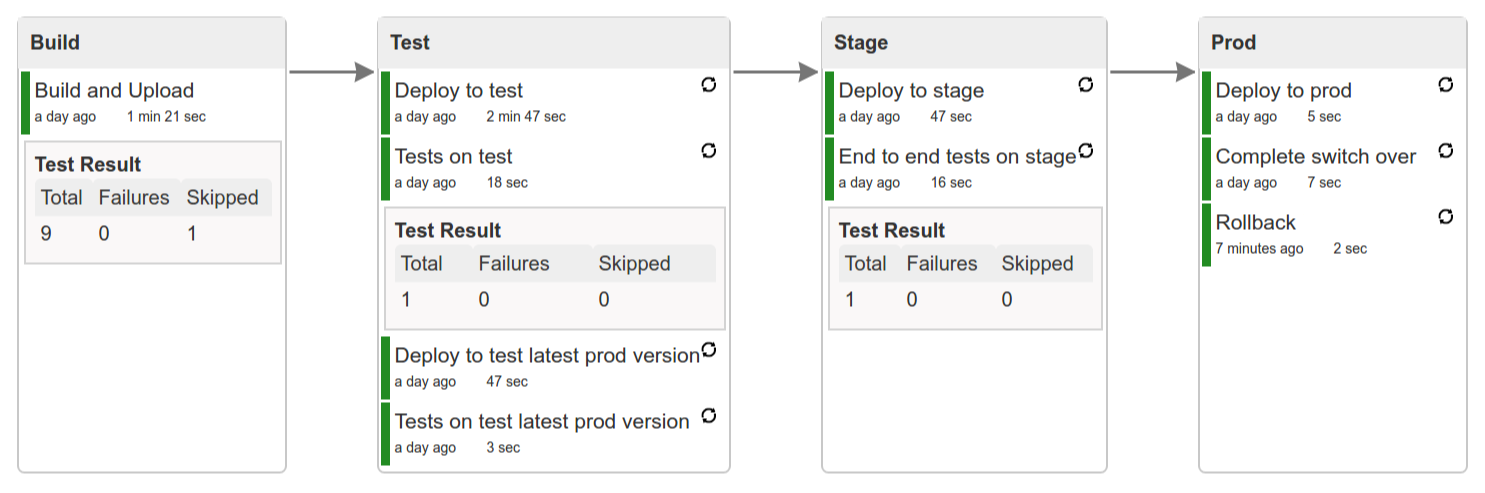
Build
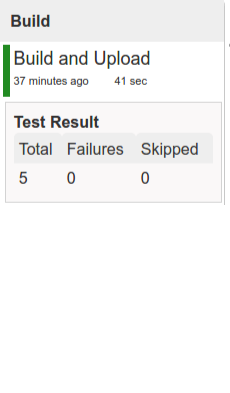
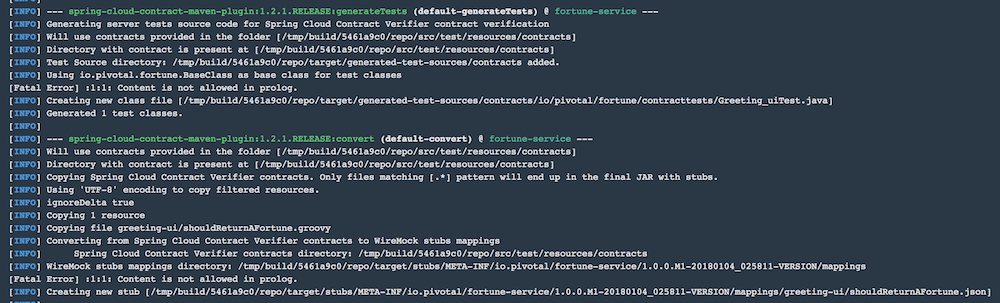
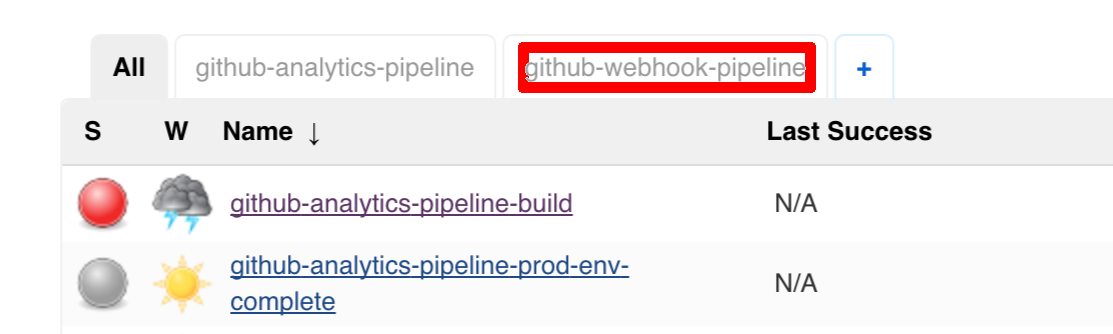
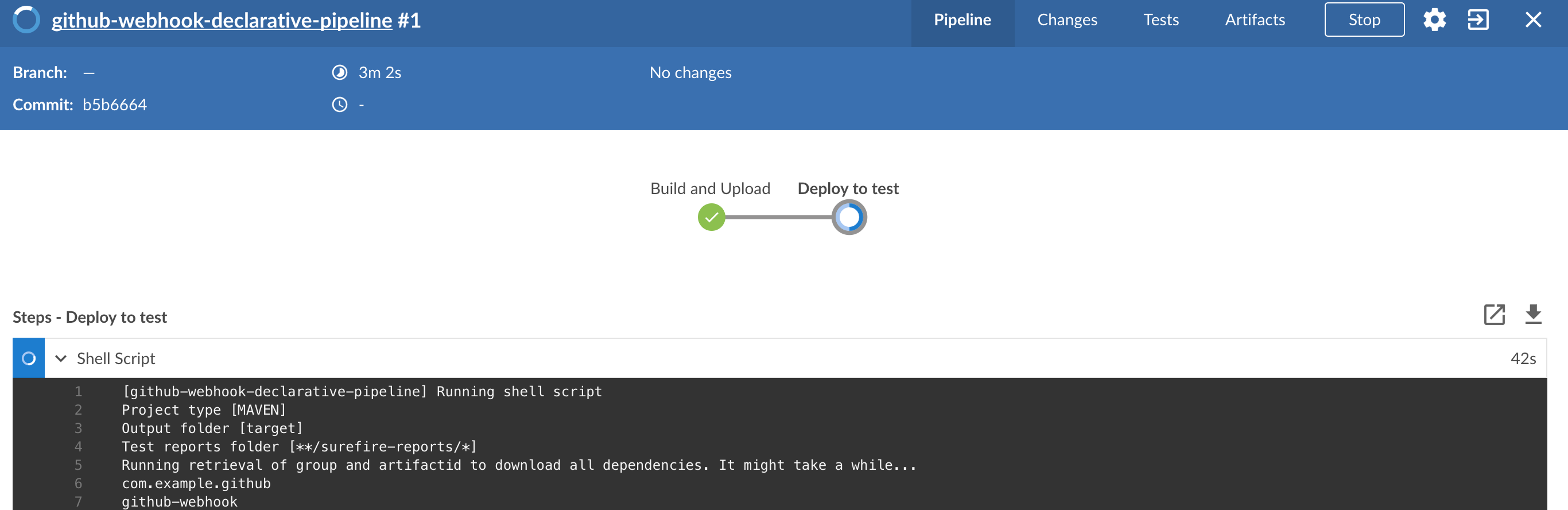
The following image shows the results of building the demo pipeline (which the rest of this chapter describes):
In this step, we generate a version of the pipeline. Next, we run unit, integration, and contract tests. Finally, we:
-
Publish a fat jar of the application.
-
Publish a Spring Cloud Contract jar containing stubs of the application.
-
For Kubernetes, upload a Docker image of the application.
During this phase, we run a Maven build by using Maven Wrapper or a Gradle build by using Gradle Wrapper,
with unit and integration tests. We also tag the repository with dev/${version}. That way, in each
subsequent step of the pipeline, we can retrieve the tagged version. Also, we know
exactly which version of the pipeline corresponds to which Git hash.
Once the artifact is built, we run API compatibility check, as follows:
-
We search for the latest production deployment.
-
We retrieve the contracts that were used by that deployment.
-
From the contracts, we generat API tests to see if the current implementation is fulfilling the HTTP and messaging contracts that the current production deployment has defined (we check backward compatibility of the API).
Test
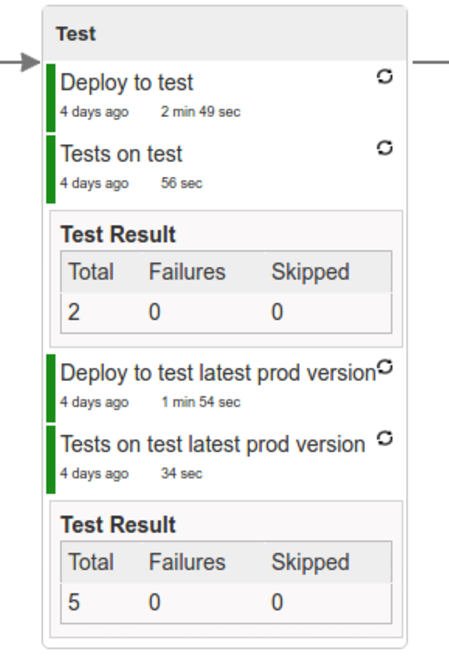
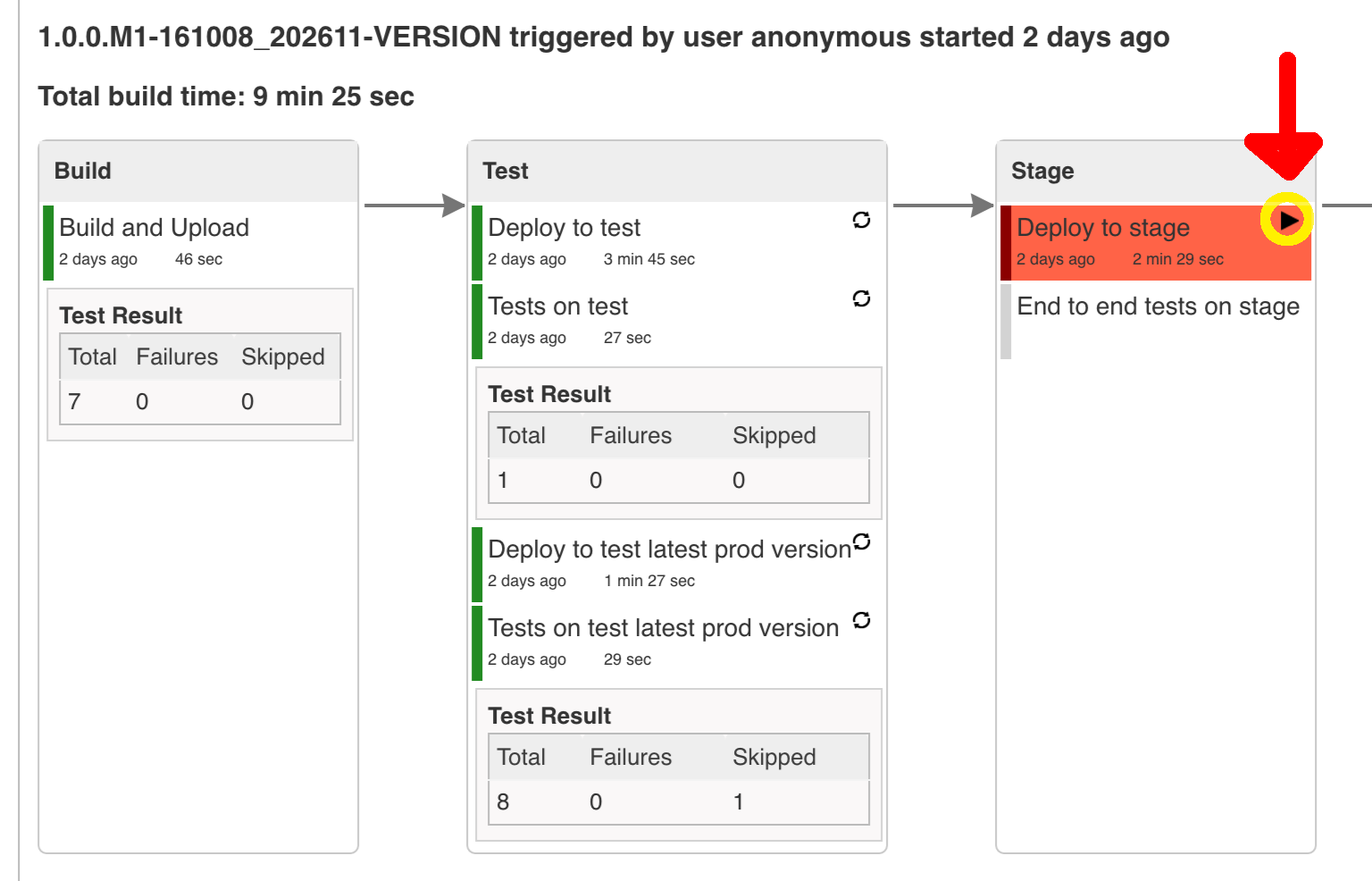
The following image shows the result of doing smoke tests and rolling back:
Here, we:
-
Start a RabbitMQ service in PaaS.
-
Deploying
Eurekainfrastructure application to PaaS. -
Download the fat jar from Nexus and upload it to PaaS. We want the application to run in isolation (be surrounded by stubs).
|
Tip
|
Currently, due to port constraints in Cloud Foundry,
we cannot run multiple stubbed HTTP services in the cloud. To fix this issue, we run
the application with the smoke Spring profile, on which you can stub out all HTTP calls to return
a mocked response.
|
-
If the application uses a database, it gets upgraded at this point by Flyway, Liquibase, or any other migration tool once the application gets started.
-
From the project’s Maven or Gradle build, we extract the
stubrunner.idsproperty that contains all thegroupId:artifactId:version:classifiernotations of dependent projects for which the stubs should be downloaded. -
We upload
Stub Runner Bootand pass the extractedstubrunner.idsto it. That way, we have a running application in Cloud Foundry that downloads all the necessary stubs of our application. -
From the checked-out code, we run the tests available under the
smokeprofile. In the case of theGitHub Analyticsapplication, we trigger a message from theGitHub Webhookapplication’s stub and send the message by RabbitMQ to GitHub Analytics. Then we check whether the message count has increased. -
Once the tests pass, we search for the last production release. Once the application is deployed to production, we tag it with
prod/${version}. If there is no such tag (there was no production release), no rollback tests are run. If there was a production release, the tests get executed. -
Assuming that there was a production release, we check out the code that corresponds to that release (we check out the tag), download the appropriate artifact (either a JAR for Cloud Foundry or a Docker image for Kubernetes), and we upload it to PaaS.
|
Important
|
The old artifact runs against the NEW version of the database. |
We run the old smoke tests against the freshly deployed application, surrounded by stubs.
If those tests pass, we have a high probability that the application is backwards compatible.
* The default behavior is that, after all of those steps, the user can manually click to deploy the
application to a stage environment.
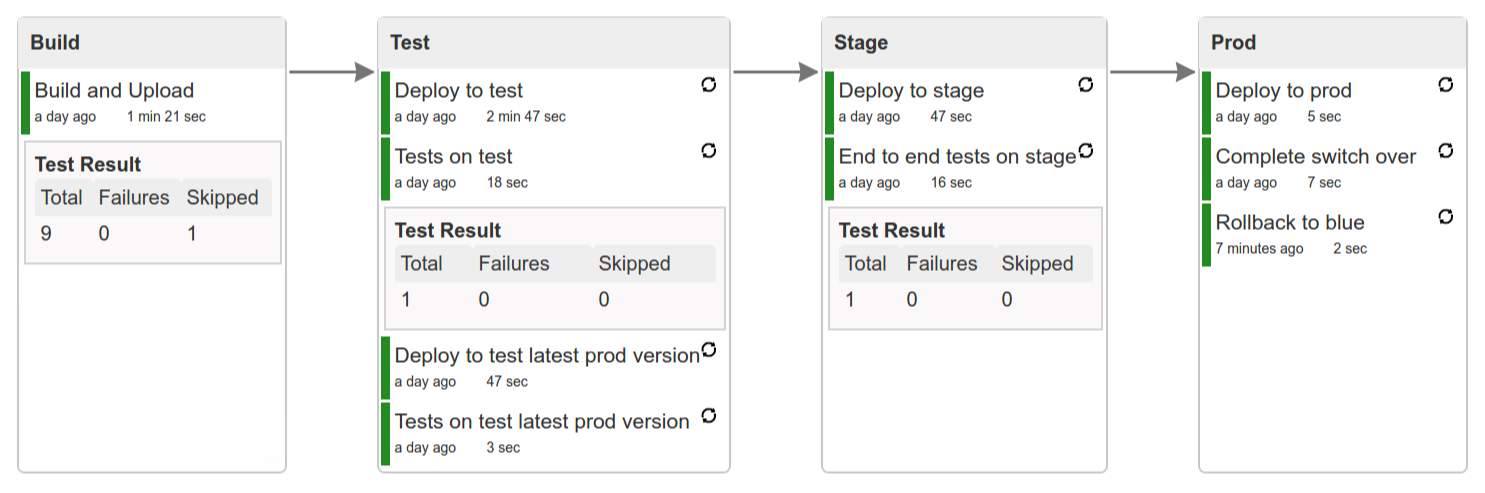
Stage
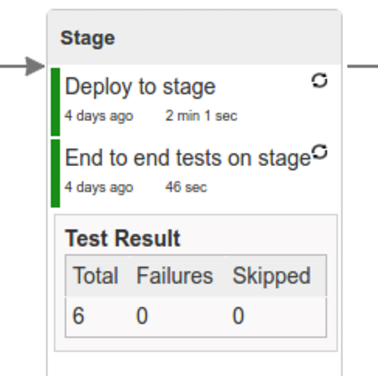
The following image shows the result of deploying to a stage environment:
Here, we:
-
Start a RabbitMQ service in PaaS.
-
Deploy
Eurekainfrastructure application to PaaS. -
Download the artifact (either a JAR for Cloud Foundry or a Docker image for Kubernetes) upload it to PaaS.
Next, we have a manual step in which, from the checked-out code, we run the tests available under the e2e profile. In the
case of the GitHub Analytics application, we send an HTTP message to the GitHub Analytics endpoint. Then we check whether
the received message count has increased.
By default, this step is manual, because the stage environment is often shared between teams and some preparations on databases and infrastructure have to take place before the tests can be run. Ideally, these step should be fully automatic.
Prod
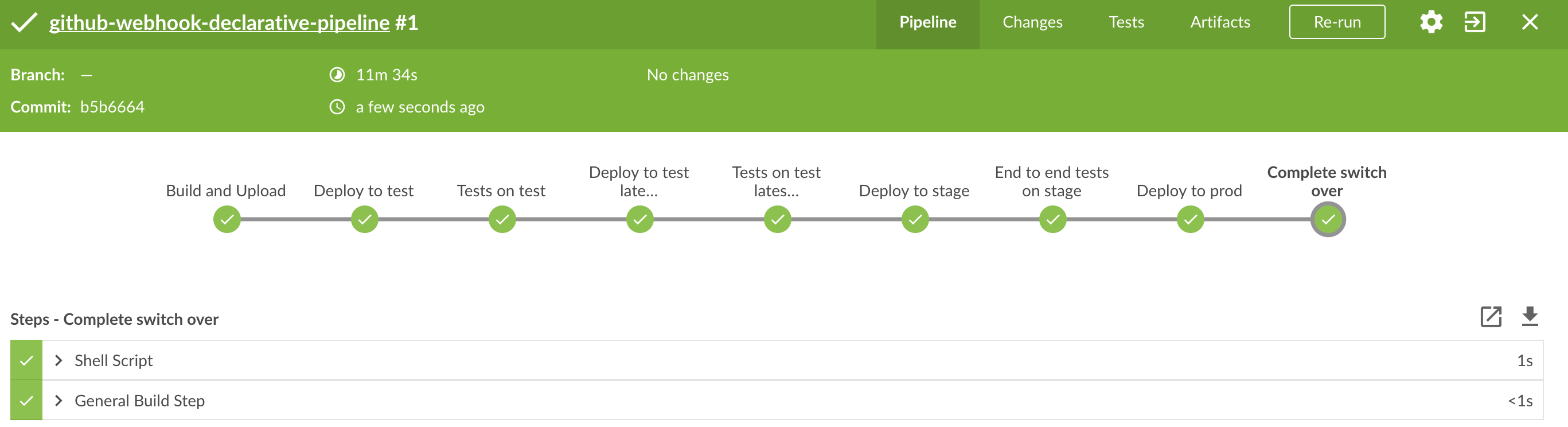
The following image shows the result of deploying to a production environment:
The step to deploy to production is manual. However, ideally, it should be automatic.
|
Important
|
This step does deployment to production. On production, we assume
that you have the infrastructure running. That is why, before you run this step, you
must run a script that provisions the services on the production environment.
For Cloud Foundry, call tools/cf-helper.sh setup-prod-infra.
For Kubernetes, call tools/k8s-helper.sh setup-prod-infra.
|
Here, we:
-
Tag the Git repo with
prod/${version}. -
Download the application artifact (either a JAR for Cloud Foundry or a Docker image for Kubernetes).
-
We do Blue Green deployment:
-
For Cloud Foundry:
-
We rename the current instance of the application (for example,
myServicetomyService-venerable). -
We deploy the new instance of the app under the
fooServicename -
Now, two instances of the same application are running on production.
-
-
For Kubernetes:
-
We deploy a service with the name of the application (for example,
myService) -
We do a deployment with the name of the application with version suffix,with the name escaped to fulfill the DNS name requirements (for example,
fooService-1-0-0-M1-123-456-VERSION). -
All deployments of the same application have the same label
name, which is equal to the application name (for example,myService). -
The service routes the traffic by basing on the
namelabel selector. -
Now two instances of the same application are running in production.
-
-
-
In the
Complete switch over, which is a manual step, we stop the old instance.NoteRemember to run this step only after you have confirmed that both instances work. -
In the
Rollback, which is a manual step,-
We route all the traffic to the old instance.
-
In CF, we do that by ensuring that blue is running and removing green.
-
In K8S, we do that by scaling the number of instances of green to 0.
-
-
We remov the latest prod Git tag.
-
Project Opinions
This section goes through the assumptions we made in the project structure and project properties.
Cloud Foundry Project Opinions
We take the following opinionated decisions for a Cloud Foundry based project:
-
The application is built by using the Maven or Gradle wrapper.
-
The application is deployed to Cloud Foundry.
-
Your application needs a
manifest.ymlCloud Foundry descriptor. -
For the Maven (example project), we assume:
-
Usage of the Maven Wrapper.
-
settings.xmlis parametrized to pass the credentials to push code to Artifactory:-
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_IDcontains the server ID for Artifactory or Nexus deployment. -
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_USERNAMEcontains the username for Artifactory or Nexus deployment. -
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_PASSWORDcontains the password for Artifactory or Nexus deployment.
-
-
Artifacts are deployed by
./mvnw clean deploy. -
We use the
stubrunner.idsproperty to retrieve list of collaborators for which stubs should be downloaded. -
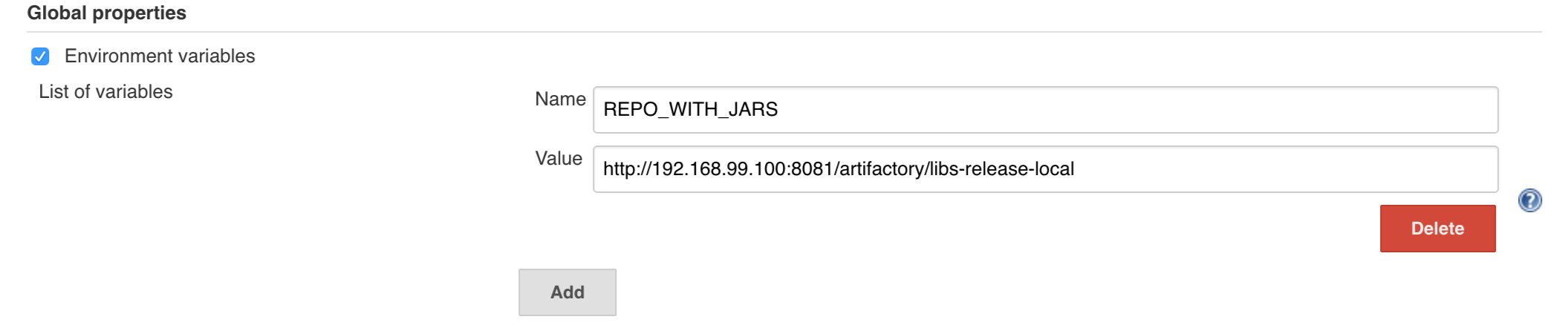
repo.with.binariesproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the URL to the repo containing binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
distribution.management.release.idproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the ID of the distribution management. It corresponds to server ID insettings.xml. -
distribution.management.release.urlproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the URL of the repository that contains binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
Running API compatibility tests with the
apicompatibilityMaven profile. -
latest.production.versionproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the latest production version for the repo (retrieved from Git tags). -
Running smoke tests on a deployed app with the
smokeMaven profile. -
Running end to end tests on a deployed app with the
e2eMaven profile.
-
-
For Gradle (example project check the
gradle/pipeline.gradlefile), we assume:-
Usage of the Gradlew Wrapper.
-
A
deploytask for artifact deployment. -
The
REPO_WITH_BINARIES_FOR_UPLOADenvironment variable (Injected by the pipeline) contains the URL to the repository that contains binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
The
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_USERNAMEenvironment variable contains the user name used to send the binary to the repository that contains binaries (for exampl,e Artifactory). -
The
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_PASSWORDenvironment variable contains the password used to send the binary to the repository that contains binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
Running API compatibility tests with the
apiCompatibilitytask. -
latestProductionVersionproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the latest production version for the repository (retrieved from Git tags). -
Running smoke tests on a deployed app with the
smoketask. -
Running end to end tests on a deployed app with the
e2etask. -
groupIdtask to retrieve the group ID. -
artifactIdtask to retrieve the artifact ID. -
currentVersiontask to retrieve the current version. -
stubIdstask to retrieve the list of collaborators for which stubs should be downloaded.
-
-
For PHP (example project), we asssume:
-
Usage of Composer.
-
composer installis called to fetch libraries. -
The whole application is compressed to
tar.gzand uploaded to binary storage.-
REPO_WITH_BINARIES_FOR_UPLOADenvironment variable (injected by the pipeline): Contains the URL of the repository that contains binaries (for example, Artifactory) -
The
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_USERNAMEenvironment variable contains the user name used to send the binary to the repo containing binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
The
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_PASSWORDenvironment variable contains the password used to send the binary to the repo containing binaries (for example, Artifactory).
-
-
group-id: Composer task that echoes the group ID. -
app-name: Composer task that echoes application name. -
stub-ids: Composer task that echoes stub runner ids. -
test-apicompatibility: Composer task that is executed for api compatibility tests. -
test-smoke: Composer task that is executed for smoke testing (theAPPLICATION_URLandSTUBRUNNER_URLenvironment variables are available here to be used). -
test-e2e: Composer task that is executed for end-to-end testing (APPLICATION_URLenv vars is available here to be used) -
targetis assumed to be the output folder. Put it in.gitignore
-
-
For NodeJS (example project), we assume:
-
Usage of npm
-
npm installis called to fetch libraries. -
npm testis called to run tests. -
npm run group-id: npm task that echoes the group ID. -
npm run app-name: npm task that echoes application name. -
npm run stub-ids: npm task that echoes stub runner IDs. -
npm run test-apicompatibility: npm task that is executed for api compatibility tests. -
npm run test-smoke: npm task that is executed for smoke testing. -
npm run test-e2e: npm task that is executed for end-to-end testing. -
targetis assumed to be the output folder. Put it in.gitignore
-
-
For .Net (example project):
-
Usage of ASP.NET core
-
dotnet buildis called to build the project. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPUnitTestsis called to run unit tests. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPIntegrationTestsis called to run integration tests. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPPublish /p:Configuration=Releaseis called to publish a ZIP with a self-contained DLL, together with all manifests and deployment files. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPGroupIdis the npm task that echos the group ID. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPAppNameis the npm task that echos application name. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPStubIdsis the npm task that echos stub runner IDs. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPApiCompatibilityTestis run for API compatibility tests. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPSmokeTestsis executed for smoke testing. -
dotnet msbuild /nologo /t:CFPE2eTestsis executed for end-to-end testing. -
targetis assumed to be the output folder. Add it to.gitignore.
-
Kubernetes Project Opinions
We use the following opinionated decisions for a Cloud Foundry based project:
-
The application is built by using the Maven or Gradle wrappers.
-
The application is deployed to Kubernetes.
-
The Java Docker image needs to allow passing of system properties through the
SYSTEM_PROPSenvironment variable. -
For Maven (example project), we assume:
-
Usage of the Maven Wrapper.
-
settings.xmlis parametrized to pass the credentials to push code to Artifactory and Docker repositories:-
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_ID: Server ID for Artifactory or Nexus deployment. -
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_USERNAME: User name for Artifactory or Nexus deployment. -
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_PASSWORD: Password for Artifactory or Nexus deployment. -
DOCKER_SERVER_ID: Server ID for Docker image pushing. -
DOCKER_USERNAME: User name for Docker image pushing. -
DOCKER_PASSWORD: Password for Docker image pushing. -
DOCKER_EMAIL: Email for Artifactory or Nexus deployment
-
-
DOCKER_REGISTRY_URLenvironment variable: Contains (Overridable - defaults to DockerHub) URL of the Docker registry. -
DOCKER_REGISTRY_ORGANIZATIONenvironment variable: Contains the organization where your Docker repository resides. -
Artifacts and Docker image deployment is done by using
./mvnw clean deploy. -
stubrunner.idsproperty: To retrieve list of collaborators for which stubs should be downloaded. -
repo.with.binariesproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the URL to the repo containing binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
distribution.management.release.idproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the ID of the distribution management. Corresponds to the server ID insettings.xml -
distribution.management.release.urlproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the URL or the repository that contains binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
deployment.ymlcontains the Kubernetes deployment descriptor. -
service.ymlcontains the Kubernetes service descriptor. -
running API compatibility tests with the
apicompatibilityMaven profile. -
latest.production.versionproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the latest production version for the repository (retrieved from Git tags). -
Running smoke tests on a deployed app with the
smokeMaven profile. -
Running end to end tests on a deployed app with the
e2eMaven profile.
-
-
For Gradle (example project check the
gradle/pipeline.gradlefile), we assume:-
Usage of the Gradlew Wrapper.
-
deploytask for artifact deployment. -
REPO_WITH_BINARIES_FOR_UPLOADenv var (injected by the pipeline): Contains the URL to the repository that contains binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_USERNAMEenvironment variable: User name used to send the binary to the repository that contains binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
M2_SETTINGS_REPO_PASSWORDenvironment variable: Password used to send the binary to the repository that contains binaries (for example, Artifactory). -
DOCKER_REGISTRY_URLenvironment variable: (Overridable - defaults to DockerHub) URL of the Docker registry. -
DOCKER_USERNAMEenvironment variable: User name used to send the the Docker image. -
DOCKER_PASSWORDenvironment variable: Password used to send the the Docker image. -
DOCKER_EMAILenvironment variable: Email used to send the the Docker image. -
DOCKER_REGISTRY_ORGANIZATIONenvironment variable: Contains the organization where your Docker repo resides. -
deployment.ymlcontains the Kubernetes deployment descriptor. -
service.ymlcontains the Kubernetes service descriptor. -
Running API compatibility tests with the
apiCompatibilitytask. -
latestProductionVersionproperty (injected by the pipeline): Contains the latest production version for the repositoryi (retrieved from Git tags). -
Running smoke tests on a deployed application with the
smoketask. -
Running end to end tests on a deployed application with the
e2etask. -
groupIdtask to retrieve group ID. -
artifactIdtask to retrieve artifact ID. -
currentVersiontask to retrieve the current version. -
stubIdstask to retrieve the list of collaborators for which stubs should be downloaded.
-
Customizing the Project
Spring Cloud Pipelines offers a number of ways to customize a Pipelines project:
Overriding Scripts
Since Spring Cloud Pipelines evolves, you may want to pull the most recent changes to your Spring Cloud Pipelines fork. To not have merge conflicts, the best approach to extending the functionality is to use a separate script with customizations.
When we execute a script that represents a step (for example, a script named build_and_upload.sh),
after we source all the deployment and build-specific scripts (such as pipeline-cf.sh
and projectType/pipeline-jvm.sh with projectType/pipeline-gradle.sh), we set
a hook that lets you customize the behavior. If the script that we run
is common/src/main/bash/build_and_upload.sh, we search for a script in the
Spring Cloud Pipelines repository under common/src/main/bash/custom/build_and_upload.sh,
and we source that script just before running any functions.
The following example shows such a customization:
#!/bin/bash
function build() {
echo "I am executing a custom build function"
}
export -f buildwhen the build function is called for our Gradle project, instead of
calling the Gradle build process, we echo the following text: I am executing a custom build function.
Overriding Pipelines
Currently, the best way to extend the Concourse and Jenkins Jenkinsfile pipelines is to make
a copy of the Concourse pipeline yaml files and the Jenkins seed and pipeline jobs.
Overriding Jenkins Job DSL pipelines
We provide an interface (called org.springframework.cloud.pipelines.common.JobCustomizer)
that lets you provide customization for:
-
all jobs
-
build jobs
-
test jobs
-
stage jobs
-
prod jobs
We use the JDK’s java.util.ServiceLoader mechanism to achieve extensibility.
You can write an implementation of that interface (for example, com.example.MyJubCustomizer)
and create a META-INF/org.springframework.cloud.pipelines.common.JobCustomizer file in which you put the
com.example.MyJubCustomizer line.
If you create a JAR with your class (for example com.example:my-customizer:1.0.0),
put it on the build classpath, as the following example shows:
dependencies {
// ...
libs "com.example:my-customizer:1.0.0"
// ...
}If you do not want to create a separate library, you can create an implementation in the
sources under src/main/resources/META-INF.
Regardless of what you chose, your implementation runs for each job. You can add notifications or any other customizations of your choosing.
Picking Features
If you want to pick only pieces (for example you want only Cloud Foundry combined with
Concourse), you can run the following command:
$ ./gradlew customizeA screen resembling the following appears:
:customize
___ _ ___ _ _ ___ _ _ _
/ __|_ __ _ _(_)_ _ __ _ / __| |___ _ _ __| | | _ (_)_ __ ___| (_)_ _ ___ ___
\__ \ '_ \ '_| | ' \/ _` | | (__| / _ \ || / _` | | _/ | '_ \/ -_) | | ' \/ -_|_-<
|___/ .__/_| |_|_||_\__, | \___|_\___/\_,_\__,_| |_| |_| .__/\___|_|_|_||_\___/__/
|_| |___/ |_|
Follow the instructions presented in the console or terminate the process to quit (ctrl + c)
=== PAAS TYPE ===
Which PAAS type do you want to use? Options: [CF, K8S, BOTH]
<-------------> 0% EXECUTING
> :customizeNow you need to answer a couple of questions. Depending on your choices, whole files and their pieces
get removed and updated accordingly. For example, if you choose the CF and Concourse options,
the Kubernetes and Jenkins configuration and folders and pieces of code in
the project get removed.
Step-by-step Cloud Foundry Migration
This section details how to migrate applications such that they become compatible with Spring Cloud Pipelines.
Preview
Click here to check out the slides by Cora Iberkleid where she migrates a set of applications to be compliant with Spring Cloud Pipelines.
Introduction
This tutorial covers refactoring applications to be compatible with, and take advantage of, Spring Cloud Pipelines.
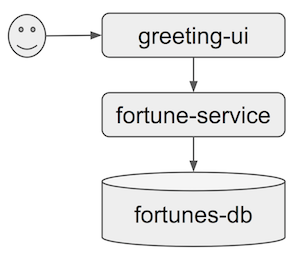
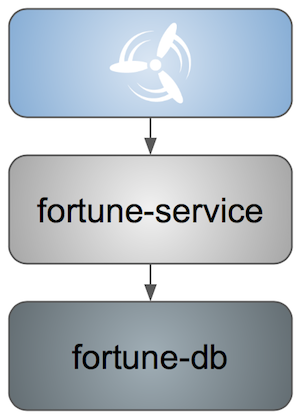
As an example, we use a simple three-tier application, shown in the following image:
At the end of this tutorial, you will be able to quickly create a Concourse pipeline for each application and run successfully through a full lifecycle, from source code commit to production deployment, following the lifecycle stages for testing and deployment recommended by Spring Cloud Pipelines. You will be able to improve application code bases with organized test coverage, a contract-based API, and a versioned database schema, letting Spring Cloud Pipelines carry out stubbed testing and ensure backward compatibility for API and database schema changes.
Sample Application — Initial State
The sample application is implemented by using Spring Boot applications for the UI and service tiers and MySQL for the database.
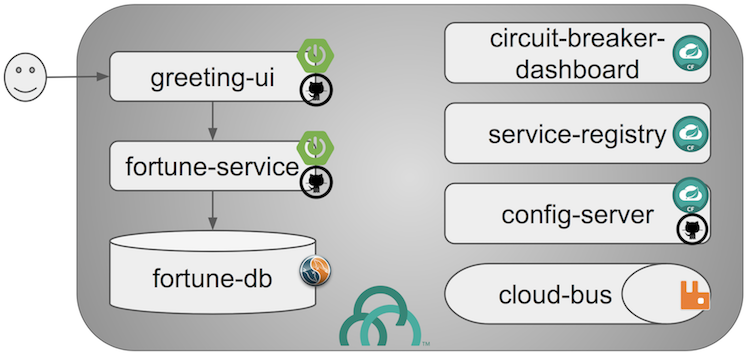
The apps are built with Maven and manually pushed to Cloud Foundry. They leverage the three Pivotal Spring Cloud Services: Config Server, Service Discovery, and Circuit Breaker Dashboard. We use Rabbit to propagate Config Server refresh triggers.
The source code for the two Spring Boot applications is stored on GitHub, as is the backing repo for Config Server.
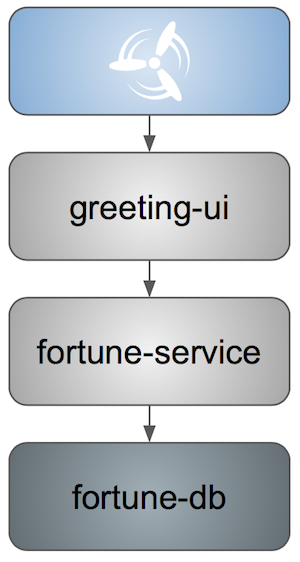
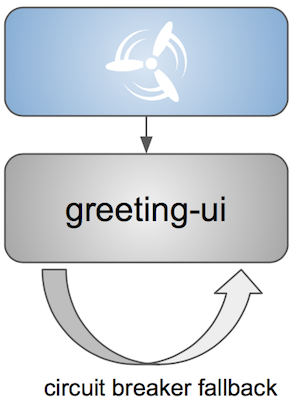
The following image shows an implementation view of the applications and their ancillary services:
Sample Application — End State
Throughout this tutorial, we add Concourse and JFrog Bintray to manage the application lifecycle.
We also refactor the applications so that they become compatible with Spring Cloud Pipelines requirements and recommendations, including adding and organizing tests and introducing database versioning by using Flyway and introducing API contracts by using Spring Cloud Contract.
Tutorial — Toolset
Throughout this tutorial, we use the following tools:
-
GitHub: Sample application source code and configuration repositories, a sample stubrunner application repository, and the Spring Cloud Pipelines code base, including the following:
-
Pivotal Web Services: Publicly hosted Cloud Foundry offering free trial accounts and including MySQL, Rabbit, and Pivotal Spring Cloud Services in the Marketplace
-
Concourse
-
JFrog Bintray: Publicly hosted Maven repository offering free OSS accounts
-
Client Tools: On your local machine, you need an IDE as well as the mvn, git, cf, and fly (Concourse) CLIs
Tutorial — Overview
We separate the migration steps into three stages:
-
Scaffolding
-
Minimal refactoring to be compatible with basic Spring Cloud Pipelines requirements.
-
At the end of this stage, each application has a corresponding pipeline on Concourse. The pipelines successfully build the applications, store the artifacts in Bintray, tag the GitHub repositories, and deploy the applications to the Test, Stage, and Prod spaces in Cloud Foundry.
-
-
Tests
-
Add and organize tests to be compatible with Spring Cloud Pipelines recommendations.
-
Incorporate flyway for database schema versioning and initial data loading.
-
At the end of this stage, the pipelines trigger unit and integration tests during the Build stage, smoke tests in the Test environment, and end-to-end tests in the Stage environment. The pipelines also ensure backward compatibility for the database, such that you can safely roll back the backend service application, even after the database schema has been updated.
-
-
Contracts
-
Incorporate Spring Cloud Contract to define the API between the UI and service apps and auto-generate tests and stubs.
-
At the end of this stage, the pipelines catch breaking API changes during the Build stage and ensure backward compatibility for the API, such that you can safely roll back the backend service (producer) app, even after an API change.
-
Tutorial — Step-by-step
The remainder of this chapter is the actual tutorial, which consists of a preparation stage and three main stages:
Prep: Before you begin
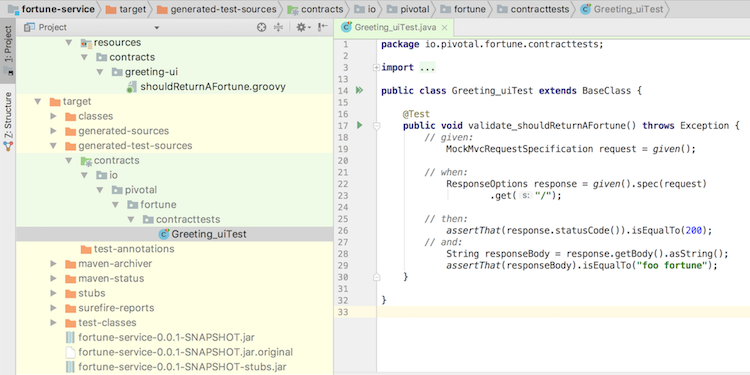
If you want to simply review the migration steps explained below, you can look at the various branches in the greeting-ui and fortune-service repositories. A branch represents the end-state of each stage, as the following image shows:
If you want to use this tutorial as a hands-on lab, fork each of the following repositories:
Then create a new directory on your local machine. You may name it anything you like. We refer to it as $SCP_HOME throughout this tutorial.
In $SCP_HOME, clone your forks of greeting-ui and fortune-service, as well as the following two repositories:
Finally, create a directory called $SCP_HOME/credentials. Leave it empty for now.
Stage One: Scaffolding
In this stage, we make minimal changes to satisfy basic Spring Cloud Pipelines requirements so that the applications can run through the entire pipeline without error. We make “scaffolding” changes only — no code changes.
|
Important
|
You must complete the steps in this stage for both greeting-ui and fortune-service.
|
1.1 Create GitHub Branches
Create branches in GitHub by using the following git commands:
git branch version
git checkout -b sc-pipelinesThe version branch is required to exist, though it can be created as an empty branch. It is used by Spring Coud Pipelines to generate a version number for each new pipeline execution.
The sc-pipelines branch is optional and can be named anything you wish. The intention is for you to use it as a working branch for the changes suggested in this tutorial (hence, you should both create it and check it out).
1.2 Add Maven Wrapper
This step covers how to add the Maven wrapper (which lets your users build without having Maven on the path). To add the Maven wrapper, run the following command:
mvn -N io.takari:maven:wrapperThis commands adds four files to a project:
.
├── mvnw
├── mvnw.cmd
└── .mvn
└── wrapper
├── maven-wrapper.jar
└── maven-wrapper.propertiesMake sure all four files are tracked by Git. One way to do so is to add the following lines to the .gitignore file:
#Exceptions
!/mvnw
!/mvnw.cmd
!/.mvn/wrapper/maven-wrapper.jar
!/.mvn/wrapper/maven-wrapper.properties1.3 Create the Bintray Maven Repository Package
We use Bintray as the Maven repository. Bintray requires that a package exist before any application artifacts can be uploaded.
Log into the Bintray UI and create the packages as follows (you can use the “Import from GitHub” option to create these):
1.4 Configure Distribution Management by Using the Bintray Maven Repository
|
Important
|
You must do this step for both application repositories. |
Edit the application pom.xml files. Make sure that the Bintray URLs match the URLs of the corresponding packages created in the previous step. The values you use should differ from the following example in that they should point to your repository:
<properties>
...
<distribution.management.release.id>bintray</distribution.management.release.id>
<distribution.management.release.url>https://api.bintray.com/maven/ciberkleid/maven-repo/fortune-service</distribution.management.release.url>
</properties>
...
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<id>${distribution.management.release.id}</id>
<url>${distribution.management.release.url}</url>
</repository>
</distributionManagement>Though not required by Spring Cloud Pipelines, it makes sense to also configure your local maven settings with the credentials to your Bintray maven repository. To do so, edit your maven settings file (usually ~/.m2/settings.xml). If the file does not exist, create it.
Note that the id must match the id specified in the previous step. Also, make sure to use your username and API token (not your account password) instead of the sample values shown in the following example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<settings>
<servers>
<server>
<id>bintray</id>
<username>ciberkleid</username>
<password>my-super-secret-api-token</password>
</server>
</servers>
</settings>1.5 Push Changes to GitHub
Push the changes you made in the preceding step to GitHub. You should be pushing the following to each of the two application repositories:
-
Four new Maven wrapper files
-
A modified
.gitignorefile -
A modified
pom.xmlfile
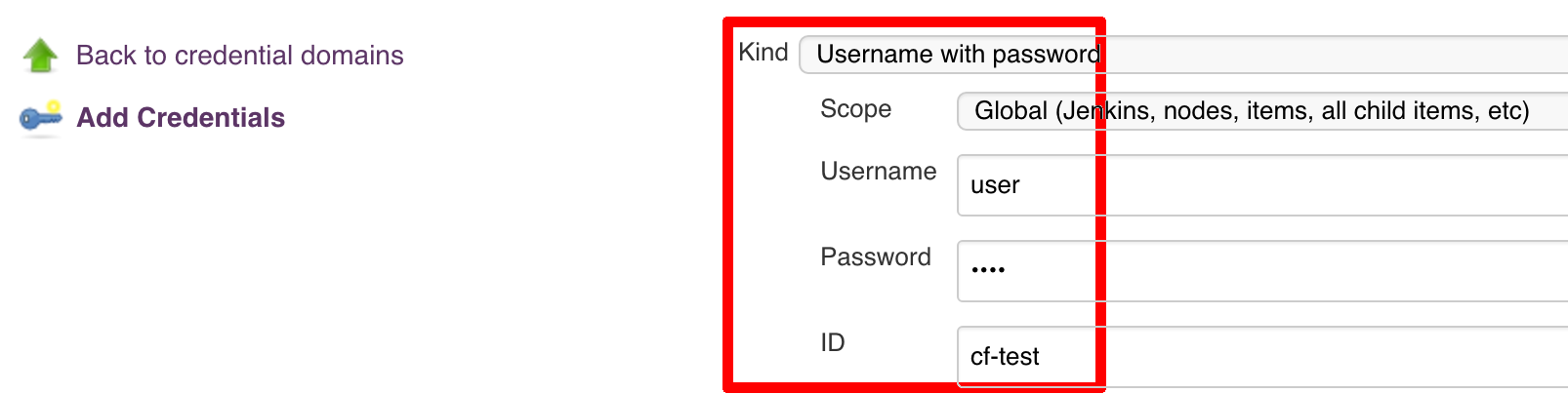
1.6 Add a Spring Cloud Pipelines Credentials File
In $SCP_HOME/credentials, make two copies of the $SCP_HOME/spring-cloud-pipelines/concourse/credentials-sample-cf.yml file. Rename them as credentials-fortune-service.yml and credentials-greeting-ui.yml.
|
Caution
|
These files will contain credentials to your GitHub repository, your Bintray repository, and your Cloud Foundry foundation. Hence, we opt to put them in a separate directory. You may choose to store these files in a private Git repository, but do not push them to a public repository. |
Edit the Git properties of each credentials file. Make sure to replace the sample values shown in our example. For tools-branch, you can use a fixed release (use v1.0.0.M8 or later for Cloud Foundry). Leave the other values as they are. We update those in later steps. The following listing shows a credentials file:
app-url: [email protected]:ciberkleid/fortune-service.git
app-branch: sc-pipelines
tools-scripts-url: https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines.git
tools-branch: master
build-options: ""
github-private-key: |
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIJKQIBAAKCAgEAvwkL97vBllOSE39Wa5ppczT1cr5Blmkhadfoa1Va2/IBVyvk
NJ9PqoTI+BahF2EgzweyiDSvKsstlTsG7QgiM9So8Voi2PlDOrXL6uOfCuAS/G8X
...
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
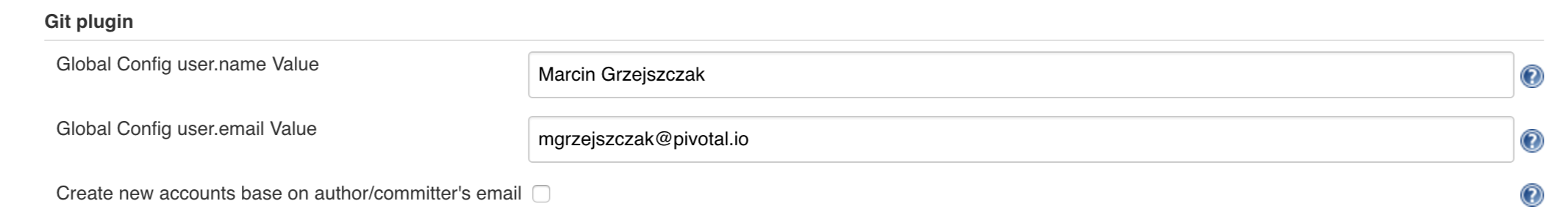
git-email: [email protected]
git-name: Cora IberkleidEdit the Maven repository properties of each credentials file. Make sure to replace the sample values shown in our example. Bintray requires separate URLs for uploads and downloads. If you use a different artifact repository, such as Artifactory or Nexus, and the repository URL is the same for uploads and downloads, you do not need to set repo-with-binaries-for-upload. The following listing shows the values to add or edit in your credentials file:
m2-settings-repo-id: bintray
m2-settings-repo-username: ciberkleid
m2-settings-repo-password: my-super-secret-api-token
repo-with-binaries: https://ciberkleid:[email protected]/ciberkleid/maven-repo
repo-with-binaries-for-upload: https://api.bintray.com/maven/ciberkleid/maven-repo/fortune-service1.7 Set the Concourse Pipeline
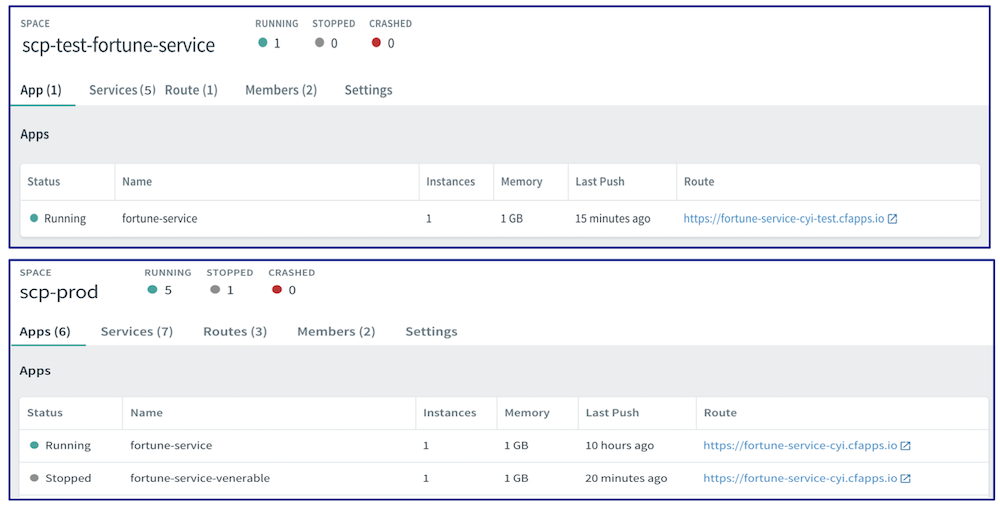
At this point, all of the build jobs, which run on Concourse workers, should succeed.
To verify this, log in to your Concourse target and set the Concourse pipelines. Update the target name in the following example:
# Set greeting-ui pipeline
fly -t myTarget set-pipeline -p greeting-ui -c "${SCP_HOME}/spring-cloud-pipelines/concourse/pipeline.yml" -l "${SCP_HOME}/credentials/credentials-greeting-ui.yml" -n
# Set fortune-service pipeline
fly -t myTarget set-pipeline -p fortune-service -c "${SCP_HOME}/spring-cloud-pipelines/concourse/pipeline.yml" -l "${SCP_HOME}/credentials/credentials-fortune-service.yml" -nLog into the Concourse UI and un-pause the pipelines. Start each pipeline. You should see that the build jobs all succeed, similar to the following image:
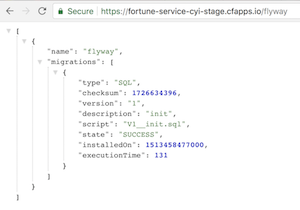
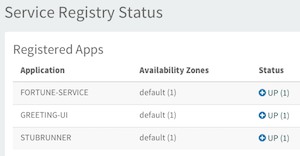
In addition, you should see a new dev/<version_number> tag in each GitHub repository and see the app jars uploaded into Bintray.
The test, stage, and prod jobs fail, because we have not yet added scaffolding for deployment to Cloud Foundry. We do that next.
1.8 Add Cloud Foundry manifest
If you are deploying to Cloud Foundry, you may already be routinely including manifest files with your applications. Our sample applications did not have manifest files, so we add them now.
In the greeting-ui repository, create a manifest.yml file as follows:
---
applications:
- name: greeting-ui
timeout: 120
services:
- config-server
- cloud-bus
- service-registry
- circuit-breaker-dashboard
env:
JAVA_OPTS: -Djava.security.egd=file:///dev/urandom
TRUST_CERTS: api.run.pivotal.ioIn the fortune-service repository, create a manifest.yml file as follows:
---
applications:
- name: fortune-service
timeout: 120
services:
- fortune-db
- config-server
- cloud-bus
- service-registry
- circuit-breaker-dashboard
env:
JAVA_OPTS: -Djava.security.egd=file:///dev/urandom
TRUST_CERTS: api.run.pivotal.ioThe TRUST_CERTS variable is used by the Pivotal Spring Cloud Services (Config Server, Service Registry, and Circuit Breaker Dashboard), which we use in this example. The value specified in the preceding example assumes deployment to Pivotal Web Services. Update it accordingly if you are deploying to a different Cloud Foundry foundation, or you can leave it out altogether if you are replacing the Pivotal Spring Cloud Services with alternative implementations (for example, deploying the services as applications and exposing them as user-provided services).
If you wishi, you can add additional values to the manifest files — for example, if additional values are useful for any manual deployment you may still want to do or if you need additional values in your Spring Cloud Pipelines deployment. For example, the following file could be an alternative manifest.yml for fortune-service:
---
applications:
- name: fortune-service
timeout: 120
instances: 3
memory: 1024M
buildpack: https://github.com/cloudfoundry/java-buildpack.git
random-route: true
path: ./target/fortune-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
services:
- fortune-db
- config-server
- cloud-bus
- service-registry
- circuit-breaker-dashboard
env:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: someProfile
JAVA_OPTS: -Djava.security.egd=file:///dev/urandom
TRUST_CERTS: api.run.pivotal.ioNote that Spring Cloud Pipelines ignores random-route and path. instances is honored in stage and prod but is overridden with a value of 1 for test.
1.9 Add the Spring Cloud Pipelines Manifest
The Cloud Foundry manifest created in the previous step includes the logical names of the services to which the applications should be bound, but it does not describe how the services can be provisioned. Hence, we add a second manifest file so that Spring Cloud Pipelines can provision the services.
Add a file called sc-pipelines.yml to each application and include the same list of services as in the corresponding manifest.yml. Add the necessary details such that Spring Cloud Pipelines can construct a cf create-service command.
|
Note
|
The `type: broker' parameter in the next example instructs Spring Cloud Pipelines to provision a service by using `cf create-service'. Other service types are also supported: cups, syslog, route, app, and stubrunner. |
More specifically, for greeting-ui, create an sc-pipelines.yml file with the following content:
test:
services:
- name: config-server
type: broker
broker: p-config-server
plan: standard
params:
git:
uri: https://github.com/ciberkleid/app-config
useExisting: true
- name: cloud-bus
type: broker
broker: cloudamqp
plan: lemur
useExisting: true
- name: service-registry
type: broker
broker: p-service-registry
plan: standard
useExisting: true
- name: circuit-breaker-dashboard
type: broker
broker: p-circuit-breaker-dashboard
plan: standard
useExisting: trueThe sc-pipelines.yml file for fortune-service is similar, with the addition of the fortune-db service, as follows:
test:
# list of required services
services:
- name: fortune-db
type: broker
broker: cleardb
plan: spark
useExisting: true
- name: config-server
type: broker
broker: p-config-server
plan: standard
params:
git:
uri: https://github.com/ciberkleid/app-config
useExisting: true
- name: cloud-bus
type: broker
broker: cloudamqp
plan: lemur
useExisting: true
- name: service-registry
type: broker
broker: p-service-registry
plan: standard
useExisting: true
- name: circuit-breaker-dashboard
type: broker
broker: p-circuit-breaker-dashboard
plan: standard
useExisting: trueThe values in the preceding two examples assume deployment to Pivotal Web Services. If you are deploying to a different Cloud Foundry foundation, update the values accordingly. Also, make sure to replace the config-server URI with the address of your fork of the app-config repository.
|
Tip
|
Notice the useExisting: true parameter in the preceding example. By default, Spring Cloud Pipelines deletes and re-creates services in the test space. To override this behavior and re-use existing services, we set useExisting: true. This is helpful in cases where services may take time to provision and initialize, where there is no risk in re-using them between pipeline runs, or where it is desirable to retain the service instance from the last pipeline run (for example, a database migration).
|
1.10 Push changes to GitHub
Push the preceding changes to GitHub. You should be pushing the following to each of the two application repositories:
-
A new app manifest file
-
A new sc-pipelines manifest file
1.11 Create Cloud Foundry Orgs and Spaces
Spring Cloud Pipelines requires that the Cloud Foundry test, stage, and prod spaces exist before a pipeline is run. If you wish, you can use different foundations, orgs, and users for each. For simplicity, in this example, we use a single foundation (PWS), a single org, and a single user.
You can name the orgs and spaces anything you like. Each app requires its own test space. The stage and prod spaces are shared.
For this example, use the following commands to create spaces:
cf create-space scp-test-greeting-ui
cf create-space scp-test-fortune-service
cf create-space scp-stage
cf create-space scp-prod1.12 Create Cloud Foundry Stage and Prod Service Instances
Spring Cloud Pipelines dynamically creates the services in the test spaces, as defined by the sc-pipelines.yml file we created previously. Optionally, you can add a second section to the sc-pipelines.yml file for the stage environment, and these are created dynamically as well. However, you must always crate prod manually.
For this example, we create both the stage and prod services manually.
Create the services listed in the application manifest files in both scp-stage and scp-prod.
1.13 Update the Spring Cloud Pipelines Credentials File
Update the greeting-ui and fortune-service credentials files with Cloud Foundry information. Replace values in the next example as appropriate for your Cloud Foundry environment.
Notice that the test space name specified is a prefix, unlike the stage and prod space names, which are literals. Spring Cloud Pipelines append the application name to the test space name, thereby matching the test space names we created manually. The stage and prod space names are not prefixes and are not altered by Spring Cloud Pipelines.
Note also the paas-hostname-uuid. The value is included in each created route. This value is optional, but it is useful in shared or multi-tenant environments (such as PWS), as it helps to ensure routes are unique. Change it to a unique uuid.
The following example shows an updated credentials file:
pipeline-descriptor: sc-pipelines.yml
paas-type: cf
paas-hostname-uuid: cyi
# test values
paas-test-api-url: https://api.run.pivotal.io
paas-test-username: [email protected]
paas-test-password: secret
paas-test-org: S1Pdemo12
paas-test-space-prefix: scp-test
# stage values
paas-stage-api-url: https://api.run.pivotal.io
paas-stage-username: [email protected]
paas-stage-password: my-super-secret-password
paas-stage-org: S1Pdemo12
paas-stage-space: scp-stage
# prod values
paas-prod-api-url: https://api.run.pivotal.io
paas-prod-username: [email protected]
paas-prod-password: my-super-secret-password
paas-prod-org: S1Pdemo12
paas-prod-space: scp-prod1.14 Update the Concourse Pipeline with Updated Credentials Files
Set the Concourse pipelines again, as we did previously, to update them with the values added to the credentials files. The test, stage, and prod jobs should all now succeed and result in output similar to the following image:
On Cloud Foundry, you should now see the apps deployed in the test, stage, and prod spaces. The following image shows the deployment of fortune-service to its dedicated test space:
Notice that the five services declared in its manifest files (sc-pipelines.yml for provisioning and manifest.yml for binding) have also been automatically provisioned. The image also shows the deployment of the same app to the shared prod space. Notice that the instance of the previous version has been renamed as venerable and stopped. If a rollback were deemed necessary, the prod-rollback job in the pipeline could be triggered to remove the currently running version, remove the prod/<version_number> tag from GitHub, and re-start the former (venerable) version.
Stage One Recap and Next Steps
What have we accomplished?
-
By adding the basic scaffolding needed to enable Spring Cloud Pipelines to manage the lifecycle of
greeting-uiandfortune-servicefrom source code commit to production deploy, we have made it possible for the application development teams to instantly and easily create pipelines for each application by using a common, standardized template. -
We can count on the pipelines to:
-
Automatically provision services in test spaces and, optionally, in stage spaces as well.
-
Dynamically clean up the test spaces between pipeline executions.
-
Upload the app artifacts to the maven repo (for example, Bintray).
-
Tag the git repositories with
dev/<version_number>andprod/<version_number>.
-
-
After each successful pipeline run, we can, if necessary, to roll back to the last deployed version byusing the
prod-rollbackjob.
These accomplishments are extremely valuable. However, to derive confidence and reliability from the pipelines, we need to incorporate testing. We do this in Stage Two of the application migration.
Stage Two: Tests
In this stage, we enable Spring Cloud Pipelines to execute tests so that we can increase confidence in the code being deployed. We do so by adding test profiles to the pom.xml files and then organizing or adding tests in a way that corresponds to the profiles. By doing so, we establish standards around testing across development teams in the enterprise.
We will also enable database schema versioning in this stage, thereby providing the foundation for rollback testing during schema changes.
2.1 Add Maven Profiles
For both greeting-ui and fortune-service, add a profiles section to the pom.xml file, as shown in the next listing. Note that we are adding four profiles:
-
default-
For unit and integration tests. Note that this profile includes all tests except those that are explicitly called by the smoke and e2e profiles.
-
Tests matching this profile run during the build-and-upload job.
-
-
apicompatibility-
For ensuring backward compatibility in case of API changes. Note that this is not effective until Stage Three, when we will add contracts. However, we add this profile now to ensure the api compatibility check during the
build-and-uploadjob does not run other tests.
-
-
smoke-
For tests to be run against the application deployed in the test space.
-
-
e2e-
For tests to be run against the application deployed in the stage space.
-
The following listing shows the necessary profiles element of a pom.xml file:
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>default</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*Tests.java</include>
<include>**/*Test.java</include>
</includes>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/smoke/**</exclude>
<exclude>**/e2e/**</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>apicompatibility</id>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/contracttests/**/*Tests.java</include>
<include>**/contracttests/**/*Test.java</include>
</includes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>smoke</id>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>smoke/**/*Tests.java</include>
<include>smoke/**/*Test.java</include>
</includes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>e2e</id>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>e2e/**/*Tests.java</include>
<include>e2e/**/*Test.java</include>
</includes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>
</profiles>2.2 Add and Organize Tests
Next, we ensure that we have a matching test package structure in our apps, as the following image shows:
Note that we are creating matching packages only for the default, smoke, and e2e profiles. We will address the package for the apicompatibility profile in Stage Three.
When working with your own applications, if you have existing tests, you would move the files into one of these packages now and rename them so that they are included by the filters declared in the profiles (that is, the file names end in Test.java or Tests.java)
In the case of our sample apps, we have no tests, so we add some now.
fortune-service Default Tests
Add your unit and integration tests so that they match the default profile, as defined in the fortune-service pom.xml file. These are run on Concourse against the fortune-service application that runs on the Concourse worker in the build-and-upload job.
As an example, we add two tests, one that loads the context and another that verifies the number of rows expected in the database. The following example defines these tests:
package io.pivotal;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = FortuneServiceApplication.class)
public class FortuneServiceApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws Exception {
}
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate template;
@Test
public void testDefaultSettings() throws Exception {
assertThat(this.template.queryForObject("SELECT COUNT(*) from FORTUNE",
Integer.class)).isEqualTo(7);
}
}fortune-service Smoke Tests
Add your smoke tests so that they match the smoke profile, as defined in the fortune-service pom.xml file. These run on Concourse against the fortune-service application deployed in the Cloud Foundry scp-test-fortune-service space. Two versions of these tests are executed against the application:
-
the current version, in the
test-smokejob. -
the latest prod version, in the
test-rollback-smokejob.
The following image shows the tests in Concourse:
In the test environment, we choose to verify that fortune-service is retrieving a fortune from fortune-db, and not returning its Hystrix fallback response. The following example defines this test:
package smoke;
import org.assertj.core.api.BDDAssertions;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SmokeTests.class,
webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE)
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SmokeTests {
@Value("${application.url}") String applicationUrl;
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
@Test
public void should_return_a_fortune() {
ResponseEntity<String> response = this.restTemplate
.getForEntity("http://" + this.applicationUrl + "/", String.class);
BDDAssertions.then(response.getStatusCodeValue()).isEqualTo(200);
// Filter out the known Hystrix fallback response
BDDAssertions.then(response.getBody()).doesNotContain("The fortuneteller will be back soon.");
}
}fortune-service End-to-end (e2e) Tests
Add your end-to-end tests so that they match the e2e profile, as defined in the fortune-service pom.xml file. These tests run on Concourse against the fortune-service application deployed in the Cloud Foundry scp-stage space. This space is shared, so we assume greeting-ui is also present.
The following image shows the tests in Concourse:
In the e2e environment, we choose to use a string replacement to obtain the URL for greeting-ui. We also choose to verify that we hit fortune-db and do not receive Hystrix fallback responses from either application. The following example shows this test:
package e2e;
import org.assertj.core.api.BDDAssertions;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = E2eTests.class,
webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE)
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class E2eTests {
// The app is running in CF but the tests are executed from Concourse worker,
// so the test will deduce the url to greeting-ui: it will assume the same host
// as fortune-service, and simply replace "fortune-service" with "greeting-ui" in the url
@Value("${application.url}") String applicationUrl;
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
@Test
public void should_return_a_fortune() {
ResponseEntity<String> response = this.restTemplate
.getForEntity("http://" + this.applicationUrl.replace("fortune-service", "greeting-ui") + "/", String.class);
BDDAssertions.then(response.getStatusCodeValue()).isEqualTo(200);
// Filter out the known Hystrix fallback responses from both fortune and greeting
BDDAssertions.then(response.getBody()).doesNotContain("This fortune is no good. Try another.").doesNotContain("The fortuneteller will be back soon.");
}
}greeting-ui Default Tests
Add your unit and integration tests so that they match the default profile, as defined in the greeting-ui pom.xml file. These run on Concourse against the greeting-ui application that runs on the Concourse worker in the build-and-upload job.
As an example, we add one test that loads the context:
package io.pivotal;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = GreetingUIApplication.class)
public class GreetingUIApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws Exception {
}
}greeting-ui Smoke Tests
Add your smoke tests so that they match the smoke profile, as defined in the greeting-ui pom.xml file. These run on Concourse against the greeting-ui application deployed in the Cloud Foundry scp-test-greeting-ui space. Two versions of these tests run against the app:
-
The current version, in the
test-smokejob. -
The latest prod version, in the
test-rollback-smokejob.
The following image shows the tests in Concourse:
Since fortune-service is not deployed to the scp-test-greeting-ui space, we expect to receive the Hystrix fallback response defined in greeting-ui. Hence, our smoke test validates that condition:
package smoke;
import org.assertj.core.api.BDDAssertions;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SmokeTests.class,
webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE)
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SmokeTests {
@Value("${application.url}") String applicationUrl;
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
@Test
public void should_return_a_fallback_fortune() {
ResponseEntity<String> response = this.restTemplate
.getForEntity("http://" + this.applicationUrl + "/", String.class);
BDDAssertions.then(response.getStatusCodeValue()).isEqualTo(200);
// Expect the hystrix fallback response
BDDAssertions.then(response.getBody()).contains("This fortune is no good. Try another.");
}
}greeting-ui End-to-end (e2e) Tests
Add your end-to-end tests so that they match the e2e profile, as defined in the greeting-ui pom.xml file. These run on Concourse against the greeting-ui application deployed in the Cloud Foundry scp-stage space. This space is shared, so we assume fortune-service is also present.
The following image shows the tests in Concourse:
In the e2e environment, we choose to verify that we hit fortune-service and do not receive the Hystrix fallback response from greeting-ui. The following example shows the test:
package e2e;
import org.assertj.core.api.BDDAssertions;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = E2eTests.class,
webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE)
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class E2eTests {
@Value("${application.url}") String applicationUrl;
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
@Test
public void should_return_a_fortune() {
ResponseEntity<String> response = this.restTemplate
.getForEntity("http://" + this.applicationUrl + "/", String.class);
BDDAssertions.then(response.getStatusCodeValue()).isEqualTo(200);
// Filter out the known Hystrix fallback response
BDDAssertions.then(response.getBody()).doesNotContain("This fortune is no good. Try another.");
}
}2.3 Enable Database Versioning
At this point, we also incorporate Flyway, an OSS database migration tool, to track database schema versions and handle schema changes and data loading.
This change needs to be made only to fortune-service, since fortune-service owns the interaction with fortune-db.
Add Flyway Dependency
We first add the Flyway dependency to the fortune-service pom.xml. We need not add a version as Spring Boot takes care of that for us. The following listing shows the Flyway dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>Create Flyway Migration
Next, we create a migration directory and our initial migration file, following Flyway’s file naming convention. The following image shows the name of the file in context:
Note that the filename specifies the version (V1), followed by two underscore characters.
We place our CREATE TABLE and INSERT statements in our src/main/resources/db/migration/V1__init.sql file, as the following listing shows:
CREATE TABLE fortune (
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
text varchar(255) not null
);
INSERT INTO fortune (text) VALUES ('Do what works.');
INSERT INTO fortune (text) VALUES ('Do the right thing.');
INSERT INTO fortune (text) VALUES ('Always be kind.');
INSERT INTO fortune (text) VALUES ('You learn from your mistakes... You will learn a lot today.');
INSERT INTO fortune (text) VALUES ('You can always find happiness at work on Friday.');
INSERT INTO fortune (text) VALUES ('You will be hungry again in one hour.');
INSERT INTO fortune (text) VALUES ('Today will be an awesome day!');Disable JPA DDL Initialization
Because we rely on Flyway to create and populate the schema, we need to disable JPA-based database initialization. We can set ddl-auto to validate, which validates the schema against the application entities and throws an error in case of a mismatch but does not actually generate the schema. The following snippet shows how to do so:
spring:
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: validateThere are a few options for where to store the ddl-auto configuration, both in terms of location (in the fortune-service app or on the app-config GitHub repo) and in terms of file name. For this example, update the application.yml in the fortune-service app for local testing. Additionally, save these values in a new file called application-flyway.yml on your fork of app-config.
By convention, fortune-service picks up the configurations in application-flyway.yml if the string flyway is in the list of active Spring profiles. Consequently, we can add flyway to the SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE environment variable in the fortune-service manifest.yml, as the following listing shows:
---
applications:
- name: fortune-service
timeout: 120
services:
- fortune-db
- config-server
- cloud-bus
- service-registry
- circuit-breaker-dashboard
env:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: flyway
JAVA_OPTS: -Djava.security.egd=file:///dev/urandom
TRUST_CERTS: api.run.pivotal.ioRemove Non-Flyway Data Loading
We can now remove the old code that populated the database. In our sample app, this was found in the io.pivotal.FortuneServiceApplication class. The following listing shows the code we now remove:
@Bean
CommandLineRunner loadDatabase(FortuneRepository fortuneRepo) {
return args -> {
// logger.debug("loading database..");
// fortuneRepo.save(new Fortune(1L, "Do what works."));
// fortuneRepo.save(new Fortune(2L, "Do the right thing."));
// fortuneRepo.save(new Fortune(3L, "Always be kind."));
// fortuneRepo.save(new Fortune(4L, "You learn from your mistakes... You will learn a lot today."));
// fortuneRepo.save(new Fortune(5L, "You can always find happiness at work on Friday."));
// fortuneRepo.save(new Fortune(6L, "You will be hungry again in one hour."));
// fortuneRepo.save(new Fortune(7L, "Today will be an awesome day!"));
logger.debug("record count: {}", fortuneRepo.count());
fortuneRepo.findAll().forEach(x -> logger.debug(x.toString()));
};
}We also no longer need the Fortune entity constructors, so we can comment these out in the io.pivotal.fortune.Fortune class as follows:
// public Fortune() {
// }
//
// public Fortune(Long id, String text) {
// super();
// this.id = id;
// this.text = text;
// }Flyway Integration Summary
With that, we have completed the setup for Flyway, and our database schema is now versioned. From this point onward, Spring Boot calls Flyway.migrate() to perform the database migration. As long as we follow Flyway conventions for future schema changes, Flyway takes care of tracking the schema version and migrating the database for us.
From a rollback perspective, Spring Cloud Pipelines includes two jobs in the test phase (test-rollback-deploy and test-rollback-smoke), wherein it validates that the latest prod jar works against the newly updated database. The purpose is to ensure that we can roll back the application in prod if a problem is discovered after the prod database schema has been updated and avoid the burden of rolling back the database.
See Spring Boot database initialization with Flyway for further information, including Flyway configuration options.
2.4 Push Changes to GitHub
For greeting-ui, you should push the following new or modified files:
-
pom.xml -
src/test/java/e2e/E2eTests.java -
src/test/java/io/pivotal/GreetingUIApplicationTests.java -
src/test/java/smoke/SmokeTests.java
For fortune-service, you should be pushing the following new or modified files:
-
pom.xml -
src/test/java/e2e/E2eTests.java -
src/test/java/io/pivotal/FortuneServiceApplicationTests.java -
src/test/java/smoke/SmokeTests.java -
src/main/resources/db/migration/V1__init.sql -
src/main/resources/application.yml -
manifest.yml -
src/main/java/io/pivotal/FortuneServiceApplication.java -
src/main/java/io/pivotal/fortune/Fortune.java
For app-config, you should be pushing the following new:
-
application-flyway.yml
2.5 Re-run the Pipelines
Run through the pipelines again and view the output for the jobs that run the default, smoke, and end-to-end (e2e) tests. You should see that the tests we added in this stage were run.
As you run through the pipelines a second time, you should see the smoke tests from the latest prod version run against the database in the test-rollback-smoke job. In this case, there is no schema upgrade. Nonetheless, the tests confirm that the latest prod version of the app can be used with the current database schema.
You can see the database version information stored in the database by Flyway either by querying the database itself or by hitting the flyway endpoint on the fortune-service URL. The following image shows an example from the scp-stage environment:
Stage Two Recap and Next Steps
What have we accomplished?
-
Increased the effectiveness of the pipelines and our confidence in them by integrating our applications with the testing strategy built into Spring Cloud Pipelines.
-
Established a standard approach to organizing tests, which brings consistency within and across development teams.
-
Enabled auto-managed database versioning and backward compatibility testing that alleviates database schema management throughout the release management lifecycle.
We can now add any unit, integration, smoke, and end-to-end tests to our code base and have a high level of reliability and confidence in our pipelines. We are also better positioned to ensure that our development teams conform to these practices, given the structure established by Spring Cloud Pipelines and the fast feedback and visibility we gain from the pipelines as they execute the tests.
However, we could benefit further by incorporating contracts to define and test the API integration points between applications. We do this in Stage Three of the application migration.
Stage Three: Contracts
In this stage, we introduce contract-based programming practices into our sample application. Doing so improves API management capabilities, including defining, communicating, and testing API semantics. It also lets us catch breaking API changes (that is, we can validate API backward compatibility) in the build phase. This extends the effectiveness of the pipelines, encourages better communication and programming practices across development teams, and provides faster feedback to developers.
We will integrate Spring Cloud Contract and add contracts, stubs, and a stub runner. We will also now complete and make use of the apicompatibility profile defined in Stage Two: Tests.
3.1 Create a Contract
We start by creating the contract for the interaction between greeting-ui and fortune-service. The contract should describe the following expectation: greeting-ui makes a GET request to the root URL of fortune-service and expects a response with status 200 and a string (new fortune) in the body
We code this buy using groovy syntax as follows:
import org.springframework.cloud.contract.spec.Contract
Contract.make {
description("""
should return a fortune string
""")
request {
method GET()
url "/"
}
response {
status 200
body "new fortune"
}
}Save this contract in the fortune-service code base in the following location (which is compliant with Spring Cloud Contract convention): src/test/resources/contracts/<service-name>/<contract-file>. The following image shows the contract file in its location within an IDE:
|
Note
|
You can optionally enable your IDE to assist with contract syntax by adding the Spring Cloud Contract Verifier to your <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-verifier</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency> |
3.2 Create a Base Class for Contract Tests
Now that we have a coded contract, we want to enable auto-generation of contract-based tests. The auto-generation, which we will configure in the next steps, requires a base class that stubs out the service that satisfies the API call, so that we can run the test without external dependencies (for example, the database). The objective is to focus on testing API semantics.
We create the base class in the fortune-service test package as follows:
package io.pivotal.fortune;
import io.restassured.module.mockmvc.RestAssuredMockMvc;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.mockito.BDDMockito;
public class BaseClass {
@Before
public void setup() {
FortuneService service = BDDMockito.mock(FortuneService.class);
BDDMockito.given(service.getFortune()).willReturn("foo fortune");
RestAssuredMockMvc.standaloneSetup(new FortuneController(service));
}
}3.3 Enable Automated Contract-based Testing
Now that we have a contract and a base class, we can use the Spring Cloud Contract Maven plugin to auto-generate contract tests, stubs, and a stub jar.
First we add the Spring Cloud Contract version to the list of properties in the fortune-service pom.xml file, since we will reference it when we enable the Spring Cloud Contract maven plugin. To do so, we add the <spring-cloud-contract.version> to the properties element, as follows:
<properties>
...
<spring-cloud-contract.version>1.2.1.RELEASE</spring-cloud-contract.version>
...
</properties>Next, we edit the default profile in the fortune-service pom.xml file to:
-
Add a plugin block for Spring Cloud Contract maven plugin.
-
Configure it to use our base class (
io.pivotal.fortune.BaseClass) to generate tests. -
Configure it to place auto-generated tests in the
io.pivotal.fortune.contractteststest package.
Note that the package of the contract tests is included by the include filter in the default profile, so these tests run against the application during the build-and-upload job. For fortune-service, this serves to validate that the application conforms to the contract.
The following listing shows the complete profile:
<profile>
<id>default</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*Tests.java</include>
<include>**/*Test.java</include>
</includes>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/smoke/**</exclude>
<exclude>**/e2e/**</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<!--Spring Cloud Contract maven plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<baseClassForTests>io.pivotal.fortune.BaseClass</baseClassForTests>
<basePackageForTests>io.pivotal.fortune.contracttests</basePackageForTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>When the app is built, the Spring Cloud Contract maven plugin also now produces a stub and a stub jar that contains the contract and stub. This stub jar is uploaded to Bintray, along with the usual app jar. As we see shortly, this stub jar can be used by the greeting-ui development team while they wait for fortune-service to be completed. In other words, this gives the greeting-ui development team a producer to test against that is based on a mutually agreed-upon contract without the lead time of having to wait for fortune-service team to implement anything more than a base class and without having to manually stub out calls to fortune-service based on arbitrary or static responses.
|
Tip
|
Package the project locally (run mvn package) to observe the tests, stubs, and stub jar that the Spring Cloud Contract Maven plugin generates. See the following image for reference:
|
3.4 Enable backward compatibility API check
To enable Spring Cloud Pipelines to catch any breaking API changes during the the API compatibility check in the build-and-upload job, we add the Spring Cloud Contract Maven plugin to the apicompatibility profile as well.
In this case, we want the plugin to generate tests based on contracts outside of the project (the ones from the latest prod version), so we configure the plugin to download the latest prod stub jar, which contains the old contract. The plugin uses the old contract and the specified base class (which, in our example, is the same as the one in the previous step) to generate contract tests. These tests are run against the new code to validate that it is still compatible with consumers that comply with the prior contract. This ensures backward compatibility for the API.
In short, we edit the apicompatibility profile in the fortune-service pom.xml file to:
-
Add a plugin block for Spring Cloud Contract Maven plugin.
-
Configure it to download the latest prod stub jar from Bintray to obtain the old contract.
-
Configure it to use our base class (
io.pivotal.fortune.BaseClass) to generate tests (we use the same one as in the prior step). -
Configure it to place auto-generated tests in the
io.pivotal.fortune.contractteststest package.
Note that the package of the contract tests matches the include filter in the apicompatibility profile, so these tests run against the app during the the API compatibility check during the build-and-upload job. For fortune-service, this serves to validate that the app conforms to the old contract.
The following listing shows the complete profile:
<profile>
<id>apicompatibility</id>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/contracttests/**/*Tests.java</include>
<include>**/contracttests/**/*Test.java</include>
</includes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!--Spring Cloud Contract maven plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<contractsRepositoryUrl>${repo.with.binaries}</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<contractDependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>${project.artifactId}</artifactId>
<classifier>stubs</classifier>
<version>${latest.production.version}</version>
</contractDependency>
<contractsPath>/</contractsPath>
<baseClassForTests>io.pivotal.fortune.BaseClass</baseClassForTests>
<basePackageForTests>io.pivotal.fortune.contracttests</basePackageForTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>Spring Cloud Pipelines dynamically injects the values for ${repo.with.binaries} and ${latest.production.version}. You can run this locally by providing these values manually as system properties in the Maven command.
3.5 Push Changes to GitHub
All changes in Stage Three thus far are in fortune-service. At this point, you should be pushing the following new or modified files:
-
pom.xml -
src/test/resources/contracts/greeting-ui/shouldReturnAFortune.groovy -
src/test/java/io/pivotal/fortune/BaseClass.java
3.6 Re-run the fortune-service Pipeline
Run through the fortune-service pipeline to generate stubs. The following output from the build-and-upload job shows the auto-generation of tests and stubs:
You should also see output in the build-and-upload job that shows the execution of these tests against the code.
Additionally, you should see the stub jar uploaded to Bintray along with the usual app jar.
Finally, as you run through the pipeline a second time, you should see that the contract tests from the latest prod version run against the new code in the output of the the API compatibility check during the build-and-upload job. In this case, there is no API change. Nonetheless, the tests confirm that the latest prod version of the API can be used with the current code base.
3.7 Enable Stubs for Integration Tests
Now we turn our attention to greeting-ui.
The following image compares the path of a request through greeting-ui in the build phase, both with and without stubs:
Without stubs, we expect the response to be the Hystrix fallback response that is hard-coded in greeting-ui. With stubs, however, we can expect the response that was declared in the contract. In this case, the stubs are loaded into the greeting-ui process. This leads us to our next task: Loading the stubs produced by fortune-service.
Enable the in-process Stub Runner
To load the stubs into the greeting-ui process, we must enable the Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner dependency. This dependency start ans in-process stub runner that automatically configures Wiremock.
Add the following dependency to the greeting-ui pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>Add Integration Tests Aligned with the Contract
Next, we add integration tests to greeting-ui to test for the expected response declared in the contract.
Add the following class to the test package in greeting-ui:
package io.pivotal.fortune;
import io.pivotal.GreetingUIApplication;
import org.assertj.core.api.BDDAssertions;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.cloud.contract.stubrunner.spring.AutoConfigureStubRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = GreetingUIApplication.class, webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE,
properties = {"spring.application.name=greeting-ui", "spring.cloud.circuit.breaker.enabled=false", "hystrix.stream.queue.enabled=false"})
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"io.pivotal:fortune-service:1.0.0.M1-20180102_203542-VERSION"},
repositoryRoot = "${REPO_WITH_BINARIES}"
//workOffline = true
)
public class FortuneServiceTests {
@Autowired FortuneService fortuneService;
@Test
public void shouldSendRequestToFortune() {
// when
String fortune = fortuneService.getFortune();
// then
BDDAssertions.then(fortune).isEqualTo("foo fortune");
}
}At this point, we can get through the build phase for greeting-ui, and the integration tests run against the fortune-service stubs that runs in the greeting-ui process on the Concourse worker.
|
Tip
|
Notice the configuration of @AutoConfigureStubRunner. You can replace the version with a + sign if using Artifactory or Nexus and it automatically chooses the latest available version on the maven repo.
|
|
Tip
|
Setting workOffline=true (commented out but shown earlier for informational purposes) would make the stub runner get the stubs from the local Maven repository. This is useful for local testing. Alternatively, set the $REPO_WITH_BINARIES environment variable to the value used in the credentials file before doing a local Maven build. Then the local build will download the stubs from your remote Maven repository (for example, Bintray).
|
3.8 Enable Stubs for Smoke Tests
The following image compares the path of a request through greeting-ui in the test phase, both with and without stubs. Note that in the build phase, where the app process runS on the Concourse worker, we ran the stubs in the same process. In the test environment (Cloud Foundry), we run the stubs in a separate process by using a standalone stub runner application. The following image shows the test flow for the greeting-ui application:
As in the build phase, without stubs, we expect the response to be the Hystrix fallback response that is hard-coded in greeting-ui. With stubs, however, we can expect the response that was declared in the contract.
We rely on Spring Cloud Pipelines to:
-
Deploy a stub runner application.
-
Provide the stub runner application with the necessary information to download the stubs.
-
Open a port on the stub runner application for each stub.
We rely on the stub runner application to:
-
Download the stubs from our Maven repository (Bintray).
-
Expose each stub on a separate port.
-
Register each stub in the Service Discovery server.
The following steps describe how to configure stubs for smoke tests.
Provide a Stand-alone Stub Runner App Jar
In the Prep step for this tutorial, you cloned the cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot repo to your local machine. The next step is to build this application and upload it to Bintray to make the jar available to Spring Cloud Pipelines.
As mentioned in Stage One: Scaffolding of this tutorial, Bintray requires that a package exist before any application artifacts can be uploaded. Log into the Bintray UI and create a package for cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot. If you forked this repo, you can use the Import from GitHub option. Otherwise, create the package manually and choose any license (for example, Apache 2.0).
Now you are ready to build and upload this app to Bintray. Edit the following script (which shows cloning, building, and uploading) to match your Bintray URL, the Bintray ID in your ~/.m2/settings/xml file, and the cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot repository URL (if you chose to fork it):
# Edit to match your Bintray URL and M2 repo ID setting (check your ~/.m2/settings.xml file)
MAVEN_REPO_URL=https://api.bintray.com/maven/ciberkleid/maven-repo/cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot
MAVEN_REPO_ID=bintray
# Clone cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot
git clone https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot.git
cd cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot
# Build and upload
./mvnw clean deploy -Ddistribution.management.release.url="${MAVEN_REPO_URL}" -Ddistribution.management.release.id="${MAVEN_REPO_ID}"You should now see the cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot artifacts uploaded on Bintray.
Provide Stand-alone Stub Runner Application Manifest
Next, we add a manifest file for the stub runner application for deployment to Cloud Foundry.
Place this file in the greeting-ui repo. The file name and location can be your choice. For this example, we use sc-pipelines/manifest-stubrunner.yml. The following image shows the file in the appropriate folder:
We populate this manifest-stubrunner.yml with the content shown in the next listing so that the stub runner binds to service-registry. The stub runner registers the fortune-service stub there so that greeting-ui can discover it in the same way it discovers the actual fortune-service app endpoint in stage and prod. From the greeting-ui perspective, there is no difference in how it interacts with Eureka and the stub runner application in test and the way it interacts with Eureka and the fortune-service application in stage and prod. The following listing shows the content of manifest-stubrunner.yml:
---
applications:
- name: stubrunner
timeout: 120
services:
- service-registry
env:
JAVA_OPTS: -Djava.security.egd=file:///dev/urandom
TRUST_CERTS: api.run.pivotal.io
----Provide a Stub Runner Jar and Manifest Information to the Pipeline
Now that we have a jar file and a manifest file for our stub runner application, we need to provide this information to our greeting-ui pipeline so that the pipeline downloads the jar from Bintray and deploys it to Cloud Foundry. We do this through the greeting-ui sc-pipelines.yml file. We add an entry to the list of services in the test section, as follows:
- name: stubrunner
type: stubrunner
coordinates: io.pivotal:cloudfoundry-stub-runner-boot:0.0.1.M1
pathToManifest: sc-pipelines/manifest-stubrunner.ymlNotice that name matches the name of the application in manifest-stubrunner.yml, coordinates corresponds to the jar coordinates of the Maven repository, and pathToManifest matches our chosen fie name for the stub runner application manifest.
Note also the type is set to stubrunner, which Spring Cloud Pipelines will recognize as a stanalone stub runner app and treat accordingly.
Provide Stub Configuration for the Stub Runner Application
The final steps in the configuration of the stand-alone stub runner app are as follows:
-
Enable the stub runner app to download the
fortune-servicestub from Bintray. -
Open a second port on the container to receive requests for this stub.
To accomplish this, we put stub and port configuration information into the properties section of the greeting-ui pom.xml file, by using a property called stubrunner.ids. This property can accept a list of stubrunner IDs. However, for this tutorial, we only have one, as follows:
<properties>
...
<!--Tell stub runner app to start this stub-->
<stubrunner.ids>io.pivotal:fortune-service:1.0.0.M1-20180102_203542-VERSION:stubs:10000</stubrunner.ids>
</properties>Spring Cloud Pipelines uses this information in two ways:
-
It provides this information to the stub runner application through the application’s environment variables.
-
Spring Cloud Pipelines also provides the
$REPO_WITH_BINARIESas an environment variable for the stub runner application. -
The stub runner application uses this information to download the stub from Bintray and expose it on the specified port.
-
-
It opens the additional port specified on the stub runner app and map a new route to it.
-
The format for each route is
<stub-runner-app-name>-<hostname-uuid>-<env>-<app-name>-<port>.<domain>. -
In our example, this would be
stubrunner-cyi-test-greeting-ui-10000.cfapps.io.
-
Since we bound our stub runner application to service-registry (Eureka), the stub runner application registers the stub URL under the FORTUNE-SERVICE application name on Eureka, as the following image shows:
This completes the process of configuring the stand-alone stub runner application.
|
Note
|
You can automate the port configuration by Spring Cloud Pipelines in the future such that you need not include the port in stubrunner.ids. However, for the moment, we are required to specify the port each stub should use.
|
Edit Smoke Tests to Align with the Contract
Finally, we edit our smoke tests for greeting-ui to ensure the response does not contain the Hystrix fallback, since we are now expecting a response from the stub. The following listing shows the edited smoke tests:
package smoke;
import org.assertj.core.api.BDDAssertions;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SmokeTests.class,
webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE)
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SmokeTests {
@Value("${application.url}") String applicationUrl;
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
@Test
public void should_return_a_fortune() {
ResponseEntity<String> response = this.restTemplate
.getForEntity("http://" + this.applicationUrl + "/", String.class);
BDDAssertions.then(response.getStatusCodeValue()).isEqualTo(200);
// Filter out the known Hystrix fallback response
BDDAssertions.then(response.getBody()).doesNotContain("This fortune is no good. Try another.");
}
}In this case, in contrast to the integration test we created earlier for greeting-ui, we do not include @AutoConfigureStubRunner, because we are using a standalone stub runner application.
3.9 Push Changes to GitHub
Push contract-based changes for greeting-ui. You should be pushing the following new or modified files:
-
pom.xml -
sc-pipelines.yml -
sc-pipelines/manifest-stubrunner.yml -
src/test/java/io/pivotal/fortune/FortuneServiceTests.java -
src/test/java/smoke/SmokeTests.java
At this point, we can run through the full pipeline for greeting-ui and leverage the contract-based stub in both the build and test environments.
Stage Three Recap
What have we accomplished?
By implementing a contract-driven approach with auto-generation of tests and stubs, we have introduced a clean, structured, and reliable way to define, communicate, document, manage, and test APIs. The benefits include the following:
-
Inter-team communication can be simpler.
-
Consumer and producer teams can now communicate requirements through coded contracts.
-
The inventory of contracts serves as a record and reference of the agreed-upon APIs.
-
-
Developer productivity will increase.
-
Producers can quickly and easily generate contract-based stubs.
-
Consumers no longer have to manually stub out APIs and write tests with arbitrary hard-coded responses. Instead, they can use the auto-generated stubs and test for contract-based responses.
-
Both producers and consumers can validate their code complies with the contract.
-
Producers can verify backward compatibility of API changes.
-
Troubleshooting will be easier.
-
Failure and feedback will be faster.
-
Conclusion
This concludes the tutorial on migrating apps for Spring Cloud Pipelines for Cloud Foundry.
Moving forward, the refactoring work shown here can be incorporated into your and your team’s standard practices. We recommend the following practices:
Good:
-
Use Maven or Gradle wrappers.
-
Include a Cloud Foundry manifest file in your application repository.
-
Include a pipeline descriptor (
sc-manifest.yml) in your app repository. -
Create an empty
versionbranch in your application repository. -
Include artifact repository configuration in the
pom.xmlfile. -
Align your Cloud Foundry spaces with the Spring Cloud Pipelines model (isolated test space and shared stage and prod spaces).
Better
-
Include
default,apicompatibility,smoke, ande2eprofiles in thepom.xmlfile. -
Organize tests accordingly in your application repository.
Best
-
Use a database migration tool, such as Flyway.
-
Use contract-based API programming.
Implementing all the “good” practices positions you to instantly create pipelines for your applications by using Spring Cloud Pipelines. This is a huge win in terms of consistency and productivity and standardization across development teams. Of course, this is an open source project, so you can modify it to meet your needs.
Implementing the “better” practices ensures the proper tests get run at the proper time. At that point, you can add as much test coverage as you need to have high confidence in your pipelines.
Implementing the “best” practices gives you additional confidence in your pipeline and encourages better programming practices for database version and API management across development teams. It also gives you higher confidence in your pipelines and lets you avoid the cumbersome business of rolling back a database.
Happy coding!
Concourse Pipeline (Cloud Foundry)
|
Important
|
In this chapter, we assume that you deploy your application to Cloud Foundry PaaS. |
The Spring Cloud Pipelines repository contains opinionated Concourse pipeline definitions. Those jobs form an empty pipeline and an opinionated sample pipeline one that you can use in your company.
There following projects take part in the microservice setup for this demo.
-
Github Analytics: The app that has a REST endpoint and uses messaging — part of our business application.
-
Github Webhook: Project that emits messages that are used by Github Analytics — part of our business application.
-
Eureka: Simple Eureka Server. This is an infrastructure application.
-
Github Analytics Stub Runner Boot: Stub Runner Boot server to be used for tests with Github Analytics and uses Eureka and Messaging. This is an infrastructure application.
Step-by-step
If you want only to run the demo as far as possible by using PCF Dev and Docker Compose, do the following:
Fork Repositories
Four applications compose the pipeline
You need to fork only the following repositories, because only then can you tag and push the tag to the repository:
Start Concourse and Artifactory
You can run Concourse + Artifactory locally. To do so, run the
start.sh script from this repository. The following listing shows the script:
git clone https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines
cd spring-cloud-pipelines/concourse
./setup_docker_compose.sh
./start.sh 192.168.99.100The setup_docker_compose.sh script should be run only once, to allow
generation of keys.
The 192.168.99.100 param is an example of an external URL of Concourse
(equal to the Docker-Machine IP in this example).
Then Concourse runs on port 8080, and Artifactory runs on 8081.
Deploy the infra JARs to Artifactory
When Artifactory is running, run the tools/deploy-infra.sh script from this repo.
The following listing shows the script:
git clone https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines
cd spring-cloud-pipelines/
./tools/deploy-infra.shAs a result, both eureka and stub runner repos are cloned, built,
and uploaded to Artifactory.
Start PCF Dev
|
Tip
|
You can skip this step if you have CF installed and do not want to use PCF Dev. The only thing you have to do is to set up spaces. |
|
Warning
|
Servers often run run out of resources at the stage step. If that happens, clear some apps from PCF Dev and continue. |
You have to download and start PCF Dev, as described here.
The default credentials for PCF Dev are as follows:
username: user
password: pass
email: user
org: pcfdev-org
space: pcfdev-space
api: api.local.pcfdev.ioYou can start the PCF Dev as follows:
cf dev startYou must create three separate spaces, as follows:
cf login -a https://api.local.pcfdev.io --skip-ssl-validation -u admin -p admin -o pcfdev-org
cf create-space pcfdev-test
cf set-space-role user pcfdev-org pcfdev-test SpaceDeveloper
cf create-space pcfdev-stage
cf set-space-role user pcfdev-org pcfdev-stage SpaceDeveloper
cf create-space pcfdev-prod
cf set-space-role user pcfdev-org pcfdev-prod SpaceDeveloperYou can also run the ./tools/cf-helper.sh setup-spaces script to create the spaces.
Setup the fly CLI
If you go to the Concourse website, you should see something resembling the following image:
You can click one of the icons (depending on your OS) to download fly, which is the Concourse CLI. Once you download that (and maybe, depending on your OS, add it to your PATH) you can run the following command:
fly --versionIf fly is properly installed, it should print out the version.
Set up Your credentials.yml File
The repository comes with credentials-sample-cf.yml, which is set up with sample data (mostly credentials) that are applicable for PCF Dev. Copy this file to a new file called credentials.yml (the file is added to .gitignore so that you cannot push it with your passwords) and edit it as you wish. For our demo, set up the following:
-
app-url: URL pointing to your forkedgithub-webhookrepository. -
github-private-key: Your private key to clone and tag GitHub repositorys. -
repo-with-binaries: The IP is set to the defaults for Docker Machine. You should update it to point to your setup.
If you do not have a Docker Machine, run th ./whats_my_ip.sh script to
get an external IP that you can pass to your repo-with-binaries, instead of the default
Docker Machine IP.
The following table describes the environment variables required by the scripts:
| Property Name | Property Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
The URL to the CF Api for TEST env |
|
|
The URL to the CF Api for STAGE env |
|
|
The URL to the CF Api for PROD env |
|
|
Name of the org for the test env |
|
|
Prefix of the name of the CF space for the test env to which the app name will be appended |
|
|
Name of the org for the stage env |
|
|
Name of the space for the stage env |
|
|
Name of the org for the prod env |
|
|
Name of the space for the prod env |
|
|
URL to repo with the deployed jars |
|
|
The id of server from Maven settings.xml |
|
|
Additional suffix for the route. In a shared environment the default routes can be already taken |
|
|
Additional options you would like to pass to the Maven / Gradle build |
The right column shows the default values for PCF Dev that we set in the credentials-sample-cf.yml. PAAS_HOSTNAME_UUID and BUILD_OPTIONS have no default values.
Build the Pipeline
Log in (for example, for a Concourse instance running at 192.168.99.100 — if you do not provide any value, localhost is assumed). If you run the login script, it assumes that either fly is on your PATH or it is in the same folder as the script. The following example shows how to specify an IP address for the login script:
./login.sh 192.168.99.100Next, run the command to create the pipeline, as follows:
./set_pipeline.shThen you can create a github-webhook pipeline under the docker alias, using the provided credentials.yml file.
You can override these values in exactly that order (for example ./set-pipeline.sh some-project another-target some-other-credentials.yml)
Run the github-webhook Pipeline
The following images show the various steps involved in running the github-webhook pipeline:
Concourse Pipeline (Kubernetes)
|
Important
|
In this chapter, we assume that you deploy your application to Kubernetes PaaS |
The Spring Cloud Pipelines repository contains opinionated Concourse pipeline definitions. Those jobs form an empty pipeline and an opinionated sample pipeline that you can use in your company.
The following projects take part in the microservice setup for this demo:
-
Github Analytics: The application that has a REST endpoint and uses messaging — part of our business application.
-
Github Webhook: Project that emits messages that are used by Github Analytics — part of our business application.
-
Eureka: Simple Eureka Server. This is an infrastructure application.
-
Github Analytics Stub Runner Boot: Stub Runner Boot server to be used for tests with Github Analytics and uses Eureka and Messaging. This is an infrastructure application.
Step-by-step
If you want only to run the demo as far as possible by using PCF Dev and Docker Compose, do the following:
Fork Repositories
Four applications compose the pipeline:
You need to fork only the following repositories, because only then can you tag and push the tag to the repository:
Concourse in K8S (Kubernetes)
The simplest way to deploy Concourse to K8S is to use Helm.
Once you have Helm installed and your kubectl is pointing to the
cluster, run the following command to install the Concourse cluster in your K8S cluster:
$ helm install stable/concourse --name concourseOnce the script is done, you should see the following output
1. Concourse can be accessed:
* Within your cluster, at the following DNS name at port 8080:
concourse-web.default.svc.cluster.local
* From outside the cluster, run these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=concourse-web" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 to use Concourse"
kubectl port-forward --namespace default $POD_NAME 8080:8080
2. Login with the following credentials
Username: concourse
Password: concourseFollow the steps and log in to Concourse under http://127.0.0.1:8080.
Deploying Artifactory to K8S
You can use Helm also to deploy Artifactory to K8S, as follows:
$ helm install --name artifactory --set artifactory.image.repository=docker.bintray.io/jfrog/artifactory-oss stable/artifactoryAfter you run this command, you should see the following output:
NOTES:
Congratulations. You have just deployed JFrog Artifactory Pro!
1. Get the Artifactory URL by running these commands:
NOTE: It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
You can watch the status of the service by running 'kubectl get svc -w nginx'
export SERVICE_IP=$(kubectl get svc --namespace default nginx -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
echo http://$SERVICE_IP/
2. Open Artifactory in your browser
Default credential for Artifactory:
user: admin
password: passwordNext, you need to set up the repositories.
First, access the Artifactory URL and log in with
a user name of admin and a password of password.
Then, click on Maven setup and click Create.
Setup the fly CLI
You can click one of the icons (depending on your OS) to download fly, which is the Concourse CLI. Once you download that (and maybe added it to your PATH, depending on your OS) you can run the following command:
fly --versionIf fly is properly installed, it should print out the version.
Setup your credentials.yml
We made a sample credentials file called credentials-sample-k8s.yml
prepared for k8s. You can use it as a base for your credentials.yml.
To allow the Concourse worker’s spawned container to connect to the Kubernetes cluster, you must pass the CA contents and the auth token.
To get the contents of CA for GCE, run the following command:
$ kubectl get secret $(kubectl get secret | grep default-token | awk '{print $1}') -o jsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}' | base64 --decodeTo get the auth token, run the following command:
$ kubectl get secret $(kubectl get secret | grep default-token | awk '{print $1}') -o jsonpath='{.data.token}' | base64 --decodeSet that value under paas-test-client-token, paas-stage-client-token, and paas-prod-client-token
Build the pipeline
After running Concourse, you should get the following output in your terminal:
$ export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=concourse-web" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
$ echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 to use Concourse"
$ kubectl port-forward --namespace default $POD_NAME 8080:8080
Visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 to use ConcourseLog in (for example, for Concourse running at 127.0.0.1 — if you do not provide any value, localhost is assumed). If you run this script, it assumes that either fly is on your PATH or that it is in the same folder as the script:
$ fly -t k8s login -c http://localhost:8080 -u concourse -p concourseNext, run the following command to create the pipeline:
$ ./set_pipeline.sh github-webhook k8s credentials-k8s.ymlRun the github-webhook Pipeline
The following images show the various steps involved in runnig the github-webhook pipeline:
Jenkins Pipeline (Common)
In this section we will present the common setup of Jenkins for any platform. We will also provide answers to most frequently asked questions.
Project setup
.
├── declarative-pipeline
│ └── Jenkinsfile-sample.groovy
├── jobs
│ ├── jenkins_pipeline_empty.groovy
│ ├── jenkins_pipeline_jenkinsfile_empty.groovy
│ ├── jenkins_pipeline_sample.groovy
│ └── jenkins_pipeline_sample_view.groovy
├── seed
│ ├── init.groovy
│ ├── jenkins_pipeline.groovy
│ ├── k8s
│ └── settings.xml
└── src
├── main
└── testIn the declarative-pipeline you can find a definition of a Jenkinsfile-sample.groovy declarative
pipeline. It’s used together with the Blueocean UI.
In the jobs folder you have all the seed jobs that will generate pipelines.
-
jenkins_pipeline_empty.groovy- is a template of a pipeline with empty steps using the Jenkins Job DSL plugin -
jenkins_pipeline_jenkinsfile_empty.groovy- is a template of a pipeline with empty steps using the Pipeline plugin -
jenkins_pipeline_sample.groovy- is an opinionated implementation using the Jenkins Job DSL plugin -
jenkins_pipeline_sample_view.groovy- builds the views for the pipelines
In the seed folder you have the init.groovy file which is executed when Jenkins starts.
That way we can configure most of Jenkins options for you (adding credentials, JDK etc.).
jenkins_pipeline.groovy contains logic to build a seed job (that way you don’t have to even click that
job - we generate it for you). Under the k8s folder there are all the configuration
files required for deployment to a Kubernetes cluster.
In the src folder you have production and test classes needed for you to build your own pipeline.
Currently we have tests only cause the whole logic resides in the jenkins_pipeline_sample file.
Optional customization steps
All the steps below are not necessary to run the demo. They are needed only when you want to do some custom changes.
Deploying infra jars to a different location
It’s enough to set the ARTIFACTORY_URL environmental variable before
executing tools/deploy-infra.sh. Example for deploying to Artifactory at IP 192.168.99.100
git clone https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines
cd spring-cloud-pipelines/
ARTIFACTORY_URL="http://192.168.99.100:8081/artifactory/libs-release-local" ./tools/deploy-infra.shSetup settings.xml for Maven deployment
|
Tip
|
If you want to use the default connection to the Docker version of Artifactory you can skip this step |
So that ./mvnw deploy works with Artifactory from Docker we’re
already copying the missing settings.xml file for you. It looks more or less like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<settings>
<servers>
<server>
<id>${M2_SETTINGS_REPO_ID}</id>
<username>${M2_SETTINGS_REPO_USERNAME}</username>
<password>${M2_SETTINGS_REPO_PASSWORD}</password>
</server>
<server>
<id>${DOCKER_SERVER_ID}</id>
<username>${DOCKER_USERNAME}</username>
<password>${DOCKER_PASSWORD}</password>
<configuration>
<email>${DOCKER_EMAIL}</email>
</configuration>
</server>
</servers>
</settings>As you can see the file is parameterized. In Maven it’s enough to pass
to ./mvnw command the proper system property to override that value. For example to pass
a different docker email you’d have to call ./mvnw -DDOCKER_EMAIL=[email protected] and the value
gets updated.
If you want to use your own version of Artifactory / Nexus you have to update
the file (it’s in seed/settings.xml).
Setup Jenkins env vars
If you want to only play around with the demo that we’ve prepared you have to set ONE variable which is the REPOS variable.
That variable needs to consists of comma separated list of URLs to repositories containing business apps. So you should pass your forked repos URLs.
You can do it in the following ways:
-
globally via Jenkins global env vars (then when you run the seed that variable will be taken into consideration and proper pipelines will get built)
-
modify the seed job parameters (you’ll have to modify the seed job configuration and change the
REPOSproperty) -
provide the repos parameter when running the seed job
For the sake of simplicity let’s go with the last option.
|
Important
|
If you’re choosing the global envs, you HAVE to remove the other approach
(e.g. if you set the global env for REPOS, please remove that property in the
seed job
|
Seed properties
Click on the seed job and pick Build with parameters. Then as presented in the screen below (you’ll have far more properties to set) just modify the REPOS property by providing the comma separated list of URLs to your forks. Whatever you set will be parsed by the seed job and passed to the generated Jenkins jobs.
|
Tip
|
This is very useful when the repos you want to build differ. E.g. use
different JDK. Then some seeds can set the JDK_VERSION param to one version
of Java installation and the others to another one.
|
Example screen:
In the screenshot we could parametrize the REPOS and REPO_WITH_BINARIES params.
Set Git email / user
Since our pipeline is setting the git user / name explicitly for the build step
you’d have to go to Configure of the build step and modify the Git name / email.
If you want to set it globally you’ll have to remove the section from the build
step and follow these steps to set it globally.
You can set Git email / user globally like this:
Add Jenkins credentials for GitHub
You have to set credentials with id: git.
Below you can find instructions on how to set a credential (e.g. for Cloud Foundry cf-test credential but
remember to provide the one with id git).
Testing Jenkins scripts
./gradlew clean build
|
Warning
|
The ran test only checks if your scripts compile. |
How to work with Jenkins Job DSL plugin
Check out the tutorial. Provide the link to this repository in your Jenkins installation.
|
Warning
|
Remember that views can be overridden that’s why the suggestion is to contain in one script all the logic needed to build a view
for a single project (check out that spring_cloud_views.groovy is building all the spring-cloud views).
|
Docker Image
If you would like to run the pre-configured Jenkins image somewhere other than your local machine, we
have an image you can pull and use on DockerHub.
The latest tag corresponds to the latest snapshot build. You can also find tags
corresponding to stable releases that you can use as well.
|
Important
|
The Jenkins docker image is setup for demo purposes. For example it has the following
system property -Dpermissive-script-security.enabled=no_security that disables script
security. YOU SHOULD NOT USE IT ON PRODUCTION UNLESS YOU KNOW WHAT YOU’RE DOING.
|
Jenkins Pipeline (Cloud Foundry)
|
Important
|
In this chapter, we assume that you deploy your application to Cloud Foundry PaaS. |
The Spring Cloud Pipelines repository contains job definitions and the opinionated setup pipeline, which uses the Jenkins Job DSL plugin. Those jobs form an empty pipeline and a opinionated sample pipeline that you can use in your company.
The following projects take part in the microservice setup for this demo.
-
Github Analytics: The app that has a REST endpoint and uses messaging — part off our business application.
-
Github Webhook: Project that emits messages that are used by Github Analytics — part of our business application.
-
Eureka: Simple Eureka Server. This is an infrastructure application.
-
Github Analytics Stub Runner Boot: Stub Runner Boot server to be used for tests with Github Analytics and using Eureka and Messaging. This is an infrastructure application.
Step-by-step
This is a guide for the Jenkins Job DSL based pipeline.
If you want only to run the demo as far as possible using PCF Dev and Docker Compose, do the following:
Fork Repositories
Four applications compose the pipeline:
You need to fork only the following, because only then can you tag and push the tag to your repository:
Start Jenkins and Artifactory
Jenkins + Artifactory can be ran locally. To do so, run the
start.sh script from this repository. The following listing shows the script:
git clone https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines
cd spring-cloud-pipelines/jenkins
./start.sh yourGitUsername yourGitPassword yourForkedGithubOrgThen Jenkins runs on port 8080, and Artifactory runs on port 8081.
The parameters are passed as environment variables to the Jenkins VM,
and credentials are set. That way, you need not do
any manual work on the Jenkins side. In the above parameters, the third parameter
could be yourForkedGithubOrg or yourGithubUsername. Also the REPOS environment variable
contains your GitHub org (in which you have the forked repos).
Instead of the Git username and password parameters, you could pass -key <path_to_private_key>
(if you prefer to use key-based authentication with your Git repositories).
Deploy the Infra JARs to Artifactory
When Artifactory is running, run the tools/deploy-infra.sh script from this repo. The following listing shows the script:
git clone https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines
cd spring-cloud-pipelines/
./tools/deploy-infra.shAs a result, both the eureka and stub runner repositories are cloned, built,
and uploaded to Artifactory.
Start PCF Dev
|
Tip
|
You can skip this step if you have CF installed and do not want to use PCF Dev. In that case, the only thing you have to do is to set up spaces. |
|
Warning
|
Servers often run run out of resources at the stage step. If that happens clear some apps from PCF Dev and continue. |
You have to download and start PCF Dev, as described here.
The default credentials when using PCF Dev are as follows:
username: user
password: pass
email: user
org: pcfdev-org
space: pcfdev-space
api: api.local.pcfdev.ioYou can start PCF Dev as follows:
cf dev startYou must create three separate spaces, as follows:
cf login -a https://api.local.pcfdev.io --skip-ssl-validation -u admin -p admin -o pcfdev-org
cf create-space pcfdev-test
cf set-space-role user pcfdev-org pcfdev-test SpaceDeveloper
cf create-space pcfdev-stage
cf set-space-role user pcfdev-org pcfdev-stage SpaceDeveloper
cf create-space pcfdev-prod
cf set-space-role user pcfdev-org pcfdev-prod SpaceDeveloperYou can also run the ./tools/cf-helper.sh setup-spaces script to do this.
Run the Seed Job
We created the seed job for you, but you have to run it. When you do run it, you have to provide some properties. By default we create a seed that has all the properties options, but you can delete most of it. If you set the properties as global environment variables, you have to remove them from the seed.
To run the demo, provide a comma-separated
list of the URLs of the two aforementioned forks (github-webhook and github-analytics') in the `REPOS variable.
The following images shows the steps involved:
jenkins-pipeline-seed-k8s for Kubernetes
REPOS parameter should already contain your forked repos (you’ll have more properties than the ones in the screenshot)
Run the github-webhook Pipeline
We already created the seed job for you, but you have to run it. When you do run it, you have to provide some properties. By default, we create a seed that has all the properties options, but you can delete most of it. If you set the properties as global environment variables, you have to remove them from the seed.
To run the demo, provide a comma-separated
list of URLs of the two aforementioned forks (github-webhook and github-analytics) in the REPOS variable.
The following images shows the steps involved:
|
Important
|
If your build fails on deploy previous version to stage due to a missing jar, that means that you forgot to clear the tags in your repository. Typically, that happens because you removed the Artifactory volume with a deployed jar while a tag in the repository still points there. See here for how to remove the tag. |
|
Important
|
Servers often run run out of resources at the stage step. For that reason, we suggest killing all applications on test. See the FAQ for more detail. |
Declarative Pipeline & Blue Ocean
You can also use the declarative pipeline approach with the Blue Ocean UI.
The Blue Ocean UI is available under the blue/ URL (for example, for Docker Machine-based setup: http://192.168.99.100:8080/blue).
The following images show the various steps involved:
|
Important
|
There is no possibility of restarting a pipeline from a specific stage after failure. See this issue for more information |
|
Warning
|
Currently, there is no way to introduce manual steps in a performant way. Jenkins blocks an executor when a manual step is required. That means that you run out of executors pretty quickly. See this issue and this StackOverflow question for more information. |
Jenkins Cloud Foundry Customization
You can customize Jenkins for Cloud Foundry by setting a variety of environment variables.
|
Note
|
You need not see all the environment variables described in this section to run the demo. They are needed only when you want to make custom changes. |
Environment Variable Summary
The environment variables that are used in all of the jobs are as follows:
| Property Name | Property Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
The URL to the CF API for the TEST environment |
|
|
The URL to the CF API for the STAGE environment |
|
|
The URL to the CF API for the PROD environment |
|
|
Name of the org for the test env |
|
|
Prefix of the name of the CF space for the test environment to which the app name is appended |
|
|
Name of the org for the stage environment |
|
|
Name of the space for the stage environment |
|
|
Name of the org for the prod environment |
|
|
Name of the space for the prod environment |
|
|
URL of the repository with the deployed jars |
|
|
The ID of server from Maven |
|
|
The name of the JDK installation |
|
|
The version of the pipeline (ultimately, also the version of the jar) |
|
|
The email used by Git to tag the repository |
|
|
The name used by Git to tag the repository |
|
|
Additional suffix for the route. In a shared environment, the default routes can be already taken |
|
|
Whether deployment to stage be automatic |
|
|
Whether deployment to prod be automatic |
|
|
Whether the API compatibility step is required |
|
|
Whether the DB rollback step is present |
|
|
Whether to the deploy-to-stage step be present |
|
|
Additional options you would like to pass to the Maven / Gradle build |
|
|
Extension of the binary uploaded to Artifactory / Nexus. Example: |
|
Jenkins Credentials
Our scripts reference the credentials by IDs. The following table describes the defaults for the credentials:
| Property Name | Property Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
Credential ID used to tag a Git repo |
|
|
SSH credential ID used to tag a Git repo |
|
|
If |
|
|
Credential ID used for the repository with jars |
|
|
Credential ID for CF Test environment access |
|
|
Credential ID for CF Stage environment access |
|
|
Credential ID for CF Prod environment access |
|
If you already have in your system a credential to (for example) tag a repository,
you can use it by passing the value of the GIT_CREDENTIAL_ID property.
|
Tip
|
See the cf-helper script for all the configuration options.
|
Jenkins Pipeline (Kubernetes)
|
Important
|
In this chapter, we assume that you deploy your application to Kubernetes PaaS. |
The Spring Cloud Pipelines repository contains job definitions and the opinionated setup pipeline that uses Jenkins Job DSL plugin. Those jobs form an empty pipeline and an opinionated sample pipeline that you can use in your company.
The following projects take part in the microservice setup for this demo.
-
Github Analytics: The app that has a REST endpoint and uses messaging — part of our business application.
-
Github Webhook: Project that emits messages that are used by Github Analytics — part of our business application.
-
Eureka: Simple Eureka Server. This is an infrastructure application.
-
Github Analytics Stub Runner Boot: Stub Runner Boot server to be used for tests with Github Analytics ad uses Eureka and Messaging. This is an infrastructure application.
Step-by-step
This is a guide for a Jenkins Job DSL based pipeline.
If you want only to run the demo as far as possible by using PCF Dev and Docker Compose, do the following:
Fork Repositories
Four applications compose the pipeline
You need to fork only the following repositories, because only then can you tag and push the tag to your repository:
Start Jenkins and Artifactory
Jenkins and Artifactory can be ran locally. To do so, run the
start.sh script from this repo. The following listing shows the script:
git clone https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines
cd spring-cloud-pipelines/jenkins
./start.sh yourGitUsername yourGitPassword yourForkedGithubOrg yourDockerRegistryOrganization yourDockerRegistryUsername yourDockerRegistryPassword yourDockerRegistryEmailThen Jenkins runs on port 8080, and Artifactory runs on port 8081.
The provided parameters are passed as environment variables to the Jenkins VM
and credentials are set. That way, you need not do
any manual work on the Jenkins side. In the preceding script, the third parameter
could be yourForkedGithubOrg or yourGithubUsername. Also the REPOS environment variable
contains your GitHub org in which you have the forked repositories.
Instead of the Git username and password parameters, you could pass -key <path_to_private_key>
if you prefer to use the key-based authentication with your Git repositories.
You need to pass the credentials for the Docker organization (by default, we search for the Docker images at Docker Hub) so that the pipeline can push images to your org.
Deploy the Infra JARs to Artifactory
When Artifactory is running, run the tools/deploy-infra.sh script from this repo.
The following listing shows the script:
git clone https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines
cd spring-cloud-pipelines/
./tools/deploy-infra-k8s.shAs a result, both the eureka and stub runner repos are cloned, built, and
uploaded to Artifactory and their docker images are built.
|
Important
|
Your local Docker process is reused by the Jenkins instance running in Docker. That is why you do not have to push these images to Docker Hub. On the other hand, if you run this sample in a remote Kubernetes cluster, the driver is not shared by the Jenkins workers, so you can consider pushing these Docker images to Docker Hub too. |
Run the seed job
We created the seed job for you, but you have to run it. When you do run it, you have to provide some properties. By default we create a seed that has all the properties options, but you can delete most of it. If you set the properties as global environment variables, you have to remove them from the seed.
To run the demo, provide a comma-separated
list of the URLs of the two aforementioned forks (github-webhook and github-analytics') in the `REPOS variable.
The following images shows the steps involved:
jenkins-pipeline-seed-k8s for Kubernetes
REPOS parameter should already contain your forked repos (you’ll have more properties than the ones in the screenshot)
Run the github-webhook pipeline
We already created the seed job for you, but you have to run it. When you do run it, you have to provide some properties. By default, we create a seed that has all the properties options, but you can delete most of it. If you set the properties as global environment variables, you have to remove them from the seed.
To run the demo, provide a comma-separated
list of URLs of the two aforementioned forks (github-webhook and github-analytics) in the REPOS variable.
The following images shows the steps involved:
|
Important
|
If your build fails on deploy previous version to stage due to a missing jar, that means that you forgot to clear the tags in your repository. Typically, that happens because you removed the Artifactory volume with a deployed jar while a tag in the repository still points there. See here for how to remove the tag. |
|
Important
|
Servers often run run out of resources at the stage step. For that reason, we suggest killing all applications on test. See the FAQ for more detail. |
Declarative pipeline & Blue Ocean
You can also use the declarative pipeline approach with the Blue Ocean UI.
The Blue Ocean UI is available under the blue/ URL (for example, for Docker Machine-based setup: http://192.168.99.100:8080/blue).
The following images show the various steps involved:
|
Important
|
There is no possibility of restarting a pipeline from a specific stage after failure. See this issue for more information |
|
Warning
|
Currently, there is no way to introduce manual steps in a performant way. Jenkins blocks an executor when a manual step is required. That means that you run out of executors pretty quickly. See this issue and this StackOverflow question for more information. |
Jenkins Kubernetes customization
You can customize Jenkins for Cloud Foundry by setting a variety of environment variables.
|
Note
|
You need not see all the environment variables described in this section to run the demo. They are needed only when you want to make custom changes. |
All env vars
The environment variables that are used in all of the jobs are as follows:
| Property Name | Property Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
Name of the docker organization to which Docker images should be deployed |
|
|
Credential ID used to push Docker images |
|
|
Server ID in |
|
|
Email used to connect to Docker registry and Maven builds |
|
|
URL of the Kubernetes cluster for the test environment |
|
|
URL of the docker registry |
|
|
URL of the API of the Kubernetes cluster for the test environment |
|
|
URL of the API of the Kubernetes cluster for the stage environment |
|
|
URL of the API of the Kubernetes cluster for the prod environment |
|
|
Path to the certificate authority for test the environment |
|
|
Path to the certificate authority for stage the environment |
|
|
Path to the certificate authority for the prod environment |
|
|
Path to the client certificate for the test environment |
|
|
Path to the client certificate for the stage environment |
|
|
Path to the client certificate for the prod environment |
|
|
Path to the client key for the test environment |
|
|
Path to the client key for the stage environment |
|
|
Path to the client key for the test environment |
|
|
Path to the file containing the token for the test environment |
|
|
Path to the file containing the token for the stage environment |
|
|
Path to the file containing the token for the prod environment |
|
|
ID of the credential containing access token for test environment |
|
|
ID of the credential containing access token for the stage environment |
|
|
ID of the credential containing access token for the prod environment |
|
|
Name of the cluster for the test environment |
|
|
Name of the cluster for the stage environment |
|
|
Name of the cluster for the prod environment |
|
|
Name of the user for the test environment |
|
|
Name of the user for the stage environment |
|
|
Name of the user for the prod environment |
|
|
Name of the system for the test environment |
|
|
Name of the system for the stage environment |
|
|
Name of the system for the prod environment |
|
|
Namespace for the test environment |
|
|
Namespace for the stage environment |
|
|
Namespace for the prod environment |
|
|
Whether to connect to Minikube |
|
|
URL of the repository with the deployed jars |
|
|
Credential ID used for the repository with jars |
|
|
The ID of server from Maven |
|
|
The name of the JDK installation |
|
|
The version of the pipeline (ultimately, also the version of the jar) |
|
|
The email used by Git to tag the repository |
|
|
The name used by Git to tag the repository |
|
|
Whether deployment to stage be automatic |
|
|
Whether deployment to prod be automatic |
|
|
Whether the API compatibility step is required |
|
|
Whether the DB rollback step is present |
|
|
Whether the deploy-to-stage step is present |
|
|
Additional options you would like to pass to the Maven / Gradle build |
Preparing to Connect to GCE
|
Important
|
Skip this step if you do not use GCE |
In order to use GCE, we need to have gcloud running. If you already have the
CLI installed, skip this step. If not run the following command to have the CLI
downloaded and an installer started:
$ ./tools/k8s-helper.sh download-gcloudNext, configure gcloud. Run gcloud init and log in
to your cluster. You are redirected to a login page. Pick the
proper Google account and log in.
Pick an existing project or create a new one.
Go to your platform page (click on Container Engine) in GCP and connect to your cluster with the following values:
$ CLUSTER_NAME=...
$ ZONE=us-east1-b
$ PROJECT_NAME=...
$ gcloud container clusters get-credentials ${CLUSTER_NAME} --zone ${ZONE} --project ${PROJECT_NAME}
$ kubectl proxyThe Kubernetes dashboard runs at http://localhost:8001/ui/.
We need a Persistent Disk for our Jenkins installation. Create it as follows:
$ ZONE=us-east1-b
$ gcloud compute disks create --size=200GB --zone=${ZONE} sc-pipelines-jenkins-diskOnce the disk has been created, you need to format it. See the instructions at https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/disks/add-persistent-disk#formatting
Connecting to a Kubo or GCE Cluster
|
Important
|
Skip this step if you do not use Kubo or GCE |
This section describes how to deploy Jenkins and Artifactory to a Kubernetes cluster deployed with Kubo.
|
Tip
|
To see the dashboard, run kubectl proxy and access localhost:8081/ui.
|
-
Log in to the cluster.
-
Deploy Jenkins and Artifactory to the cluster:
-
./tools/k8s-helper.sh setup-tools-infra-vspherefor a cluster deployed on VSphere -
./tools/k8s-helper.sh setup-tools-infra-gcefor a cluster deployed to GCE
-
-
Forward the ports so that you can access the Jenkins UI from your local machine, by using the following settings
$ NAMESPACE=default
$ JENKINS_POD=jenkins-1430785859-nfhx4
$ LOCAL_PORT=32044
$ CONTAINER_PORT=8080
$ kubectl port-forward --namespace=${NAMESPACE} ${JENKINS_POD} ${LOCAL_PORT}:${CONTAINER_PORT}
-----
Go to
Credentials, clickSystemandGlobal credentials, as the following image shows: image::https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines/master/docs-sources/src/main/asciidoc/images/jenkins/kubo_credentials.png[caption="Click `Global credentials`"] -
Update
git,repo-with-binariesanddocker-registrycredentials -
Run the
jenkins-pipeline-k8s-seedseed job and fill it out with the following data -
Put
kubernetes.default:443here (orKUBERNETES_API:KUBERNETES_PORT)-
PAAS_TEST_API_URL -
PAAS_STAGE_API_URL -
PAAS_PROD_API_URL
-
-
Put
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crtdata here:-
PAAS_TEST_CA_PATH -
PAAS_STAGE_CA_PATH -
PAAS_PROD_CA_PATH
-
-
Uncheck the
Kubernetes Minikubevalue.-
Clear the following variables:
-
PAAS_TEST_CLIENT_CERT_PATH -
PAAS_STAGE_CLIENT_CERT_PATH -
PAAS_PROD_CLIENT_CERT_PATH -
PAAS_TEST_CLIENT_KEY_PATH -
PAAS_STAGE_CLIENT_KEY_PATH -
PAAS_PROD_CLIENT_KEY_PATH
-
-
-
Set
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/tokenvalue to these variables:-
PAAS_TEST_CLIENT_TOKEN_PATH -
PAAS_STAGE_CLIENT_TOKEN_PATH -
PAAS_STAGE_CLIENT_TOKEN_PATH-
Set the cluster name to these variables (you can get the cluster name by calling
kubectl config current-context):
-
-
PAAS_TEST_CLUSTER_NAME -
PAAS_STAGE_CLUSTER_NAME -
PAAS_PROD_CLUSTER_NAME
-
-
Set the system name to these variables (you can get the system name by calling
kubectl config current-context):-
PAAS_TEST_SYSTEM_NAME -
PAAS_STAGE_SYSTEM_NAME -
PAAS_PROD_SYSTEM_NAME
-
-
Update the
DOCKER_EMAILproperty with your email address. -
Update the
DOCKER_REGISTRY_ORGANIZATIONwith your Docker organization name. -
If you do not want to upload the images to DockerHub, update
DOCKER_REGISTRY_URL. image::https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines/master/docs-sources/src/main/asciidoc/images/jenkins/pks_seed.png[caption="Example of a filled out seed job"] -
Run the pipeline
Kubernetes Setup
This section describes how to set up Kubernetes.
Kubernetes CLI Installation
First, you need to install the kubectl command-line interface (CLI).
Script Installation
You can use the tools/k8s-helper.sh script to install kubectl. To do so, run the following script:
$ ./tools/minikube-helper download-kubectlThen the kubectl gets downloaded.
Manual Installation
You can perform a manual installation for either OSX or Linux.
Example for OSX
The following listing shows how to manually install on OSX:
$ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/darwin/amd64/kubectl
$ chmod +x ./kubectl
$ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
----Example for Linux
The following listing shows how to manually install on Linux:
$ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
$ chmod +x ./kubectl
$ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectlSee this page for more information.
Kubernetes Cluster Setup
We need a cluster of Kubernetes. The best choice is Minikube.
|
Tip
|
You can skip this step if you have a Kubernetes cluster installed and do not want to use Minikube. In that case, the only thing you have to do is to set up spaces. |
|
Warning
|
Servers often run run out of resources at the stage step. If that happens, clear some apps from PCF Dev and continue. |
Script Installation
You can use the tools/k8s-helper.sh script to install Minikube. To do so, run the following script:
$ ./tools/minikube-helper download-minikubeThen the Minikube cluster gets downloaded.
Manual Installation
You can perform a manual installation for either OSX or Linux.
Example for OSX
The following listing shows how to manually install on OSX:
$ curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/v0.20.0/minikube-darwin-amd64 && chmod +x minikube && sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/Feel free to skip running sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin if you want to add minikube to your path manually.
Example for Linux
The following listing shows how to manually install on Linux:
$ curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/v0.20.0/minikube-linux-amd64 && chmod +x minikube && sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/You can skip running sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin if you want to add minikube to your path manually.
See this page for more information on the installation.
Run Minikube
To start Kubernetes on your local box, run minikube start.
To add the dashboard, run minikube dashboard.
Certificates and Workers
Minikube Certificates and Workers
By default, if you install Minikube, all the certificates get installed in your
~/.minikube folder. Your kubectl configuration under ~/.kube/config also
gets updated to use Minikube.
Manual Certificates and Workers Setup
|
Note
|
If you want to run the default demo setup, you can skip this section. |
To target a given Kubernetes instance, you need to pass around Certificate Authority key and also user keys.
You can read more about the instructions on how to generate those keys here.
Generally speaking, if you have a Kubernetes installation (such as minikube), this step
has already been done for you. Now you can reuse those keys on the workers.
The following inormation has been extracted from the Kubernetes official documentation.
Configure kubectl to connect to the target cluster using the following commands, replacing the following values:
-
Replace
${MASTER_HOST}with the master node address or name used in previous steps. -
Replace
${CA_CERT}with the absolute path to theca.pemcreated in previous steps. -
Replace
${ADMIN_KEY}with the absolute path to theadmin-key.pemcreated in previous steps. -
Replace
${ADMIN_CERT}with the absolute path to theadmin.pemcreated in previous steps.
The following commands show how to perform these steps:
$ kubectl config set-cluster default-cluster --server=https://${MASTER_HOST} --certificate-authority=${CA_CERT}
$ kubectl config set-credentials default-admin --certificate-authority=${CA_CERT} --client-key=${ADMIN_KEY} --client-certificate=${ADMIN_CERT}
$ kubectl config set-context default-system --cluster=default-cluster --user=default-admin
$ kubectl config use-context default-systemGenerate Minikube Namespaces
With the Minikube cluster running, we need to generate namespaces. To do so, run the
./tools/k8s-helper.sh setup-namespaces.
The demo setup (Cloud Foundry)
The demo uses two applications: Github Webhook and Github analytics code. The following image shows how these application communicate with each other:
For the demo scenario we have two applications. Github Analytics and Github Webhook.
Let’s imagine a case where Github is emitting events via HTTP. Github Webhook has
an API that could register to such hooks and receive those messages. Once this happens
Github Webhook sends a message by RabbitMQ to a channel. Github Analytics is
listening to those messages and stores them in a MySQL database.
Github Analytics has its KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) monitored. In the case
of that application the KPI is number of issues.
Let’s assume that if we go below the threshold of X issues then an alert should be sent to Slack.
Deploying Production Applications to PCF Dev
In a real-world scenario, we would not want to automatically provision services such as
RabbitMQ, MySQL, or Eureka each time we deploy a new application to production. Typically,
production is provisioned manually (often by using automated solutions). In our case, before
you deploy to production, you can provision the pcfdev-prod space by using the
cf-helper.sh. To do so, call the following script:
$ ./cf-helper.sh setup-prod-infraThe CF CLI:
-
Logs in to PCF Dev,
-
Targets the
pcfdev-prodspace -
Sets up:
-
RabbitMQ (under the
rabbitmq-githubname) -
MySQL (under
mysql-github-analyticsname) -
Eureka (under
github-eurekaname)
-
Running Prometheus on CF
You can check out Toshiaki Maki’s code on how to automate Prometheus installation on CF.
Go to https://prometheus.io/download/ and download the Linux binary. Then run the following command:
cf push sc-pipelines-prometheus -b binary_buildpack -c './prometheus -web.listen-address=:8080' -m 64mAlso, localhost:9090 in prometheus.yml should be localhost:8080.
The file should resemble the following listing to work with the demo setup (change github-analytics-sc-pipelines.cfapps.io
to your github-analytics installation).
# my global config
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # Set the scrape interval to every 15 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 15s # Evaluate rules every 15 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
# Attach these labels to any time series or alerts when communicating with
# external systems (federation, remote storage, Alertmanager).
external_labels:
monitor: 'codelab-monitor'
# Load rules once and periodically evaluate them according to the global 'evaluation_interval'.
rule_files:
# - "first.rules"
# - "second.rules"
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape:
# Here it's Prometheus itself.
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: 'prometheus'
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:8080']
- job_name: 'demo-app'
# Override the global default and scrape targets from this job every 5 seconds.
scrape_interval: 5s
metrics_path: '/prometheus'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ['github-analytics-sc-pipelines.cfapps.io']A deployed version for the Spring Cloud Pipelines demo is available here.
Running Grafana on CF
You can check out Toshiaki Maki’s code to see how to automate Prometheus installation on CF.
Download the tarball from https://grafana.com/grafana/download?platform=linux
and set http_port = 8080 in conf/default.ini. Then run the following the command:
cf push sc-pipelines-grafana -b binary_buildpack -c './bin/grafana-server web' -m 64mThe demo uses Grafana Dashboard with an ID of 2471.
A deployed version for the Spring Cloud Pipelines demo is available here
The demo setup (Kubernetes)
The demo uses two applications: Github Webhook and Github analytics code. The following image shows how these application communicate with each other:
For the demo scenario we have two applications. Github Analytics and Github Webhook.
Let’s imagine a case where Github is emitting events via HTTP. Github Webhook has
an API that could register to such hooks and receive those messages. Once this happens
Github Webhook sends a message by RabbitMQ to a channel. Github Analytics is
listening to those messages and stores them in a MySQL database.
Github Analytics has its KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) monitored. In the case
of that application the KPI is number of issues.
Let’s assume that if we go below the threshold of X issues then an alert should be sent to Slack.
Deploying Production Applications to Minikube
In a real-world scenario, we would not want to automatically provision services such as
RabbitMQ, MySQL, or Eureka each time we deploy a new application to production. Typically,
production is provisioned manually (often by using automated solutions). In our case, before
you deploy to production, you can provision the sc-pipelines-prod namespace by using the
k8s-helper.sh. To do so, call the following script:
$ ./k8s-helper.sh setup-prod-infraRunning Prometheus on Kubernetes
Use Helm to install Prometheus. Later in this demo, we point it to the services deployed to our cluster.
Create a file called values.yaml with the following content:
rbac:
create: false
alertmanager:
## If false, alertmanager will not be installed
##
enabled: true
# Defines the serviceAccountName to use when `rbac.create=false`
serviceAccountName: default
## alertmanager container name
##
name: alertmanager
## alertmanager container image
##
image:
repository: prom/alertmanager
tag: v0.9.1
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Additional alertmanager container arguments
##
extraArgs: {}
## The URL prefix at which the container can be accessed. Useful in the case the '-web.external-url' includes a slug
## so that the various internal URLs are still able to access as they are in the default case.
## (Optional)
baseURL: ""
## Additional alertmanager container environment variable
## For instance to add a http_proxy
##
extraEnv: {}
## ConfigMap override where fullname is {{.Release.Name}}-{{.Values.alertmanager.configMapOverrideName}}
## Defining configMapOverrideName will cause templates/alertmanager-configmap.yaml
## to NOT generate a ConfigMap resource
##
configMapOverrideName: ""
ingress:
## If true, alertmanager Ingress will be created
##
enabled: false
## alertmanager Ingress annotations
##
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: 'true'
## alertmanager Ingress hostnames
## Must be provided if Ingress is enabled
##
hosts: []
# - alertmanager.domain.com
## alertmanager Ingress TLS configuration
## Secrets must be manually created in the namespace
##
tls: []
# - secretName: prometheus-alerts-tls
# hosts:
# - alertmanager.domain.com
## Alertmanager Deployment Strategy type
# strategy:
# type: Recreate
## Node labels for alertmanager pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
persistentVolume:
## If true, alertmanager will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim
## If false, use emptyDir
##
enabled: true
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume access modes
## Must match those of existing PV or dynamic provisioner
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/persistent-volumes/
##
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume Claim annotations
##
annotations: {}
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume existing claim name
## Requires alertmanager.persistentVolume.enabled: true
## If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim: ""
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume mount root path
##
mountPath: /data
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume size
##
size: 2Gi
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume Storage Class
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
## set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
## GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
##
# storageClass: "-"
## Subdirectory of alertmanager data Persistent Volume to mount
## Useful if the volume's root directory is not empty
##
subPath: ""
## Annotations to be added to alertmanager pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
replicaCount: 1
## alertmanager resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
service:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
clusterIP: ""
## List of IP addresses at which the alertmanager service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 80
# nodePort: 30000
type: ClusterIP
## Monitors ConfigMap changes and POSTs to a URL
## Ref: https://github.com/jimmidyson/configmap-reload
##
configmapReload:
## configmap-reload container name
##
name: configmap-reload
## configmap-reload container image
##
image:
repository: jimmidyson/configmap-reload
tag: v0.1
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## configmap-reload resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
kubeStateMetrics:
## If false, kube-state-metrics will not be installed
##
enabled: true
# Defines the serviceAccountName to use when `rbac.create=false`
serviceAccountName: default
## kube-state-metrics container name
##
name: kube-state-metrics
## kube-state-metrics container image
##
image:
repository: gcr.io/google_containers/kube-state-metrics
tag: v1.1.0-rc.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Node labels for kube-state-metrics pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Annotations to be added to kube-state-metrics pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
replicaCount: 1
## kube-state-metrics resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 16Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 16Mi
service:
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels: {}
clusterIP: None
## List of IP addresses at which the kube-state-metrics service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 80
type: ClusterIP
nodeExporter:
## If false, node-exporter will not be installed
##
enabled: true
# Defines the serviceAccountName to use when `rbac.create=false`
serviceAccountName: default
## node-exporter container name
##
name: node-exporter
## node-exporter container image
##
image:
repository: prom/node-exporter
tag: v0.15.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Additional node-exporter container arguments
##
extraArgs: {}
## Additional node-exporter hostPath mounts
##
extraHostPathMounts: []
# - name: textfile-dir
# mountPath: /srv/txt_collector
# hostPath: /var/lib/node-exporter
# readOnly: true
## Node tolerations for node-exporter scheduling to nodes with taints
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
##
tolerations: []
# - key: "key"
# operator: "Equal|Exists"
# value: "value"
# effect: "NoSchedule|PreferNoSchedule|NoExecute(1.6 only)"
## Node labels for node-exporter pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Annotations to be added to node-exporter pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
## node-exporter resource limits & requests
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 200m
# memory: 50Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 30Mi
service:
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels: {}
clusterIP: None
## List of IP addresses at which the node-exporter service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
hostPort: 9100
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 9100
type: ClusterIP
server:
## Prometheus server container name
##
name: server
# Defines the serviceAccountName to use when `rbac.create=false`
serviceAccountName: default
## Prometheus server container image
##
image:
repository: prom/prometheus
tag: v1.8.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## (optional) alertmanager URL
## only used if alertmanager.enabled = false
alertmanagerURL: ""
## The URL prefix at which the container can be accessed. Useful in the case the '-web.external-url' includes a slug
## so that the various internal URLs are still able to access as they are in the default case.
## (Optional)
baseURL: ""
## Additional Prometheus server container arguments
##
extraArgs: {}
## Additional Prometheus server hostPath mounts
##
extraHostPathMounts: []
# - name: certs-dir
# mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/certs
# hostPath: /etc/kubernetes/certs
# readOnly: true
## ConfigMap override where fullname is {{.Release.Name}}-{{.Values.server.configMapOverrideName}}
## Defining configMapOverrideName will cause templates/server-configmap.yaml
## to NOT generate a ConfigMap resource
##
configMapOverrideName: ""
ingress:
## If true, Prometheus server Ingress will be created
##
enabled: false
## Prometheus server Ingress annotations
##
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: 'true'
## Prometheus server Ingress hostnames
## Must be provided if Ingress is enabled
##
hosts: []
# - prometheus.domain.com
## Prometheus server Ingress TLS configuration
## Secrets must be manually created in the namespace
##
tls: []
# - secretName: prometheus-server-tls
# hosts:
# - prometheus.domain.com
## Server Deployment Strategy type
# strategy:
# type: Recreate
## Node tolerations for server scheduling to nodes with taints
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
##
tolerations: []
# - key: "key"
# operator: "Equal|Exists"
# value: "value"
# effect: "NoSchedule|PreferNoSchedule|NoExecute(1.6 only)"
## Node labels for Prometheus server pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
nodeSelector: {}
persistentVolume:
## If true, Prometheus server will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim
## If false, use emptyDir
##
enabled: true
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume access modes
## Must match those of existing PV or dynamic provisioner
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/persistent-volumes/
##
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume annotations
##
annotations: {}
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume existing claim name
## Requires server.persistentVolume.enabled: true
## If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim: ""
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume mount root path
##
mountPath: /data
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume size
##
size: 8Gi
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume Storage Class
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
## set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
## GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
##
# storageClass: "-"
## Subdirectory of Prometheus server data Persistent Volume to mount
## Useful if the volume's root directory is not empty
##
subPath: ""
## Annotations to be added to Prometheus server pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
# iam.amazonaws.com/role: prometheus
replicaCount: 1
## Prometheus server resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 500m
# memory: 512Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 500m
# memory: 512Mi
service:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
clusterIP: ""
## List of IP addresses at which the Prometheus server service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 80
type: ClusterIP
## Prometheus server pod termination grace period
##
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300
## Prometheus data retention period (i.e 360h)
##
retention: ""
pushgateway:
## If false, pushgateway will not be installed
##
enabled: true
## pushgateway container name
##
name: pushgateway
## pushgateway container image
##
image:
repository: prom/pushgateway
tag: v0.4.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Additional pushgateway container arguments
##
extraArgs: {}
ingress:
## If true, pushgateway Ingress will be created
##
enabled: false
## pushgateway Ingress annotations
##
annotations:
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: 'true'
## pushgateway Ingress hostnames
## Must be provided if Ingress is enabled
##
hosts: []
# - pushgateway.domain.com
## pushgateway Ingress TLS configuration
## Secrets must be manually created in the namespace
##
tls: []
# - secretName: prometheus-alerts-tls
# hosts:
# - pushgateway.domain.com
## Node labels for pushgateway pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Annotations to be added to pushgateway pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
replicaCount: 1
## pushgateway resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
service:
annotations:
prometheus.io/probe: pushgateway
labels: {}
clusterIP: ""
## List of IP addresses at which the pushgateway service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 9091
type: ClusterIP
## alertmanager ConfigMap entries
##
alertmanagerFiles:
alertmanager.yml: |-
global:
# slack_api_url: ''
receivers:
- name: default-receiver
# slack_configs:
# - channel: '@you'
# send_resolved: true
route:
group_wait: 10s
group_interval: 5m
receiver: default-receiver
repeat_interval: 3h
## Prometheus server ConfigMap entries
##
serverFiles:
alerts: ""
rules: ""
prometheus.yml: |-
rule_files:
- /etc/config/rules
- /etc/config/alerts
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'demo-app'
scrape_interval: 5s
metrics_path: '/prometheus'
static_configs:
- targets:
- github-analytics.sc-pipelines-prod.svc.cluster.local:8080
- job_name: prometheus
static_configs:
- targets:
- localhost:9090
# A scrape configuration for running Prometheus on a Kubernetes cluster.
# This uses separate scrape configs for cluster components (i.e. API server, node)
# and services to allow each to use different authentication configs.
#
# Kubernetes labels will be added as Prometheus labels on metrics via the
# `labelmap` relabeling action.
# Scrape config for API servers.
#
# Kubernetes exposes API servers as endpoints to the default/kubernetes
# service so this uses `endpoints` role and uses relabelling to only keep
# the endpoints associated with the default/kubernetes service using the
# default named port `https`. This works for single API server deployments as
# well as HA API server deployments.
- job_name: 'kubernetes-apiservers'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
# Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to
# `http`.
scheme: https
# This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape
# endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth
# configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in
# Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside
# the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the
# <kubernetes_sd_config>.
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
# If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the
# master CA, then disable certificate verification below. Note that
# certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure
# so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can
# disable certificate verification by uncommenting the line below.
#
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
# Keep only the default/kubernetes service endpoints for the https port. This
# will add targets for each API server which Kubernetes adds an endpoint to
# the default/kubernetes service.
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace, __meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name]
action: keep
regex: default;kubernetes;https
- job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes'
# Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to
# `http`.
scheme: https
# This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape
# endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth
# configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in
# Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside
# the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the
# <kubernetes_sd_config>.
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
# If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the
# master CA, then disable certificate verification below. Note that
# certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure
# so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can
# disable certificate verification by uncommenting the line below.
#
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/${1}/proxy/metrics
# Scrape config for service endpoints.
#
# The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured
# via the following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/scrape`: Only scrape services that have a value of `true`
# * `prometheus.io/scheme`: If the metrics endpoint is secured then you will need
# to set this to `https` & most likely set the `tls_config` of the scrape config.
# * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this.
# * `prometheus.io/port`: If the metrics are exposed on a different port to the
# service then set this appropriately.
- job_name: 'kubernetes-service-endpoints'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: (.+)(?::\d+);(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_name
- job_name: 'prometheus-pushgateway'
honor_labels: true
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe]
action: keep
regex: pushgateway
# Example scrape config for probing services via the Blackbox Exporter.
#
# The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured
# via the following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/probe`: Only probe services that have a value of `true`
- job_name: 'kubernetes-services'
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [http_2xx]
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- target_label: __address__
replacement: blackbox
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
target_label: kubernetes_name
# Example scrape config for pods
#
# The relabeling allows the actual pod scrape endpoint to be configured via the
# following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/scrape`: Only scrape pods that have a value of `true`
# * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this.
# * `prometheus.io/port`: Scrape the pod on the indicated port instead of the default of `9102`.
- job_name: 'kubernetes-pods'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
regex: (.+):(?:\d+);(\d+)
replacement: ${1}:${2}
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_pod_name
networkPolicy:
## Enable creation of NetworkPolicy resources.
##
enabled: falseNext, create the prometheus installation with the predefined values. To do so, run the following command:
$ helm install --name sc-pipelines-prometheus stable/prometheus -f values.yamlThen you should see the following output:
NOTES:
The Prometheus server can be accessed via port 80 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
sc-pipelines-prometheus-prometheus-server.default.svc.cluster.local
Get the Prometheus server URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=prometheus,component=server" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 9090
The Prometheus alertmanager can be accessed via port 80 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
sc-pipelines-prometheus-prometheus-alertmanager.default.svc.cluster.local
Get the Alertmanager URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=prometheus,component=alertmanager" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 9093
The Prometheus PushGateway can be accessed via port 9091 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
sc-pipelines-prometheus-prometheus-pushgateway.default.svc.cluster.local
Get the PushGateway URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=prometheus,component=pushgateway" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 9093
For more information on running Prometheus, visit:
https://prometheus.io/Running Grafana on Kubernetes
Use Helm to install Grafana, by running the following command:
$ helm install --name sc-pipelines-grafana stable/grafanaYou should see the following output:
NOTES:
1. Get your 'admin' user password by running:
kubectl get secret --namespace default sc-pipelines-grafana-grafana -o jsonpath="{.data.grafana-admin-password}" | base64 --decode ; echo
2. The Grafana server can be accessed via port 80 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
sc-pipelines-grafana-grafana.default.svc.cluster.local
Get the Grafana URL to visit by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=sc-pipelines-grafana-grafana,component=grafana" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 3000
3. Login with the password from step 1 and the username: adminPerform the steps listed in the preceding output and add the Grafana’s datasource
as Prometheus with the following URL: http://sc-pipelines-prometheus-prometheus-server.default.svc.cluster.local
You can pick up the dashboard with the Grafana ID (2471). This is the default dashboard for the Spring Cloud Pipelines demo apps.
If you have both apps (github-webhook and github-analytics) running on production,
you can now trigger the messages. Download the JSON with a sample request
from the github-webhook repository.
Next, pick one of the github-webhook pods and forward its port
locally to a port 9876, as follows:
$ kubectl port-forward --namespace=sc-pipelines-prod $( kubectl get pods --namespace=sc-pipelines-prod | grep github-webhook | head -1 | awk '{print $1}' ) 9876:8080Next, send a couple of requests (more than four), by using cURL as follows:
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:9876/ -d @path/to/issue-created.json \
--header "Content-Type: application/json"Then, if you use Grafana, you can see that you went above the threshold.
Building the Project
This section covers how to build the project. It covers:
Project Setup
The following diagram shows the folder structure of Spring Cloud Pipelines:
.
├── common
├── concourse
├── dist
├── docs
├── docs-sources
└── jenkinsIn the common folder, you can find all the Bash scripts that contain the pipeline logic. These
scripts are reused by both the Concourse and Jenkins pipelines.
In the concourse folder, you can find all the necessary scripts and setup information to run the Concourse demo.
In the dist folder, you can find the packaged sources of the project. Since the package
contains no tests or documentation, it is extremely small and can be used in the pipelines.
In the docs folder, you can find the whole generated documentation of the project.
In the docs-source folder, you can find the sources required to generate the documentation.
In the jenkins folder, you can find all the necessary scripts and setup information to run the Jenkins demo.
Prerequisites
As prerequisites, you need to have shellcheck,
bats, jq
and ruby installed. If you use a Linux
machine, bats and shellcheck are installed for you.
To install the required software on Linux, type the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install -y ruby jqIf you use a Mac, run the following commands to install the missing software:
$ brew install jq
$ brew install ruby
$ brew install bats
$ brew install shellcheckBats Submodules
To make bats work properly, we needed to attach Git submodules. To have them
initialized, either clone the project or (if you have already cloned the project)
pull to update it. The following command clones the project:
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-pipelines.gitThe following commands pull the project:
$ git submodule init
$ git submodule updateIf you forget about this step, Gradle runs these steps for you.
Build and test
Once you have installed all the prerequisites, you can run the following command to build and test the project:
$ ./gradlew clean buildGenerate Documentation
To generate the documentation, run the following command:
$ ./gradlew generateDocsDistributions
Spring Cloud Pipelines has a lot of tests, including Git repositories. Those
and the documentation “weigh” a lot. That is why, under the dist folder, we
publish zip and tar.gz distributions of the sources without tests and documentation.
Whenever we release a distribution, we attach a VERSION file to it that contains
build and SCM information (build time, revision number, and other details). To skip the
distribution generation pass the skipDist property on the command line, as follows:
$ ./gradlew build -PskipDistMaking a Release
You can run the release task to automatically test the project,
build the distributions, change the versions, build the docs, upload the docs to Spring Cloud Static,
tag the repo, and then revert the changed versions back to default. To do so, run the
following command:
$ ./gradlew release -PnewVersion=1.0.0.RELEASEReleasing the Project
This section covers how to release the project by publishing a Docker image.
Publishing A Docker Image
When doing a release, you also need to push a Docker image to Dockerhub.
From the project root, run the following commands, replacing <version> with the
version of the release:
$ docker login
$ docker build -t springcloud/spring-cloud-pipeline-jenkins:<version> ./jenkins
$ docker push springcloud/spring-cloud-pipeline-jenkins:<version>CI Server Worker Prerequisites
Spring Cloud Pipelines uses Bash scripts extensively. The following list shows the software that needs to be installed on a CI server worker for the build to pass:
apt-get -y install \
bash \
git \
tar \
zip \
curl \
ruby \
wget \
unzip \
python \
jq|
Tip
|
In the demo setup all of these libraries are already installed. |
|
Important
|
In the Jenkins case, you also need bats and shellcheck. They are not
included in the preceding list, because the versions installed by Linux distributions might be old.
That is why this project’s Gradle tasks download the latest versions of both libraries
for you.
|
Concourse FAQ
This section covers the most commonly asked questions about using Concourse with Spring Cloud Pipeline:
- Can I use the pipeline for some other repos?
-
Yes To do so, change the
app-urlincredentials.yml! - Does this work for ANY project out of the box?
-
Not really. This is an
opinionated pipeline. That is why we took some opinionated decisions. See the documentation to learn what those decisions are. - Can I modify this to reuse in my project?
-
Yes It is an open-source project. The important thing is that the core part of the logic is written in Bash scripts. That way, in the majority of cases, you could change only the bash scripts without changing the whole pipeline. You can check out the scripts here.
Furthermore, if you want only to customize a particular function under
common/src/main/bash, you can provide your own function undercommon/src/main/bash/<some custom identifier>where<some custom identifier>is equal to the value of theCUSTOM_SCRIPT_IDENTIFIERenvironment variable. It defaults tocustom. - I ran out of resources! (PCF Dev)
-
When deploying the application to stage or prod, you can get an
Insufficient resourcesexception. The way to resolve it is to kill some apps from the test or stage environment. To do so, run the following commands:cf target -o pcfdev-org -s pcfdev-test cf stop github-webhook cf stop github-eureka cf stop stubrunner
You can also run
./tools/cf-helper.sh kill-all-appsto remove all demo-related apps deployed to PCF Dev. - The rollback step fails due to a missing JAR.
-
You must have pushed some tags and must have also removed the Artifactory volume that contained them. To fix this, remove the tags by running the following command:
git tag -l | xargs -n 1 git push --delete origin - Can I see the output of a job from the terminal?
-
Yes. Assuming that pipeline name is
github-webhookand the job name isbuild-and-uploadyou can see the output by running the following command:fly watch --job github-webhook/build-and-upload -t docker
- I clicked the job and it is constantly pending.
-
Most likely, you forgot to click the
playbutton to unpause the pipeline. Click the top left, expand the list of pipelines, and click theplaybutton next togithub-webhook.Another problem that might occur is that you need to have the
versionbranch. Concourse waits for theversionbranch to appear in your repository. So, for the pipeline to start, ensure that when doing some git operations, you have not forgotten to create and copy theversionbranch too. - The route is already in use (CF)
-
If you play around with Jenkins and Concourse you might end up with the routes occupied, as indicated by a message similar to the following:
Using route github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io Binding github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io to github-webhook... FAILED The route github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io is already in use.To fix the problem, you can delete the routes, as follows:
yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n stubrunner-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-stage yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-stage yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-prod yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-prod
You can also run the
./tools/cf-helper.sh delete-routesscript. - I mm unauthorized to deploy infrastructure jars
-
Most likely, you forgot to update your local
settings.xmlfile with Artifactory’s setup. See this section of the docs and update yoursettings.xmlfile. - The
versionresource is broken. When I click on it, I get the following error
resource script '/opt/resource/check []' failed: exit status 128
stderr:
Identity added: /tmp/git-resource-private-key (/tmp/git-resource-private-key)
Cloning into '/tmp/git-resource-repo-cache'...
warning: Could not find remote branch version to clone.
fatal: Remote branch version not found in upstream originThat means that your repo does not have the version branch. You need
set it up.
Jenkins FAQ
This section provides answers to the most frequently asked questions about using Jenkins with Spring Cloud Pipelines.
- Pipeline version contains ${PIPELINE_VERSION}
-
You can check the Jenkins logs and see the following warning:
WARNING: Skipped parameter `PIPELINE_VERSION` as it is undefined on `jenkins-pipeline-sample-build`. Set `-Dhudson.model.ParametersAction.keepUndefinedParameters`=true to allow undefined parameters to be injected as environment variables or `-Dhudson.model.ParametersAction.safeParameters=[comma-separated list]` to whitelist specific parameter names, even though it represents a security breach
To fix it, you have to do exactly what the warning suggests. Also, you should ensure that the
Groovy token macro processingcheckbox is set. - Pipeline version is not passed to the build
-
You can see that the Jenkins version is properly set. However, in the build version, it is still snapshot and the
echo "${PIPELINE_VERSION}"does not print anything.You can check the Jenkins logs and see the following warning:
WARNING: Skipped parameter `PIPELINE_VERSION` as it is undefined on `jenkins-pipeline-sample-build`. Set `-Dhudson.model.ParametersAction.keepUndefinedParameters`=true to allow undefined parameters to be injected as environment variables or `-Dhudson.model.ParametersAction.safeParameters=[comma-separated list]` to whitelist specific parameter names, even though it represents a security breach
To fix it, you have to do exactly what the warning suggests.
- The build times out with
pipeline.shinformation -
This is a Docker compose issue. The problem is that for some reason, only in Docker, the execution of Java hangs. However, it hangs randomly and only the first time you try to run the pipeline.
The solution to this issue is to run the pipeline again. If it passes once, it will pass for any subsequent build.
Another thing that you can try is to run it with plain Docker. That helps sometimes.
- Can I use the pipeline for some other repositories?
-
Yes. You can pass the
REPOSvariable with a comma-separated list ofproject_name$project_urlformat. If you do not provide thePROJECT_NAME, the repository name is extracted and used as the name of the project.For example, a
REPOSvalue equal tohttps://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/github-analytics,https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/github-webhookresults in the creation of pipelines with root namesgithub-analyticsandgithub-webhook.For example, a
REPOSequal tomyanalytics$https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/github-analytics,myfeed$https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/atom-feedresults in the creation of pipelines with root namesmyanalyticsforgithub-analyticsandmyfeedforgithub-webhook. - Can this work for ANY project out of the box?
-
Not really. This is an “opinionated pipeline”. That is why we took some opinionated decisions, such as:
-
Using Spring Cloud, Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner, and Spring Cloud Eureka.
-
Application deployment to Cloud Foundry.
-
Maven, including:
-
Using the Maven Wrapper.
-
Artifacts deployment by using
./mvnw clean deploy. -
The
stubrunner.idsproperty to retrieve the list of collaborators for which stubs should be downloaded. -
Running smoke tests on a deployed app with the
smokeMaven profile. -
Running end to end tests on a deployed app with the
e2eMaven profile.
-
-
Gradle (in the
github-analyticsapplication check in thegradle/pipeline.gradlefile), including:-
Using the Gradlew Wrapper.
-
A
deploytask for artifacts deployment. -
Running smoke tests on a deployed application with the
smoketask. -
Running end to end tests on a deployed application with the
e2etask. -
A
groupIdtask to retrieve group ID. -
An
artifactIdtask to retrieve artifact ID. -
A
currentVersiontask to retrieve the current version. -
A
stubIdstask to retrieve the list of collaborators for which stubs should be downloaded.This is the initial approach that can be easily changed in the future.
-
-
- Can I modify this to reuse in my project?
-
Yes. It is open-source. The important thing is that the core part of the logic is written in Bash scripts. That way, in the majority of cases, you could change only the bash scripts without changing the whole pipeline.
- The rollback step fails due to a missing JAR
-
You must have pushed some tags and have removed the Artifactory volume that contained them. To fix this, remove the tags by using the following command:
git tag -l | xargs -n 1 git push --delete origin - I want to provide a different JDK version.
-
-
By default, we assume that you have configured a JDK with an ID of
jdk8. -
If you want a different one, override the
JDK_VERSIONenvironment variable to point to the proper one.TipThe docker image comes in with Java installed at /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64. You can go toGlobal Toolsand create a JDK with an ID ofjdk8and setJAVA_HOMEto/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64.
-
To change the default settings, follow the steps shown in the following images:
- How can I enable groovy token macro processing?
-
We scripted that. However, if you need to this manually, follow the steps shown in the following images:
- How can I make deployment to stage and prod be automatic?
-
Set the relevant property or environment variable to
true:-
AUTO_DEPLOY_TO_STAGEto automatically deploy to stage. -
AUTO_DEPLOY_TO_PRODto automatically deploy to prod.
-
- How can I skip testing API compatibility?
-
Set the
API_COMPATIBILITY_STEP_REQUIREDenvironment variable tofalseand re-run the seed (you can pick it from the seed job’s properties, too). - I can’t tag the repo.
-
You may get an error similar to the following:
19:01:44 stderr: remote: Invalid username or password. 19:01:44 fatal: Authentication failed for 'https://github.com/marcingrzejszczak/github-webhook/' 19:01:44 19:01:44 at org.jenkinsci.plugins.gitclient.CliGitAPIImpl.launchCommandIn(CliGitAPIImpl.java:1740) 19:01:44 at org.jenkinsci.plugins.gitclient.CliGitAPIImpl.launchCommandWithCredentials(CliGitAPIImpl.java:1476) 19:01:44 at org.jenkinsci.plugins.gitclient.CliGitAPIImpl.access$300(CliGitAPIImpl.java:63) 19:01:44 at org.jenkinsci.plugins.gitclient.CliGitAPIImpl$8.execute(CliGitAPIImpl.java:1816) 19:01:44 at hudson.plugins.git.GitPublisher.perform(GitPublisher.java:295) 19:01:44 at hudson.tasks.BuildStepMonitor$3.perform(BuildStepMonitor.java:45) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.AbstractBuild$AbstractBuildExecution.perform(AbstractBuild.java:779) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.AbstractBuild$AbstractBuildExecution.performAllBuildSteps(AbstractBuild.java:720) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.Build$BuildExecution.post2(Build.java:185) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.AbstractBuild$AbstractBuildExecution.post(AbstractBuild.java:665) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.Run.execute(Run.java:1745) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.FreeStyleBuild.run(FreeStyleBuild.java:43) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.ResourceController.execute(ResourceController.java:98) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.Executor.run(Executor.java:404)
Most likely, you passed a wrong password. Check the credentials section for how to update your credentials.
- I am unauthorized to deploy infrastructure jars.
-
Most likely, you forgot to update your local
settings.xmlfile with the Artifactory’s setup. Check out this section of the docs and update yoursettings.xmlfile. - Signing Artifacts
-
In some cases, it may be required that, when you perform a release, that the artifacts be signed before you push them to the repository. To do this, you need to import your GPG keys into the Docker image that runs Jenkins. This can be done by placing a file called
public.keythat contains your public key and a file calledprivate.keythat contains your private key in theseeddirectory. These keys are imported by theinit.groovyscript runs when Jenkins starts. - Using SSH keys for Git
-
The seed job checks whether an environment variable called
GIT_USE_SSH_KEYis set totrue. If it istrue, the environment variable calledGIT_SSH_CREDENTIAL_IDis chosen as the one that contains the ID of the credential that contains SSH private key. By default,GIT_CREDENTIAL_IDis picked as the one that contains the username and password to connect to git.You can set these values in the seed job by filling out the form and toggling a checkbox.
- Deploy to stage fails and does not redeploy a service (Kubernetes).
-
There can be a number of reasons for this issue. Remember, though, that, for stage, we assume that a sequence of manual steps needs to be performed. We do not redeploy any existing services, because, most likely, you deliberately have it set up that way. If, in the logs of your application, you can see that you cannot connect to a service, first ensure that the service is forwarding traffic to a pod. Next, if that is not the case, delete the service and re-run the step in the pipeline. That way, Spring Cloud Pipelines redeploy the service and the underlying pods.
- I ran out of resources. (Cloud Foundry)
-
[jenkins-cf-resources]] When deploying the application to stage or prod, you can get an
Insufficient resourcesexception. The way to solve it is to kill some applications from the test and stage environments. To do so, run the following commands:cf target -o pcfdev-org -s pcfdev-test cf stop github-webhook cf stop github-eureka cf stop stubrunner
You can also run
./tools/cf-helper.sh kill-all-appsto remove all demo-related apps deployed to PCF Dev. - Deploying to test or stage or prod fails with an error about finding space (Cloud Foundry)
-
You receive an exception similar to the following:
20:26:18 API endpoint: https://api.local.pcfdev.io (API version: 2.58.0) 20:26:18 User: user 20:26:18 Org: pcfdev-org 20:26:18 Space: No space targeted, use 'cf target -s SPACE' 20:26:18 FAILED 20:26:18 Error finding space pcfdev-test 20:26:18 Space pcfdev-test not foundIt means that you forgot to create the spaces in your PCF Dev installation.
- The route is already in use (Cloud Foundry).
-
If you play around with Jenkins and Concourse, you can end up with routes that are already occupied, as identified by errors similar to the following:
Using route github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io Binding github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io to github-webhook... FAILED The route github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io is already in use.To resolve the issue, delete the offending routes, by using commands similar to the following:
yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n stubrunner-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-stage yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-stage yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-prod yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-prod
You can also run the
./tools/cf-helper.sh delete-routesscript. - How can I run helper scripts against a real Cloud Foundry instance that I’m logged into?
-
Assuming that you are already logged into the cluster, uyou can run the helper script with the
REUSE_CF_LOGIN=trueenv variable, as shown in the following example:REUSE_CF_LOGIN=true ./tools/cf-helper.sh setup-prod-infra
This script create the MySQL database and the RabbitMQ service and downloads and deploys Eureka to the space and organization you are logged into.