Ops CLI
From version 2.0 onward, ops-cli requires Python3.
If you're still using Python2, use ops-cli version <2.0
ops-cli is a python wrapper for Terraform, Ansible and SSH for cloud automation.
We use multiple tools to manage our infrastructure at Adobe. The purpose of ops-cli is to gather the common cluster configurations in a single place and, based on these, interact with the above mentioned tools. In this way, we can avoid duplication and can quickly spin up new clusters (either production or development ones). All we need to do is customize the cluster configuration file (example here).
ops-cli integrates with the Azure and AWS cli, in order to provide inventory, ssh, sync, tunnel and the possibility to run ansible playbooks on a fleet of EC2 instances.
It can be used to add a layer of templating (using jinja2) on top of Terraform files. This is useful for removing duplicated code when it comes to spinning up infrastructure across multiple environments (stage/sandbox/prod) and across teams. Useful for both AWS and Kubernetes deployments.
Table of Contents
- How it works?
- Use cases
- Installing
- Development
- Troubleshooting
- License
How it works?
You define a cluster configuration, using a yaml file. The yaml file contains different kind of sections, one for each plugin. For instance, you could have a section for Terraform files, a section for AWS instructions, Kubernetes Helm charts and so forth.
Use cases
Manage AWS EC2 instances
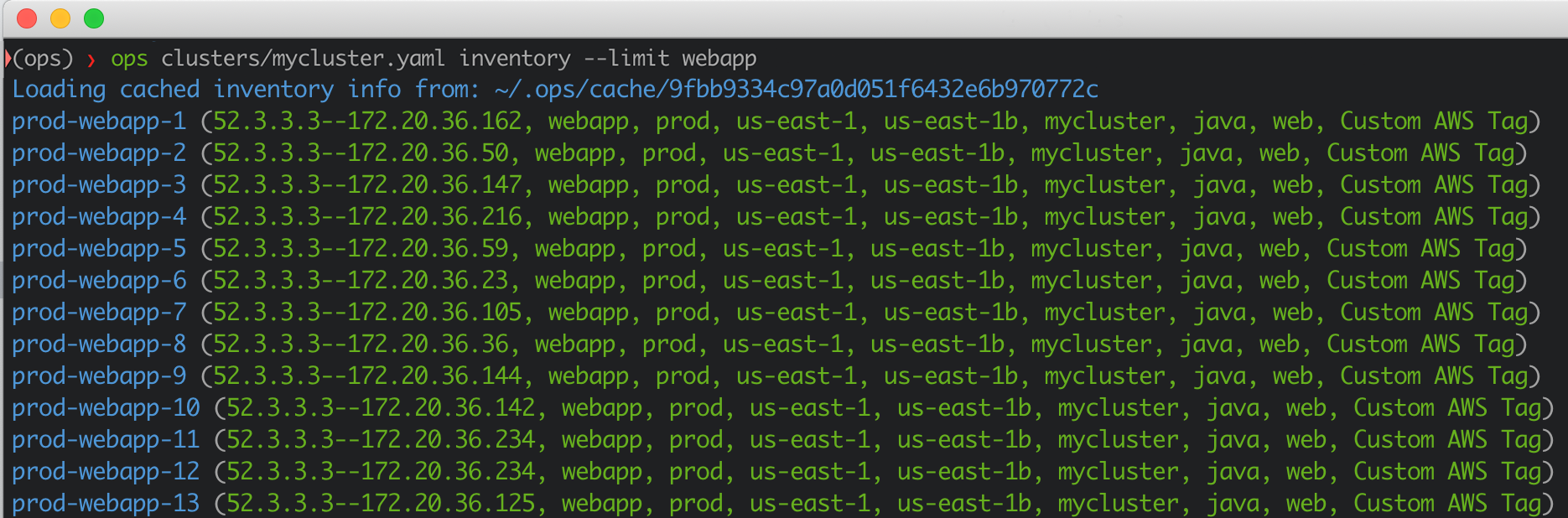
Once you define your cluster configuration, you can run ops commands such as seeing the instance inventory.
# fetch instances from AWS and prints them
ops clusters/mycluster.yaml inventory --limit webapp This would output something like:
Then you can run ssh, play, run, sync etc.
# SSH to one of the nodes (can handle bastion as well)
ops clusters/mycluster.yaml ssh webapp-01
# run a deployment playbook via ansible
ops clusters/mycluster.yaml play ansible/playbooks/task/webapp/deployment.yaml -- -e version=5.36.2 -u ec2-user --limit webapp
# run command on all selected nodes
ops clusters/mycluster.yaml run "sudo yum upgrade myawesomeapp; sudo service myawesomeapp restart" -- -u ec2-user --limit '"aam_app_group=canary;az=us-east-1a"'
# copy file to all servers
ops clusters/mycluster.yaml sync /tmp/myfile webapp: -l ec2-user
# create a tunnel
ops clusters/stage.yaml ssh --tunnel --local 8080 --remote 8080 stage-thanos-1 -l ec2-userSee examples/features/inventory
Terraform
# Performs jinja templating (if any) and runs terraform plan
ops clusters/mycluster.yaml terraform --path-name aws-eks plan
# Run terraform apply, with the possibility to sync the tf state files remotely (currently, AWS S3 bucket is supported + DynamoDB for locking).
ops clusters/mycluster.yaml terraform --path-name aws-eks applyRun terraform by using hierarchical configs
See examples/features/terraform-hierarchical
Create Kubernetes cluster (using AWS EKS)
Installing
Local
Virtualenv
Here is a link about how to install and use virtualenv: https://virtualenv.pypa.io/en/stable/
Ops tool installation
Python 3
# Make sure pip is up to date
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python3
# Install virtualenv
pip install --upgrade virtualenv
pip install --upgrade virtualenvwrapper
echo 'export WORKON_HOME=$HOME/.virtualenvs' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'source /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh' >> ~/.bash_profile
source ~/.bash_profile
# create virtualenv
mkvirtualenv ops
workon ops
# uninstall previous `ops` version (if you have it)
pip uninstall ops --yes
# install ops-cli v2.2.0 stable release
pip install --upgrade ops-cliTerraform
Optionally, install terraform to be able to access terraform plugin. See https://www.terraform.io/intro/getting-started/install.html Also for pretty formatting of terraform plan output you can install https://github.com/coinbase/terraform-landscape (use gem install for MacOS)
Using docker image
You can try out ops-cli, by using docker. The docker image has all required prerequisites (python, terraform, helm, git, ops-cli etc).
To start out a container, running the latest ops-cli docker image run:
docker run -it ghcr.io/adobe/ops-cli:2.2.0 bashAfter the container has started, you can start using ops-cli:
ops help
# usage: ops [-h] [--root-dir ROOT_DIR] [--verbose] [-e EXTRA_VARS]
# cluster_config_path
# {inventory,terraform,packer,ssh,play,run,sync,noop} ...
git clone https://github.com/adobe/ops-cli.git
cd ops-cli
ls examples
# aws-kubernetes
# cassandra-stress
# features
cd examples/aws-kubernetes
ops clusters/my-kubernetes-cluster.yaml terraform --path-name aws-eks plan
# in order to setup aws-kubernetes follow the steps from https://github.com/adobe/ops-cli/blob/master/examples/aws-kubernetes/README.mdConfiguring
AWS
If you plan to use ops with AWS, you must configure credentials for each account
$ aws configure --profile aws_account_nameAzure
TBD
Examples
See examples/ folder:
- cassandra-stress - n-node cassandra cluster used for stress-testing; a basic stress profile is included
- spin up a Kubernetes cluster
- distinct
opsfeatures
Usage help
To see all commands and a short description run ops --help
usage: ops [-h] [--root-dir ROOT_DIR] [--verbose] [-e EXTRA_VARS]
cluster_config_path
{inventory,terraform,packer,ssh,play,run,sync,noop} ...
Run commands against a cluster definition
positional arguments:
cluster_config_path The cluster config path cluster.yaml
{inventory,terraform,packer,ssh,play,run,sync,noop}
inventory Show current inventory data
terraform Wrap common terraform tasks with full templated
configuration support
packer Wrap common packer tasks and inject variables from a
cluster file
ssh SSH or create an SSH tunnel to a server in the cluster
play Run an Ansible playbook
run Runs a command against hosts in the cluster
sync Sync files from/to a cluster
noop used to initialize the full container for api usage
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--root-dir ROOT_DIR The root of the resource tree - it can be an absolute
path or relative to the current dir
--verbose, -v Get more verbose output from commands
-e EXTRA_VARS, --extra-vars EXTRA_VARS
Extra variables to use. Eg: -e ssh_user=ssh_user
More help
Each sub-command includes additional help information that you can get by running:
ops examples/inventory/aam.yaml sync --help
Tool configuration: .opsconfig.yaml
Some tool settings are available via a .opsconfig.yaml configuration file.
The file is looked-up in /etc/opswrapper/.opsconfig.yaml, then in ~/.opsconfig.yaml and then in the project folder starting from the current dir and up to the root dir.
All the files found this way are merged together so that you can set some global defaults, then project defaults in the root dir of the project and
overwrite them for individual envs. Eg: ~/.opsconfig.yaml, /project/.opsconfig.yaml, /project/clusters/dev/.opsconfig.yaml
Inventory
The inventory command will list all the servers in a given cluster and cache the results for further operations on them (for instance, SSHing to a given node or running an ansible playbook).
You can always filter which nodes you want to display or use to run an ansible playbook on, by using the --limit argument (eg. --limit webapp). The extra filter is applied on the instance tags, which includes the instance name.
The way inventory works is by doing a describe command in AWS/Azure. The describe command matches all the nodes that have the tag "cluster" equal to the cluster name you have defined.
In order to configure it, you need to add the inventory section in your cluster configuration file (example here).
AWS example
---
inventory:
- plugin: cns
args:
clusters:
- region: us-east-1
boto_profile: aam-npe # make sure you have this profile in your ~/.aws/credentials file
names: [mycluster1] # this assumes the EC2 nodes have the Tag Name "cluster" with Value "mycluster1"
Azure example
---
inventory:
- plugin: azr
args:
tags: environment=prod
locations: westeurope,northeurope
Inventory usage
usage: ops cluster_config_path inventory [-h] [-e EXTRA_VARS]
[--refresh-cache] [--limit LIMIT]
[--facts]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-e EXTRA_VARS, --extra-vars EXTRA_VARS
Extra variables to use. Eg: -e ssh_user=ssh_user
--refresh-cache Refresh the cache for the inventory
--limit LIMIT Limit run to a specific server subgroup. Eg: --limit
newton-dcs
--facts Show inventory facts for the given hosts
Terraform
usage: ops cluster_config_path terraform [-h] [--var VAR] [--module MODULE]
[--resource RESOURCE] [--name NAME]
[--plan]
subcommand
positional arguments:
subcommand apply | console | destroy | import | output | plan |
refresh | show | taint | template | untaint
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--var VAR the output var to show
--module MODULE for use with "taint", "untaint" and "import". The
module to use. e.g.: vpc
--resource RESOURCE for use with "taint", "untaint" and "import". The
resource to target. e.g.: aws_instance.nat
--name NAME for use with "import". The name or ID of the imported
resource. e.g.: i-abcd1234
--plan for use with "show", show the plan instead of the
statefile
--skip-refresh for use with "plan". Skip refresh of statefile
--raw-output for use with "plan". Show raw plan output without piping through terraform landscape (if terraform landscape is not enabled in opsconfig.yaml this will have no impact)
--path-name PATH_NAME in case multiple terraform paths are defined, this
allows to specify which one to use when running
terraform
Examples:
# Create a new cluster with Terraform
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform plan
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform apply
# Update an existing cluster
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform plan
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform apply
# Get rid of a cluster and all of its components
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform destroy
# Retrieve all output from a previously created Terraform cluster
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform output
# Retrieve a specific output from a previously created Terraform cluster
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform output --var nat_public_ip
# Refresh a statefile (no longer part of plan)
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform refresh
# Taint a resource- forces a destroy, then recreate on next plan/apply
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform taint --module vpc --resource aws_instance.nat
# Untaint a resource
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform untaint --module vpc --resource aws_instance.nat
# Show the statefile in human-readable form
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform show
# Show the plan in human-readable form
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform show --plan
# View parsed jinja on the terminal
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform template
# Import an unmanaged existing resource to a statefile
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform import --module vpc --resource aws_instance.nat --name i-abcd1234
# Use the Terraform Console on a cluster
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform console
# Validate the syntax of Terraform files
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform validate
# Specify which terraform path to use
ops clusters/qe1.yaml terraform plan --path-name terraformFolder1
Terraform landscape
For pretty formatting of terraform plan output you can install https://github.com/coinbase/terraform-landscape (use gem install for MacOS).
To make ops use it you need to add terraform.landscape: True in opsconfig.yaml file.
SSH
usage: ops cluster_config_path ssh [-h] [-e EXTRA_VARS] [-l USER]
[--ssh-config SSH_CONFIG] [--index INDEX]
[--tunnel] [--ipaddress] [--local LOCAL]
[--remote REMOTE] [--proxy] [--nossh]
role [ssh_opts [ssh_opts ...]]
positional arguments:
role Server role to ssh to. Eg: dcs
ssh_opts Manual ssh options
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-e EXTRA_VARS, --extra-vars EXTRA_VARS
Extra variables to use. Eg: -e ssh_user=ssh_user
-l USER, --user USER SSH User
--ssh-config SSH_CONFIG
Ssh config file name in the ./ansible dir
--index INDEX Index of the server from the group
--tunnel Use SSH tunnel, must pass --local and --remote
--ipaddress
--local LOCAL local port for ssh proxy or ssh tunnel
--remote REMOTE remote port for ssh tunnel
--proxy Use SSH proxy, must pass --local
--nossh Port tunnel a machine that does not have SSH. Implies
--ipaddress, and --tunnel; requires --local and
--remote
--keygen Create a ssh keys pair to use with this infrastructure
--noscb Disable use of Shell Control Box (SCB) even it is
enabled in the cluster config
--auto_scb_port When using Shell Control Box (SCB) and creating a
proxy,a random port is generated, which will be used
in the ssh config for all playbook, run and sync
operations
Examples:
# SSH using current username as remote username
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh nagios
# SSH using a different username
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh nagios -l ec2-user
# SSH to the second nagios instance
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh nagios --index 2
# SSH to a specific hostname, instead of the tagged role
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh full-hostname-here-1
# Create an SSH tunnel to Nagios forwarding the remote port 80 to local port 8080
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh --tunnel --remote 80 --local 8080 nagios
# Create an SSH tunnel to a host where the service is NOT listening on `localhost`
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh --tunnel --remote 80 --local 8080 nagios --ipaddress
# Create an SSH tunnel to a host with an open port which does NOT have SSH itself (Windows)
# Note that the connection will be made from the Bastion host
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh --tunnel --local 3389 --remote 3389 --nossh windowshost
# Create a proxy to a remote server that listens on a local port
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh --proxy --local 8080 bastion
# In case Shell Control Box (SCB) is configured and enabled on the cluster a proxy which
# will be used by all ops play, run and sync operations, can be created either using
# either the port configured the cluster config file or an auto generated port.
# In this case --local param must not be used
# Example for using the port configured in the cluster config
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh bastion --proxy
# Example for using the auto generated port
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh bastion --proxy --auto_scb_port
# Disable use of Shell Control Box (SCB) even it is enabled in the cluster config
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh bastion --noscb
SSHPass
In case you want to use the OSX Keychain to store your password and reuse across multiple nodes (e.g. running a playbook on 300 nodes and not having to enter the password for every node) follow the tutorial below:
-
Open
Keychain Accessapp on OSX -
Create a new keychain (
File -> New Keychain), let's sayaam -
Select the
aamkeychain and add a new password entry in this (File -> New Password Item): - Name:idm- Kind:application password- Account:your_ldap_account(e.g.johnsmith) - Where:idm -
Create
$HOME/bindir - this is where the scripts below are saved -
Create
~/bin/askpassscript and update the ldap account there:
cat > ~/bin/askpass <<"EOF"
#!/usr/bin/env bash
/usr/bin/security find-generic-password -a <your_ldap_account> -s idm -w $HOME/Library/Keychains/aam.keychain
EOF
chmod +x ~/bin/askpass-
Checkout notty github repo, build and move the binary to
$HOME/bin/ -
Create
~/bin/sshpassscript:
cat > $HOME/bin/sshpass <<"EOF"
#!/usr/bin/env bash
export DISPLAY=:99
export SSH_ASKPASS="$HOME/bin/askpass"
[[ $1 == -d* ]] && shift
$HOME/bin/notty $@
EOF
chmod +x $HOME/bin/sshpass- Verify the setup works:
# Connect to bastion
~/bin/sshpass ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -l <your_ldap_account> <52.5.5.5>- Run
opstool
SCB
Shell Control Box (SCB) is an activity monitoring appliance from Balabit (now One Identity) that controls privileged access to remote servers.
ops has support for using SCB as ssh proxy for the following operations: ssh, tunnel, proxy, ansible play, run and sync
In order to use SCB an extra section needs to be added to the cluster config file:
scb:
enabled: true
host: "scb.example.com"
proxy_port: 2222 # optional
Having this config all ssh operations will be done via the scb host, unless the --noscb flag is used.
When using SCB, SSHPass will not be used.
For ansible play, run and sync operations to work via SCB a proxy needs to be created first and then run ops in a different terminal window or tab:
# 1. Create a proxy in a terminal window
# Example for using the port configured in the cluster config
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh bastion --proxy
# Example for using the auto generated port
ops clusters/qe1.yaml ssh bastion --proxy --auto_scb_port
# 2. Run the play/run/sync command normally in a different terminal window or tab
# A message will indicate the scb proxy is used
ops clusters/qe1.yaml play ansible/plays/cluster/configure.yaml
...
Connecting via scb proxy at 127.0.0.1:2222.
This proxy should have already been started and running in a different terminal window.
If there are connection issues double check that the proxy is running.
...
Play
Run an ansible playbook.
usage: ops cluster_config_path play [-h] [-e EXTRA_VARS] [--ask-sudo-pass]
[--limit LIMIT] [--noscb]
playbook_path
[ansible_args [ansible_args ...]]
positional arguments:
playbook_path The playbook path
ansible_args Extra ansible args
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-e EXTRA_VARS, --extra-vars EXTRA_VARS
Extra variables to use. Eg: -e ssh_user=ssh_user
--ask-sudo-pass Ask sudo pass for commands that need sudo
--limit LIMIT Limit run to a specific server subgroup. Eg: --limit
newton-dcs
--noscb Disable use of Shell Control Box (SCB) even if it is
enabled in the cluster config
Examples:
# Run an ansible playbook
ops clusters/qe1.yaml play ansible/plays/cluster/configure.yaml
# Limit the run of a playbook to a subgroup
ops clusters/qe1.yaml play ansible/plays/cluster/configure.yaml -- --limit dcs
# Overwrite or set a variable
ops clusters/qe1.yaml play ansible/plays/cluster/configure.yaml -- -e city=paris
# Filter with tags
ops clusters/qe1.yaml play ansible/plays/cluster/configure.yaml -- -t common
# Run a playbook and overwrite the default user
ops clusters/qe1.yaml play ansible/plays/cluster/configure.yaml -- -u ec2-user
Run command
Run a bash command on the selected nodes.
usage: ops cluster_config_path run [-h] [--ask-sudo-pass] [--limit LIMIT]
[--noscb]
host_pattern shell_command
[extra_args [extra_args ...]]
positional arguments:
host_pattern Limit the run to the following hosts
shell_command Shell command you want to run
extra_args Extra ansible arguments
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--ask-sudo-pass Ask sudo pass for commands that need sudo
--limit LIMIT Limit run to a specific server subgroup. Eg: --limit
newton-dcs
--noscb Disable use of Shell Control Box (SCB) even if it is
enabled in the cluster config
Examples:
# Last 5 installed packages on each host
ops qe1.yaml run all 'sudo grep Installed /var/log/yum.log | tail -5'
# See nodetool status on each cassandra node
ops qe1.yaml run qe1-cassandra 'nodetool status'
# Complex limits
ops qe1.yaml run 'qe1-cassandra,!qe1-cassandra-0' 'nodetool status'
# Show how to pass other args
Sync files
Performs rsync to/from a given set of nodes.
usage: ops cluster_config_path sync [-h] [-l USER] [--noscb]
src dest [opts [opts ...]]
positional arguments:
src Source dir
dest Dest dir
opts Rsync opts
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l USER, --user USER Value for remote user that will be used for ssh
--noscb Disable use of Shell Control Box (SCB) even if it is
enabled in the cluster config
rsync wrapper for ops inventory conventions
Example:
# rsync from remote dcs role
ops cluster.yml sync 'dcs[0]:/usr/local/demdex/conf' /tmp/configurator-data --user remote_user
# extra rsync options
ops cluster.yml sync 'dcs[0]:/usr/local/demdex/conf' /tmp/configurator-data -l remote_user -- --progress
Noop
usage: ops cluster_config_path noop [-h]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Packer
Runs packer, for creating images.
usage: ops cluster_config_path packer [-h] subcommand
positional arguments:
subcommand build | validate
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Examples:
# Validate a packer file
ops clusters/centos7.yaml packer validate
# Build a packer file
ops clusters/centos7.yaml packer build
Secrets Management
There are cases where you need to reference sensitive data in your cluster.yaml file (credentials, passwords, tokens etc). Given that the cluster configuration file can be stored in a version control system (such as Git), the best practice is to not put sensitive data in the file itself. Instead, we can use ops-cli to fetch the desired credentials from a secrets manager such as Vault or Amazon SSM, at runtime.
Vault
Ops can manage the automatic generation of secrets and their push in Vault, without actually persisting the secrets in the cluster file. A cluster file will only need to use a construct like the following:
db_password: "{{'secret/campaign/generated_password'|managed_vault_secret(policy=128)}}"
Which will translate behind the scenes in :
- look up in vault the secrets at secret/campaign/generated_password in the default key 'value' (Adobe convention that can be overridden with the key parameter)
- if the value there is missing, generate a new secret using the engine passgen with a policy of length 128 characters
- return the generated value
- if the value at that path already exist, just return that value. This allows us to just refer in cluster files a secret that actually exists in vault and make sure we only generate it once - if it was already created by os or any other system, we will just use what is already there. The reference is by means of fixed form jinja call added to the cluster file, which ends up interpreted later during the templating phase.
Amazon Secrets Manager (SSM)
Amazon offers the possibility to use their Secrets Manager in order to manage configuration data such as credentials, passwords and license keys.
We can use ops-cli to fetch the sensitive data from SSM, at runtime. Just define this in your cluster configuration file (eg. mycluster.yaml).
db_password: "{{ '/my/ssm/path' | read_ssm(aws_profile='myprofile') }}"
ops-cli will read the SSM value by running a command similar to: AWS_PROFILE=aam-npe aws ssm get-parameter --name "/my/ssm/path" --region us-east-1 --with-decryption.
Note that you can specify the AWS region via read_ssm(aws_profile='myprofile', region_name='us-west-2').
Using jinja2 filters in playbooks and terraform templates
You can register your own jinja2 filters that you can use in the cluster config file, terraform templates and ansible playbooks
All ops commands look for filters in the following locations:
- the python path
- the .opsconfig.yaml ansible.filter_plugins setting (defaults to plugins/filter_plugins)
Example simple filter:
# plugins/filter_plugin/myfilters.py
def my_filter(string):
return 'filtered: ' + string
class FilterModule(object):
def filters(self):
return {
'my_filter': my_filter
}
# usage in playbook, templates, cluster config
# test_custom_filters: "{{ 'value' | my_filter }}"
SKMS
Create a file in ~/.skms/credentials.yaml which looks like the following:
endpoint: "api.skms.mycompany.com"
username: <username>
password: <password>Development
Install ops in development mode
git clone https://github.com/adobe/ops-cli.git
cd ops
# Install openssl
brew install openssl libyaml
env LDFLAGS="-L$(brew --prefix openssl)/lib" CFLAGS="-I$(brew --prefix openssl)/include" python setup.py develop
Running tests
- on your machine:
py.test tests
Troubleshooting
-
Permission issues when installing: you should install the tool in a python virtualenv
-
Exception when running:
opspkg_resources._vendor.packaging.requirements.InvalidRequirement: Invalid requirement, parse error at "'!= 2.4'"Caused by a broken paramiko version, reinstall paramiko:
pip2 uninstall paramiko; pip2 install paramiko -
Exception when installing ops because the cryptography package fails to install:
Either install the tool in a virtualenv or:
brew install libffi
brew link libffi --force
brew install openssl
brew link openssl --force