videocoreiv-qpu
NOTE On 2014-02-28, Broadcom announced the release of full documentation for the VideoCore IV graphics core, and a complete source release of the graphics stack at https://www.raspberrypi.org/blog/a-birthday-present-from-broadcom/. Their release largely obsoletes the information contained here. But we have left it here for historical reasons.
Fun and Games with the Videocoreiv Quad Processor Units
The BCM2835 SoC (System on a Chip) in the RaspberryPi has the following significant computation units:
- ARM1176JZF-S 700 MHz processor which acts as the "main" processor and typically runs Linux.
- Dualcore Videocore IV CPU @250MHz with SIMD Parallel Pixel Units (PPU) which runs scalar (integer and float) and vector (integer only) programs. Runs ThreadX OS, and generally coordinates all functional blocks such as video codecs, power management, video out.
- Image Sensor Pipeline (ISP) providing lens shading, satistics and distortion correction.
- QPU units which provide 24 GFLOPS compute performance for coordinate, vertex and pixel shaders.
Let's focus on the QPU here.
Disclaimer:
There is good precedent in Copyright Law for the following assumption:
- Given, an input I, with copyright holder C(I)
- a program or algorithm A with copyright holder C(A)
- a program output O, given by O=A(I)
that C(O) = C(I), given C(A) injects no artistic work during the operation of A().
We aim to feed different inputs into functions provided by the blob, and
document and analyse the outputs - without violating copyright law.
We will feed various inputs such as shader programs into the blob via entry
points (such as provided by OpenGL ES) and observe the outputs.
At all times we will obey:
"This software may only be used for the purposes of developing for,
running or using a Raspberry Pi device."
as stipulated in the license:
https://github.com/raspberrypi/firmware/blob/master/boot/LICENCE.broadcom.
Key Patent Applications
In recommended reading order:
- US20110227920 Method and System for a Shader Processor With Closely Couple Peripherals
- US20110154307 Method and System for Utilizing Data Flow Graphs to Compile Shaders
- US20110148901 Method and System for Tile Mode Renderer With Coordinate Shader
- US20110216069 Method and System for Compressing Tile Lists Used for 3d Rendering
- US20110221743 Method and System for Controlling a 3d Processor Using a Control List in Memory
- US20110242113 Method and System for Processing Pixels Utilizing Scoreboarding
- US20110261059 Method and System for Decomposing Complex Shapes Into Curvy RHTS For Rasterization
- US20080291208 Method and System for Processing Data Via a 3d Pipeline Coupled to a Generic Video Processing Unit
Recommended Background
In recommended reading order:
QPU Instruction Set
- Fixed length instruction word of 64 bits.
- Instructions contain multiple issue slots.
- There is a slot for the Add vector ALU and Multiply vector ALU.
- Registers written in one cycle, should not be read back for 1 instruction cycle.
- Branch instructions have 3 delay slots.
- Thread switching is handled by (cooperative) thread switch instructions.
- Program may be terminated by instruction with program end signal, two delay slots will be executed before the unit becomes idle.
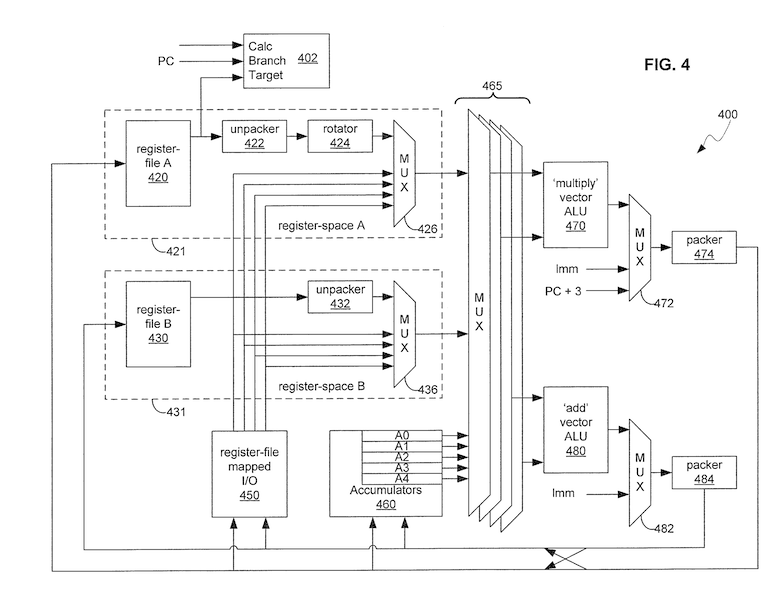
Instruction and Register Pipeline
- Decoupled memory access operations are: reciprocal, reciprocal square root, logarithm and exponential (US20110227920-0078).
- Accumulators written in one cycle are available immediately in the next instruction (US20110227920-0092).
- Accumulators are a0...a4 or r0...r5 (here) (US20110227920-0094).
- The two register files have 32 registers each (US20110227920-0095), whilst the other 32 register addresses refer to peripheral IO.
- The rotator allows a vector to be rotated by any one of 16 horizontal rotations (US20110227920-0096).
- The unpackers can unpack register data, whilst the packers pack it (US20110227920-0097).
- Support for zero-extension of 8-bit data, sign extension of 16-bit data, convert 16-bit floats to 32-bit floats. (US20110227920-0099).
- Values written to registers (not accumulators) are not available in the next cycle (US20110227920-0103).
- Condition field allows conditional write back of ALU results (US20110227920-0104), and updating of condition flags is optional.
- 32-bit bit data may be written back to registers/accumulators as an alternative to ALU results (US20110227920-0105).
- Branches have 3-delay slots (no prediction), and may be conditional based on ALU flag bits. Branches may provide link functionality. (US20110227920-0106).
- Instructions may include a signalling field (US20110227920-0107) without costing an additional instruction. Typical uses include tile buffer access, or end of program / thread switch (both with 2 delay slots).
Instruction Encodings
I'm realigning the names with those found in some of the blobs. For instance thread-switch becomes thrsw, gl_FragColor becomes tlbc, min8 becomes v8min and so forth. The main purpose of this change is in the vain hope that if any of the work here becomes useful the names are common for anyone doing this in a commercial context.
Add/Mul Operations:
<addop><addcc> wa, radda, raddb [setf] ; <mulop><mulcc> wb, rmula, rmulb [setf] ; <op> <addop><addcc> wb, radda, raddb [setf] ; <mulop><mulcc> wa, rmula, rmulb [setf] ; <op> radda = ra | ra >> shift | imm6 | rb | r0..r5 raddb = rb | ra >> shift | imm6 | rb | r0..r5 rmula = ra | ra >> shift | imm6 | rb | r0..r5 rmulb = rb | ra >> shift | imm6 | rb | r0..r5
Encoding:
mulop:3 addop:5 ra:6 rb:6 adda:3 addb:3 mula:3 mulb:3, op:4 packbits:8 addcc:3 mulcc:3 F:1 X:1 wa:6 wb:6 mulop:3 addop:5 ra:6 imm:6 adda:3 addb:3 mula:3 mulb:3, 1101 packbits:8 addcc:3 mulcc:3 F:1 X:1 wa:6 wb:6
Where:
addop is the add ALU operation.
00000 nop
00001 fadd rd = ra + rb (floating point addition)
00010 fsub rd = ra - rb (floating point subtraction)
00011 fmin rd = fmin(ra, rb) (floating point minimum)
00100 fmax rd = fmax(ra, rb) (floating point maximum)
00101 fminabs rd = fminabs(ra, rb)
00110 fmaxabs rd = fmaxabs(ra, rb)
00111 ftoi rd = int(rb) (convert float to int)
01000 itof rd = float(rb) (convert int to float)
01001
01010
01011
01100 add rd = ra + rb (integer addition)
01101 sub rd = ra - rb (integer subtraction)
01110 shr rd = ra >>> rb (logical shift right)
01111 asr rd = ra >> rb (arithmetic shift right)
10000 ror rd = ror(ra, rb) (rotate right)
10001 shl rd = ra << rb (logical shift left)
10010 min rd = min(ra, rb) (integer min)
10011 max rd = max(ra, rb) (integer max)
10100 and rd = ra & rb (bitwise and)
10101 or rd = ra | rb (bitwise or, note: or rd, ra, ra is used for mov)
10110 xor rd = ra ^ rb (bitwise xor)
10111 not rd = ~rb (bitwise not)
11000 clz rd = clz(rb) (count leading zeros)
11001
11010
11011
11100
11101
11110 v8adds rd[i] = sat8(ra[i]+rb[i]), i = 0..3 / a..d
11111 v8subs rd[i] = sat8(ra[i]-rb[i]), i = 0..3 / a..d
mulop is the multiplication ALU operation.
000 nop
001 fmul rd = ra * rb
010 mul24
011 v8muld rd[i] = ra[i] * rb[3], i = 0..3 / a..d
100 v8min rd[i] = min(ra[i], rb[i]), i = 0..3 / a..d, (note: v8min rd, ra, ra is used for mov)
101 v8max rd[i] = max(ra[i], rb[i]), i = 0..3 / a..d
110 v8adds rd[i] = sat8(ra[i] + rb[i]), i = 0..3 / a..d
111 v8subs rd[i] = sat8(ra[i] - rb[i]), i = 0..3 / a..d
op is the signaling or control flow operation.
0000 bpkt
0001 nop
0010 thrsw thread switch
0011 thrend thread end
0100 sbwait scoreboard wait
0101 sbdone scoreboard done
0110 lthrsw last thread switch
0111 loadcv
1000 loadc load tlb color
1001 ldcend load tlb color and thread end
1010 ldtmu0 load tmu0
1011 ldtmu1 load tmu1
1100 loadam
1101 nop (small constant encoded in field rb)
1110 ldi load immediate
1111 bra branch
(Replacing the following names, thread-switch, thread-end, scoreboard-wait, scoreboard-done, last-thread-switch,
(openvg coverage?), load-gl_FragColor, load-gl_FragColor-and-thread-end, load-tmu0, load-tmu1,
(openvg alpha mask?))
adda, addb encode which accumulator or ra, rb value will be supplied to the add ALU.
mula, mulb encode which accumulator or ra, rb value will be supplied to the multiplication ALU.
000 r0 accumulator 0
001 r1 accumulator 1
010 r2 accumulator 2
011 r3 accumulator 3
100 r4 accumulator 4
101 r5 accumulator 5
110 ra register from bank a
111 rb register from bank b
packbits control the packing/unpacking operation.
Each 32 bit value can be viewed as (a:8, b:8, c:8, d:8) or (a:16, b:16)
uuu0pppp unpack from ra0-31 only, pack to ra0-31 only.
uuu1pppp unpack from r4 only, pack (multiply dst only) to r0-r3, ra0-31 or rb0-31.
uuu unpacking add/mul source (rb)
000 (32) full 32 bit value
001 16a unpack from 16a
010 16b unpack from 16b
011 8dr unpack as 8d replicated, ie (d:8, d:8, d:8, d:8)
100 8a unpack from 8a
101 8b unpack from 8b
110 8c unpack from 8c
111 8d unpack from 8d
0pppp pack add result
0000 (32)
0001 16a
0010 16b
0011 8abcd
0100 8a
0101 8b
0110 8c
0111 8d
1000 s
1001 16as
1010 16bs
1011 8abcds
1100 8as
1101 8bs
1110 8cs
1111 8ds
1pppp pack mul result
0000 (32)
0001
0010
0011 8abcd
0100 8a
0101 8b
0110 8c
0111 8d
1000
1001
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
addcc holds the cc predicate for conditional execution of the add instruction.
mulcc holds the cc predicate for conditional execution of the mul instruction.
000 .never never
001 always
010 .zs zero set
011 .zc zero clear
100 .ns negative set
101 .nc negative clear
110 .cs carry set
111 .cc carry clear
F is set to update cc flags (there are Zero, Negative and Carry flags per unit) - SETF
Normally the result of the add operation is used to determine the new cc flags.
If the add operation is a nop, then the result of the multiply operation is used.
X is set to exchange values on the writeback (ie the crossed lines in the diagram).
ra is register bank A value to read.
ra0..ra31 are registers, whilst ra32..ra63 are peripheral addresses.
rb is register bank B value to read.
rb0..rb31 are registers, whilst rb32..rb63 are peripheral addresses.
wa is destination for the add or mul result (depends on X).
ra0..ra31 are registers, whilst ra32..ra63 are peripheral addresses.
wb is destination for the add or mul result (depends on X).
rb0..rb31 are registers, whilst rb32..rb63 are peripheral addresses.
ra rb wa wb
000000 ra00 rb00 ra00 rb00
000001 ra01 rb01 ra01 rb01
000010 ra02 rb02 ra02 rb02
000011 ra03 rb03 ra03 rb03
000100 ra04 rb04 ra04 rb04
000101 ra05 rb05 ra05 rb05
000110 ra06 rb06 ra06 rb06
000111 ra07 rb07 ra07 rb07
001000 ra08 rb08 ra08 rb08
001001 ra09 rb09 ra09 rb09
001010 ra10 rb10 ra10 rb10
001011 ra11 rb11 ra11 rb11
001100 ra12 rb12 ra12 rb12
001101 ra13 rb13 ra13 rb13
001110 ra14 rb14 ra14 rb14
001111 ra15 (w) rb15 (z) ra15 (w) rb15 (z)
001000 ra16 rb16 ra16 rb16
001001 ra17 rb17 ra17 rb17
001010 ra18 rb18 ra18 rb18
001011 ra19 rb19 ra19 rb19
001100 ra20 rb20 ra20 rb20
001101 ra21 rb21 ra21 rb21
001110 ra22 rb22 ra22 rb22
001111 ra23 rb23 ra23 rb23
011000 ra24 rb24 ra24 rb24
011001 ra25 rb25 ra25 rb25
011010 ra26 rb26 ra26 rb26
011011 ra27 rb27 ra27 rb27
011100 ra28 rb28 ra28 rb28
011101 ra29 rb29 ra29 rb29
011110 ra30 rb30 ra30 rb30
011111 ra31 rb31 ra31 rb31
100000 unif unif r0 r0
100001 r1 r1
100010 r2 r2
100011 vary vary r3 r3
100100 tmurs tmurs
100101 r5quad r5rep
100110 elem_num qpu_num irq irq
100111 (nop) (nop) (nop) (nop)
101000 unif_addr unif_addr_rel
101001 x_coord y_coord x_coord y_coord
101010 ms_mask rev_flag ms_mask rev_flag
101011 stencil stencil
101100 tlbz tlbz
101101 tlbm tlbm
101110 tlbc tlbc
101111 tlbam? tlbam?
110000 vpm vpm vpm vpm
110001 vr_busy vw_busy vr_setup vw_setup
110010 vr_wait vw_wait vr_addr vw_addr
110011 mutex mutex mutex mutex
110100 recip recip
110101 recipsqrt recipsqrt
110110 exp exp
110111 log log
111000 t0s t0s
111001 t0t t0t
111010 t0r t0r
111011 t0b t0b
111100 t1s t1s
111101 t1t t1t
111110 t1r t1r
111111 t1b t1b
rb - Small constants, active when signal/control operation is 1101:
imm ra rb
0 i:5 ra i Signed 4 bit immediate
10 i:4 ra 1.0 << i Shift by signed 4 bit quantity
11 0000 ra >> A5 -
11 d:4 ra >> d -
Branches:
# Branch absolute to addr+ra, optionally save return address to wa and/or wb. bra[<cond>] [wa|wb], addr[+ra] # Branch relative to pc+addr+ra, optionally save return address to wa and/or wb. brr[<cond>] [wa|wb], addr[+ra]
Encoding:
addr:32, 1111 0000 cond:4 relative:1 register:1 ra:5 X:1 wa:6 wb:6
Where:
addr is the target address
cond is the condition code:
0000 .allz all zero set
0001 .allnz all zero clear
0010 .anyz any zero set
0011 .anynz any zero clear
0100 .alln all negative set
0101 .allnn all negative clear
0110 .anyn any negative set
0111 .anynn any negative clear
1000 .allc all carry set
1001 .allnc all carry clear
1010 .anycs any carry set
1011 .anycc any carry clear
xxxx unknown
relative is set if the target is relative.
register is set if the target should be addr + ra
X, wa, wb are used to write the return address to a register
(ie. branch and link).
Move Immediate:
movi[<addcc>] wa, data [setf] ; movi[<mulcc>] wb, data [setf] movi[<addcc>] wb, data [setf] ; movi[<mulcc>] wa, data [setf]
Encoding:
data:32, 1110 unknown:8 addcc:3 mulcc:3 F:1 X:1 wa:6 wb:6
Where:
data is constant to be loaded. addcc, mulcc, F, X, wa and wb as above.
Catching QPU Instruction Fragments
Automatically
Use qpu-sniff from the qpu-sniff directory. Example:
- First fragment is the fragment shader.
- Second fragment is the full vertex shader.
- Third fragment is the coordinate shader (vertex shader only concerned with Vertex positions - used for tiling).
vs/null.vs:
void main(void) {
}
fs/add.fs:
uniform vec4 c1;
uniform vec4 c2;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = c1+c2;
}
('shader code' 18402720 88)
00000000: 15827d80 10020827 mov r0, unif
00000002: 01827c00 40020867 fadd r1, unif, r0; nop; sbwait
00000004: 15827d80 10020827 mov r0, unif
00000006: 01827c00 10020827 fadd r0, unif, r0
00000008: 95827d80 114258a0 mov r2, unif; mov r0.8a, r0
0000000a: 81827c89 11525860 fadd r1, unif, r2; mov r0.8b, r1
0000000c: 95827d89 11625860 mov r1, unif; mov r0.8c, r1
0000000e: 01827c40 10020867 fadd r1, unif, r1
00000010: 809e7009 317059e0 nop; mov r0.8d, r1; thrend
00000012: 159e7000 10020ba7 mov tlbc, r0
00000014: 009e7000 500009e7 nop; nop; sbdone
('shader code' 184027a0 104)
00000000: 15827d80 10120027 mov ra0.16a, unif
00000002: 15827d80 10220027 mov ra0.16b, unif
00000004: 15827d80 10021c67 mov vw_setup, unif
00000006: 15827d80 10020c27 mov vpm, unif
00000008: 15827d80 10020c27 mov vpm, unif
0000000a: 15827d80 10020c27 mov vpm, unif
0000000c: 15827d80 10020c27 mov vpm, unif
0000000e: 95020dbf 10024c20 mov vpm, ra0; mov r0, unif
00000010: 01827c00 10020c27 fadd vpm, unif, r0
00000012: 15827d80 10020c27 mov vpm, unif
00000014: 009e7000 300009e7 nop; nop; thrend
00000016: 009e7000 100009e7 nop
00000018: 009e7000 100009e7 nop
('shader code' 185092a0 72)
00000000: 15827d80 10120027 mov ra0.16a, unif
00000002: 15827d80 10220027 mov ra0.16b, unif
00000004: 15827d80 10021c67 mov vw_setup, unif
00000006: 95020dbf 10024c20 mov vpm, ra0; mov r0, unif
00000008: 01827c00 10020c27 fadd vpm, unif, r0
0000000a: 15827d80 10020c27 mov vpm, unif
0000000c: 009e7000 300009e7 nop; nop; thrend
0000000e: 009e7000 100009e7 nop
00000010: 009e7000 100009e7 nop
Manually
Under Raspbian /opt/vc/bin/ and /opt/vc/bin/vcdbg and /opt/vc/bin/vcgencmd may be used to poke about on the videocore side. See https://github.com/nezticle/RaspberryPi-BuildRoot/wiki/VideoCore-Tools for more information.
- Run a OpenGL ES program, and whilst it is running (or ideally paused so the shaders are static):
$ sudo vcdbg reloc
This gives for example (removing the non relevant entries):
[ 23] 0x1c509340: used 160 (refcount 3 lock count 0, size 116, align 4, data 0x1c509360, d0rual) 'EGL_SERVER_SURFACE_T' [ 24] 0x1c5093e0: used 7.9M (refcount 512 lock count 511, size 8294400, align 4096, data 0x1c50a000, d1Rual) 'KHRN_IMAGE_T.storage' [ 40] 0x1ccf33e0: used 7.9M (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 8294400, align 4096, data 0x1ccf4000, d1Rual) 'KHRN_IMAGE_T.storage' [ 39] 0x1d4dd3e0: used 7.9M (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 8294400, align 4096, data 0x1d4de000, d1Rual) 'KHRN_IMAGE_T.storage' [ 27] 0x1dcc73e0: used 160 (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 118, align 1, data 0x1dcc7400, d0rual) 'mem_strdup' [ 42] 0x1dcc7480: used 1.2K (refcount 2 lock count 0, size 1200, align 4, data 0x1dcc74a0, d0rual) 'GL20_PROGRAM_T' [ 26] 0x1dcc7960: used 64 (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 24, align 4, data 0x1dcc7980, d0rual) 'GL20_PROGRAM_T.uniform_data' [ 25] 0x1dcc79a0: used 640 (refcount 2 lock count 0, size 588, align 4, data 0x1dcc79c0, d0rual) 'GLXX_BUFFER_T' [ 37] 0x1dcc7c20: used 96 (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 64, align 4, data 0x1dcc7c40, D1rual) 'GLXX_BUFFER_INNER_T.storage' [ 16] 0x1dcc7c80: used 96 (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 48, align 8, data 0x1dcc7ca0, d1rual) 'shader code' [ 33] 0x1dcc7ce0: used 256 (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 216, align 8, data 0x1dcc7d00, d1rual) 'shader code' [ 30] 0x1dcc7de0: used 128 (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 96, align 4, data 0x1dcc7e00, d0rual) 'uniform map' [ 15] 0x1dcc7e60: used 256 (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 208, align 8, data 0x1dcc7e80, d1rual) 'shader code' [ 28] 0x1dd381e0: used 3.0K (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 3072, align 4, data 0x1dd38200, d0RUal) 'GLSL_COPY_CONTEXT_T.mh_blob' [ 29] 0x1dd38e00: used 128 (refcount 1 lock count 0, size 96, align 4, data 0x1dd38e20, d0rual) 'uniform map'
The fragments can then be saved via:
$ sudo vcdbg save shader_code_1 0x1dcc7c80 96 $ sudo vcdbg save shader_code_2 0x1dcc7ce0 256 $ sudo vcdbg save shader_code_3 0x1dcc7e60 256 $ sudo vcdbg save uniform_map_1 0x1dcc7de0 128 $ sudo vcdbg save uniform_map_2 0x1dd38e00 128 $ sudo vcdbg save GL20_PROGRAM_T 0x1dcc7480 1200 $ sudo vcdbg save GL20_PROGRAM_T.uniform_data 0x1dcc7960 64 $ sudo vcdbg save GLXX_BUFFER_T 0x1dcc79a0 640 $ sudo vcdbg save GLXX_BUFFER_INNER_T.storage 0x1dcc7c20 96