grab-site
grab-site is an easy preconfigured web crawler designed for backing up websites. Give grab-site a URL and it will recursively crawl the site and write WARC files. Internally, grab-site uses a fork of wpull for crawling.
grab-site gives you
-
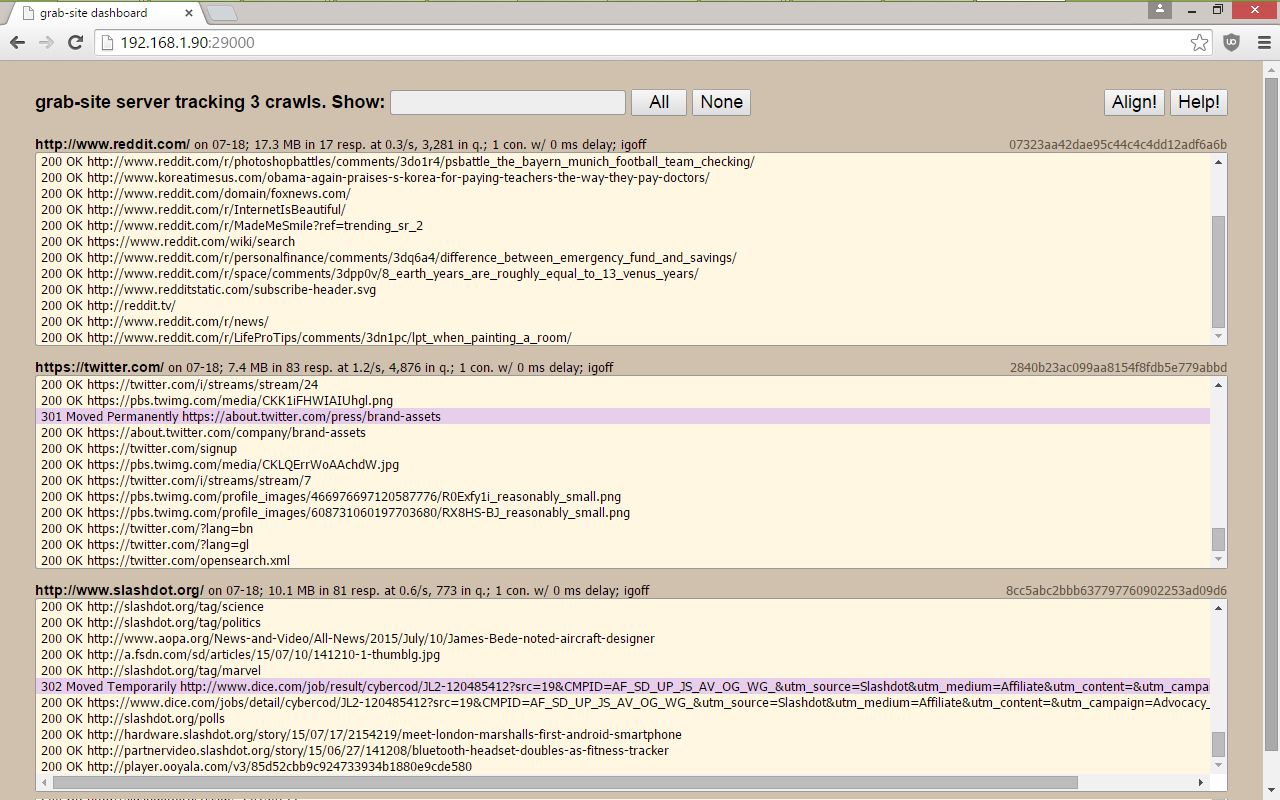
a dashboard with all of your crawls, showing which URLs are being grabbed, how many URLs are left in the queue, and more.
-
the ability to add ignore patterns when the crawl is already running. This allows you to skip the crawling of junk URLs that would otherwise prevent your crawl from ever finishing. See below.
-
an extensively tested default ignore set (global) as well as additional (optional) ignore sets for forums, reddit, etc.
-
duplicate page detection: links are not followed on pages whose content duplicates an already-seen page.
The URL queue is kept on disk instead of in memory. If you're really lucky, grab-site will manage to crawl a site with ~10M pages.
Note: if you have any problems whatsoever installing or getting grab-site to run, please file an issue - thank you!
The installation methods below are the only ones supported in our GitHub issues. Please do not modify the installation steps unless you really know what you're doing, with both Python packaging and your operating system. grab-site runs on a specific version of Python (3.7 or 3.8) and with specific dependency versions.
Contents
- Install on Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04, 22.04, Debian 10 (buster), Debian 11 (bullseye)
- Install on NixOS
- Install on another distribution lacking Python 3.7.x or 3.8.x
- Install on macOS
- Install on Windows 10 (experimental)
- Upgrade an existing install
- Usage
- Changing ignores during the crawl
- Inspecting the URL queue
- Preventing a crawl from queuing any more URLs
- Stopping a crawl
- Advanced
gs-serveroptions - Viewing the content in your WARC archives
- Inspecting WARC files in the terminal
- Automatically pausing grab-site processes when free disk is low
- Thanks
- Help
Install on Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04, 22.04, Debian 10 (buster), Debian 11 (bullseye)
-
On Debian, use
suto become root ifsudois not configured to give you access.sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install --no-install-recommends \ wget ca-certificates git build-essential libssl-dev zlib1g-dev \ libbz2-dev libreadline-dev libsqlite3-dev libffi-dev libxml2-dev \ libxslt1-dev libre2-dev pkg-configIf you see
Unable to locate package, run the two commands again. -
As a non-root user:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pyenv/pyenv-installer/master/bin/pyenv-installer chmod +x pyenv-installer ./pyenv-installer ~/.pyenv/bin/pyenv install 3.8.15 ~/.pyenv/versions/3.8.15/bin/python -m venv ~/gs-venv ~/gs-venv/bin/pip install --no-binary lxml --upgrade git+https://github.com/ArchiveTeam/grab-site--no-binary lxmlis necessary for the html5-parser build. -
Add this to your
~/.bashrcor~/.zshrc:PATH="$PATH:$HOME/gs-venv/bin"and then restart your shell (e.g. by opening a new terminal tab/window).
Install on NixOS
As a non-root user:
nix-env -f https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/archive/release-22.11.tar.gz -iA grab-site
Install on another distribution lacking Python 3.7.x or 3.8.x
grab-site and its dependencies are available in nixpkgs, which can be used on any Linux distribution.
-
As root:
Where
USERis your non-root username:mkdir /nix chown USER:USER /nix -
As the non-root user, install Nix: https://nixos.org/nix/download.html
-
As the non-root user:
nix-env -f https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/archive/release-22.11.tar.gz -iA grab-siteand then restart your shell (e.g. by opening a new terminal tab/window).
Install on macOS
On OS X 10.10 - macOS 11:
-
Run
localein your terminal. If the output includes "UTF-8", you are all set. If it does not, your terminal is misconfigured and grab-site will fail to start. This can be corrected with:-
Terminal.app: Preferences... -> Profiles -> Advanced -> check Set locale environment variables on startup
-
iTerm2: Preferences... -> Profiles -> Terminal -> Environment -> check Set locale variables automatically
-
Using Homebrew (Intel Mac)
For M1 Macs, use the next section instead of this one.
-
Install Homebrew using the install step on https://brew.sh/
-
Run:
brew update brew install [email protected] libxslt re2 pkg-config /usr/local/opt/[email protected]/bin/python3 -m venv ~/gs-venv PKG_CONFIG_PATH="/usr/local/opt/libxml2/lib/pkgconfig" ~/gs-venv/bin/pip install --no-binary lxml --upgrade git+https://github.com/ArchiveTeam/grab-site -
To put the
grab-sitebinaries in your PATH, add this to your~/.zshrc(macOS 10.15, 11+) or~/.bash_profile(earlier):PATH="$PATH:$HOME/gs-venv/bin"and then restart your shell (e.g. by opening a new terminal tab/window).
Using Homebrew (M1 Mac)
-
Install Homebrew using the install step on https://brew.sh/
If you already have a Homebrew install at
/usr/local, you may need to first remove that old Intel-based Homebrew install. -
Run:
brew update brew install [email protected] libxslt re2 pkg-config /opt/homebrew/opt/[email protected]/bin/python3 -m venv ~/gs-venv PKG_CONFIG_PATH="/opt/homebrew/opt/libxml2/lib/pkgconfig" ~/gs-venv/bin/pip install --no-binary lxml --upgrade git+https://github.com/ArchiveTeam/grab-site -
To put the
grab-sitebinaries in your PATH, add this to your~/.zshrc(macOS 10.15, 11+) or~/.bash_profile(earlier):PATH="$PATH:$HOME/gs-venv/bin"and then restart your shell (e.g. by opening a new terminal tab/window).
Install on Windows 10 (experimental)
On Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (1703) or newer:
-
Start menu -> search "feature" -> Turn Windows features on or off
-
Scroll down, check "Windows Subsystem for Linux" and click OK.
-
Wait for install and click "Restart now"
-
Start menu -> Store
-
Search for "Ubuntu" in the store and install Ubuntu (publisher: Canonical Group Limited).
-
Start menu -> Ubuntu
-
Wait for install and create a user when prompted.
-
Follow the Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04, 22.04, Debian 10 (buster), Debian 11 (bullseye) steps.
Upgrade an existing install
To update grab-site, simply run the ~/gs-venv/bin/pip install ... or
nix-env ... command used to install it originally (see above).
After upgrading, stop gs-server with kill or ctrl-c, then start it again.
Existing grab-site crawls will automatically reconnect to the new server.
Usage
First, start the dashboard with:
gs-server
and point your browser to http://127.0.0.1:29000/
Note: gs-server listens on all interfaces by default, so you can reach the dashboard by a non-localhost IP as well, e.g. a LAN or WAN IP. (Sub-note: no code execution capabilities are exposed on any interface.)
Then, start as many crawls as you want with:
grab-site 'URL'
Do this inside tmux unless they're very short crawls.
grab-site outputs WARCs, logs, and control files to a new subdirectory in the
directory from which you launched grab-site, referred to here as "DIR".
(Use ls -lrt to find it.)
You can pass multiple URL arguments to include them in the same crawl,
whether they are on the same domain or different domains entirely.
warcprox users: warcprox breaks the dashboard's WebSocket; please make your browser skip the proxy for whichever host/IP you're using to reach the dashboard.
grab-site options, ordered by importance
Options can come before or after the URL.
-
--1: grab justURLand its page requisites, without recursing. -
--igsets=IGSET1,IGSET2: use ignore setsIGSET1andIGSET2.Ignore sets are used to avoid requesting junk URLs using a pre-made set of regular expressions. See the full list of available ignore sets.
The global ignore set is implied and enabled unless
--no-global-igsetis used.The ignore sets can be changed during the crawl by editing the
DIR/igsetsfile. -
--no-global-igset: don't add the global ignore set. -
--no-offsite-links: avoid following links to a depth of 1 on other domains.grab-site always grabs page requisites (e.g. inline images and stylesheets), even if they are on other domains. By default, grab-site also grabs linked pages to a depth of 1 on other domains. To turn off this behavior, use
--no-offsite-links.Using
--no-offsite-linksmay prevent all kinds of useful images, video, audio, downloads, etc from being grabbed, because these are often hosted on a CDN or subdomain, and thus would otherwise not be included in the recursive crawl. -
-i/--input-file: Load list of URLs-to-grab from a local file or from a URL; likewget -i. File must be a newline-delimited list of URLs. Combine with--1to avoid a recursive crawl on each URL. -
--igon: Print all URLs being ignored to the terminal and dashboard. Can be changed during the crawl bytouching orrming theDIR/igofffile. This is slower because it needs to find the specific regexp to blame. -
--no-video: Skip the download of videos by both mime type and file extension. Skipped videos are logged toDIR/skipped_videos. Can be changed during the crawl bytouching orrming theDIR/videofile. -
--no-sitemaps: don't queue URLs fromsitemap.xmlat the root of the site. -
--max-content-length=N: Skip the download of any response that claims a Content-Length larger thanN. (default: -1, don't skip anything). Skipped URLs are logged toDIR/skipped_max_content_length. Can be changed during the crawl by editing theDIR/max_content_lengthfile. -
--no-dupespotter: Disable dupespotter, a plugin that skips the extraction of links from pages that look like duplicates of earlier pages. Disable this for sites that are directory listings, because they frequently trigger false positives. -
--concurrency=N: UseNconnections to fetch in parallel (default: 2). Can be changed during the crawl by editing theDIR/concurrencyfile. -
--delay=N: WaitNmilliseconds (default: 0) between requests on each concurrent fetcher. Can be a range like X-Y to use a random delay between X and Y. Can be changed during the crawl by editing theDIR/delayfile. -
--import-ignores: Copy this file to toDIR/ignoresbefore the crawl begins. -
--warc-max-size=BYTES: Try to limit each WARC file to aroundBYTESbytes before rolling over to a new WARC file (default: 5368709120, which is 5GiB). Note that the resulting WARC files may be drastically larger if there are very large responses. -
--level=N: recurseNlevels instead ofinflevels. -
--page-requisites-level=N: recurse page requisitesNlevels instead of5levels. -
--ua=STRING: Send User-Agent:STRINGinstead of pretending to be Firefox on Windows. -
--id=ID: Use idIDfor the crawl instead of a random 128-bit id. This must be unique for every crawl. -
--dir=DIR: Put control files, temporary files, and unfinished WARCs inDIR(default: a directory name based on the URL, date, and first 8 characters of the id). -
--finished-warc-dir=FINISHED_WARC_DIR: absolute path to a directory into which finished.warc.gzand.cdxfiles will be moved. -
--permanent-error-status-codes=STATUS_CODES: A comma-separated list of HTTP status codes to treat as a permanent error and therefore not retry (default:401,403,404,405,410). Other error responses tried another 2 times for a total of 3 tries (customizable with--wpull-args=--tries=N). Note that, unlike wget, wpull puts retries at the end of the queue. -
--wpull-args=ARGS: String containing additional arguments to pass to wpull; seewpull --help.ARGSis split withshlex.splitand individual arguments can contain spaces if quoted, e.g.--wpull-args="--youtube-dl \"--youtube-dl-exe=/My Documents/youtube-dl\""Examples:
--wpull-args=--no-skip-getaddrinfoto respect/etc/hostsentries.--wpull-args=--no-warc-compressionto write uncompressed WARC files.
-
--which-wpull-args-partial: Print a partial list of wpull arguments that would be used and exit. Excludes grab-site-specific features, and removesDIR/from paths. Useful for reporting bugs on wpull without grab-site involvement. -
--which-wpull-command: PopulateDIR/but don't start wpull; instead print the command that would have been used to start wpull with all of the grab-site functionality. -
--debug: print a lot of debug information. -
--help: print help text.
Warnings
If you pay no attention to your crawls, a crawl may head down some infinite bot trap and stay there forever. The site owner may eventually notice high CPU use or log activity, then IP-ban you.
grab-site does not respect robots.txt files, because they frequently
whitelist only approved robots,
hide pages embarrassing to the site owner,
or block image or stylesheet resources needed for proper archival.
See also.
Because of this, very rarely you might run into a robot honeypot and receive
an abuse@ complaint. Your host may require a prompt response to such a complaint
for your server to stay online. Therefore, we recommend against crawling the
web from a server that hosts your critical infrastructure.
Don't run grab-site on GCE (Google Compute Engine); as happened to me, your entire API project may get nuked after a few days of crawling the web, with no recourse. Good alternatives include OVH (OVH, So You Start, Kimsufi), and online.net's dedicated and Scaleway offerings.
Tips for specific websites
Website requiring login / cookies
Log in to the website in Chrome or Firefox. Use the cookies.txt extension
for Chrome or
for Firefox
extension to copy Netscape-format cookies. Paste the cookies data into a new
file. Start grab-site with --wpull-args=--load-cookies=ABSOLUTE_PATH_TO_COOKIES_FILE.
Static websites; WordPress blogs; Discourse forums
The defaults usually work fine.
Blogger / blogspot.com blogs
The defaults work fine except for blogs with a JavaScript-only Dynamic Views theme.
Some blogspot.com blogs use "Dynamic Views"
themes that require JavaScript and serve absolutely no HTML content. In rare
cases, you can get JavaScript-free pages by appending ?m=1
(example). Otherwise, you
can archive parts of these blogs through Google Cache instead
(example)
or by using https://archive.is/ instead of grab-site.
Tumblr blogs
Either don't crawl from Europe (because tumblr redirects to a GDPR /privacy/consent page), or add Googlebot to the user agent:
--ua "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:64.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/70.0 but not really nor Googlebot/2.1"
Use --igsets=singletumblr
to avoid crawling the homepages of other tumblr blogs.
If you don't care about who liked or reblogged a post, add \?from_c= to the
crawl's ignores.
Some tumblr blogs appear to require JavaScript, but they are actually just hiding the page content with CSS. You are still likely to get a complete crawl. (See the links in the page source for https://X.tumblr.com/archive).
Subreddits
Use --igsets=reddit
and add a / at the end of the URL to avoid crawling all subreddits.
When crawling a subreddit, you must get the casing of the subreddit right for the recursive crawl to work. For example,
grab-site https://www.reddit.com/r/Oculus/ --igsets=reddit
will crawl only a few pages instead of the entire subreddit. The correct casing is:
grab-site https://www.reddit.com/r/oculus/ --igsets=reddit
You can hover over the "Hot"/"New"/... links at the top of the page to see the correct casing.
Directory listings ("Index of ...")
Use --no-dupespotter to avoid triggering false positives on the duplicate
page detector. Without it, the crawl may miss large parts of the directory tree.
Very large websites
Use --no-offsite-links to stay on the main website and avoid crawling linked pages on other domains.
Websites that are likely to ban you for crawling fast
Use --concurrency=1 --delay=500-1500.
MediaWiki sites with English language
Use --igsets=mediawiki.
Note that this ignore set ignores old page revisions.
MediaWiki sites with non-English language
You will probably have to add ignores with translated Special:* URLs based on
ignore_sets/mediawiki.
Forums that aren't Discourse
Forums require more manual intervention with ignore patterns.
--igsets=forums
is often useful for non-SMF forums, but you will have to add other ignore
patterns, including one to ignore individual-forum-post pages if there are
too many posts to crawl. (Generally, crawling the thread pages is enough.)
GitHub issues / pull requests
Find the highest issue number from an issues page (example) and use:
grab-site --1 https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/{1..30000}
This relies on your shell to expand the argument to thousands of arguments.
If there are too many arguments, you may have to write the URLs to a file
and use grab-site -i instead:
for i in {1..30000}; do echo https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/$i >> .urls; done
grab-site --1 -i .urls
Websites whose domains have just expired but are still up at the webhost
Use a DNS history
service to find the old IP address (the DNS "A" record) for the domain. Add a
line to your /etc/hosts to point the domain to the old IP. Start a crawl
with --wpull-args=--no-skip-getaddrinfo to make wpull use /etc/hosts.
twitter.com/user
Use snscrape to get a list
of tweets for a user. Redirect snscrape's output to a list of URLs with
> urls and pass this file to grab-site --1 -i urls.
Alternatively, use webrecorder.io instead of grab-site. It has an autoscroll feature and you can download the WARCs.
Keep in mind that scrolling twitter.com/user returns a maximum of 3200 tweets,
while a from:user
query can return more.
Changing ignores during the crawl
While the crawl is running, you can edit DIR/ignores and DIR/igsets; the
changes will be applied within a few seconds.
DIR/igsets is a comma-separated list of ignore sets to use.
DIR/ignores is a newline-separated list of Python 3 regular expressions
to use in addition to the ignore sets.
You can rm DIR/igoff to display all URLs that are being filtered out
by the ignores, and touch DIR/igoff to turn it back off.
Note that ignores will not apply to any of the crawl's start URLs.
Inspecting the URL queue
Inspecting the URL queue is usually not necessary, but may be helpful for adding ignores before grab-site crawls a large number of junk URLs.
To dump the queue, run:
gs-dump-urls DIR/wpull.db todo
Four other statuses can be used besides todo:
done, error, in_progress, and skipped.
You may want to pipe the output to sort and less:
gs-dump-urls DIR/wpull.db todo | sort | less -S
Preventing a crawl from queuing any more URLs
rm DIR/scrape. Responses will no longer be scraped for URLs. Scraping cannot
be re-enabled for a crawl.
Stopping a crawl
You can touch DIR/stop or press ctrl-c, which will do the same. You will
have to wait for the current downloads to finish.
Advanced gs-server options
These environmental variables control what gs-server listens on:
GRAB_SITE_INTERFACE(default0.0.0.0)GRAB_SITE_PORT(default29000)
These environmental variables control which server each grab-site process connects to:
GRAB_SITE_HOST(default127.0.0.1)GRAB_SITE_PORT(default29000)
Viewing the content in your WARC archives
Try ReplayWeb.page or webrecorder-player.
Inspecting WARC files in the terminal
zless is a wrapper over less that can be used to view raw WARC content:
zless DIR/FILE.warc.gz
zless -S will turn off line wrapping.
Note that grab-site requests uncompressed HTTP responses to avoid double-compression in .warc.gz files and to make zless output more useful. However, some servers will send compressed responses anyway.
Automatically pausing grab-site processes when free disk is low
If you automatically upload and remove finished .warc.gz files, you can still run into a situation where grab-site processes fill up your disk faster than your uploader process can handle. To prevent this situation, you can customize and run this script, which will pause and resume grab-site processes as your free disk space crosses a threshold value.
Thanks
grab-site is made possible only because of wpull, written by Christopher Foo who spent a year making something much better than wget. ArchiveTeam's most pressing issue with wget at the time was that it kept the entire URL queue in memory instead of on disk. wpull has many other advantages over wget, including better link extraction and Python hooks.
Thanks to David Yip, who created ArchiveBot. The wpull hooks in ArchiveBot served as the basis for grab-site. The original ArchiveBot dashboard inspired the newer dashboard now used in both projects.
Thanks to Falcon Darkstar Momot for the many wpull 2.x fixes that were rolled into ArchiveTeam/wpull.
Thanks to JustAnotherArchivist for investigating my wpull issues.
Thanks to BrowserStack for providing free browser testing for grab-site, which we use to make sure the dashboard works in various browsers.
Help
grab-site bugs and questions are welcome in grab-site/issues.
Terminal output in your bug report should be surrounded by triple backquotes, like this:
``` very long output ```
Please report security bugs as regular bugs.