Introduction
ProtoQuill is the Scala 3 version of Quill: Free/Libre Compile-time Language Integrated Queries for Scala. For those migrating, or exploring migration from Scala2-Quill, most Queries written in Scala2-Quill should work readily in ProtoQuill but they will become Dynamic. Change them to inline def expressions and they should once-again be compile-time (see the Rationale section for some info on why I chose to do this). Also see the Migration Notes section.
Not all Contexts and not all Functionality is Supported yet. Here is a rough list of both:
Currently Supported:
- Basic Quotation, Querying, Lifting, and Types (Compile-Time and Dynamic)
- Inner/Outer, Left/Right joins
- Query.map/flatMap/concatMap/filter other query constructs.
- Insert, Update, Delete Actions (Compile-Time and Dynamic)
- Batch Insert, Batch Update, and Batch Delete Actions, both Compile-Time and Runtime! (Scala2-Quill only supports Compile-Time batch queries)
- ZIO, Synchronous JDBC, and Jasync Postgres contexts.
- SQL OnConflict Clauses
- Prepare Query (i.e.
context.prepare(query)) - Translate Query (i.e.
context.translate(query)) - Cassandra Contexts (using V4 drivers!)
- Dynamic Query API (i.e. this)
Not Supported:
- Implicit class based extensions. Please see the Extensions section below on how to do this.
Planned Future Support
- Monix JDBC (and Cassandra) Contexts (Coming Soon!)
- OrientDB Contexts
- Spark Context
There are also quite a few new features that ProtoQuill has:
- Scala Methods and Typeclasses Transforming ProtoQuill queries (see Shareable Code and Advanced Example).
- Custom Parsing - Write parsers for custom user code!
- Co-Product Rows (Highly experimental, use with caution!)
- Caliban-Integration (Experimental deep integration with Caliban. Trivially filter/exclude any columns you want!)
- Dependent Contexts - In Scala2-Quill Dependent Contexts were demonstrated as a typical example of the limitations of working with Quoted blocks. In ProtoQuill these work as expected since there are no path dependant types in the ProtoQuill output. Have a look at this scastie example for more information.
One other note that this documentation is not yet a fully-fledged reference for ProtoQuill features. Have a look at the original Quill documentation for basic information about how Quill constructs (e.g. Queries, Joins, Actions, Batch Actions, etc...) are written in lieu of any documentation missing here.
For further information, watch:
- ProtoQuill Release Party - Overview of new Quill features in Scala 3 and discussion about the future of Metaprogramming.
- Quill, Dotty, And The Awesome Power of 'Inline' - Many examples of new things that can be done with this library that cannot be done with standard Quill.
- ScQuilL Sessions - Quill, Dotty, and Macros - A tutorial on developing Dotty-Quill from scratch (covers quoting, liftables, and liftables).
- Generic Derivation is the New Reflection - A tutorial on how Dotty Generic Derivation works covering a Dotty-Quill use-case.
Getting Started
The simplest way to get started with ProtoQuill is with the standard JDBC contexts. These are sychronous so for a high-throughput system you will ultimately need to switch to either the ZIO-based contexts, Jasync, or the Monix ones (Monix contexts coming soon!)
Add the following to your SBT file:
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
// Syncronous JDBC Modules
"io.getquill" %% "quill-jdbc" % "4.5.0",
// Or ZIO Modules
"io.getquill" %% "quill-jdbc-zio" % "4.5.0",
// Or Postgres Async
"io.getquill" %% "quill-jasync-postgres" % "4.5.0",
// Or Cassandra
"io.getquill" %% "quill-cassandra" % "4.5.0",
// Or Cassandra + ZIO
"io.getquill" %% "quill-cassandra-zio" % "4.5.0",
// Add for Caliban Integration
"io.getquill" %% "quill-caliban" % "4.5.0"
)Assuming we are using Postgres, add the following application.conf.
testPostgresDB.dataSourceClassName=org.postgresql.ds.PGSimpleDataSource
testPostgresDB.dataSource.databaseName=<my-database>
testPostgresDB.dataSource.url=<my-jdbc-url>
Have a look at this list to see how to configure other databases.
Create a context and a case class representing your table.
import io.getquill._
object MyApp {
case class Person(firstName: String, lastName: String, age: Int)
// SnakeCase turns firstName -> first_name
val ctx = new PostgresJdbcContext(SnakeCase, "ctx")
import ctx._
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val named = "Joe"
inline def somePeople = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.firstName == lift(named))
}
val people: List[Person] = run(somePeople)
// TODO Get SQL
println(people)
}
}Tutorial
Queries
ProtoQuill queries are built using inline quoted expressions.
// With just this import you can use quote, query, insert/update/delete and lazyLift
import io.getquill._
inline def people = quote {
query[Person]
}
inline def joes = quote {
people.filter(p => p.name == "Joe")
}
> You *do not* need to import a context in ProtoQuill to make a quoation, just `io.getquill._`. Contexts are only needed for lifting. See the `Lifting and Lazy Lifting` section for more detail.
run(joes)
// TODO Get SQLQuotation is (Mostly) Optional
If all parts of a Query are inline def, quotation is not strictly necessary:
inline def people = query[Person]
inline def joes = people.filter(p => p.name == "Joe")
run(joes)
// TODO Get SQLHowever, if parts of the the query are dynamic (i.e. not inline def) it is needed:
inline def people = quote {
query[Person]
}
val joes = quote {
people.filter(p => p.name == "Joe")
}
run(joes)
// TODO Warning Dynamic QueryQuoted Operations
ProtoQuill supports Quill query[T] constructs including:
- Outer/Inner, Left/Right Join (both monadic and applicative)
- Map, FlatMap, ConcatMap
- Union, Union-All
- Distinct, Nested
- querySchema
Please refer to quotation-queries in the Scala2-Quill documentation for more information.
Keep in mind that in ProtoQuill for these to generate compile-time queries, they need to be inline def.
Batch Queries
ProtoQuill supports Insert/Update/Delete actions as well as their batch variations.
Please refer to quotation-actions in the Scala2-Quill documentation for more information.
Keep in mind that in ProtoQuill for these to generate compile-time queries, they need to be inline def.
The onConflict instructions are not yet supported in ProtoQuill.
In the latest release, ProtoQuill supports the full range of batch queries that Scala2-Quill supports, including:
// batch queries with different entities
liftQuery(vips).foreach(v => query[Person].insertValue(Person(v.first + v.last, v.age)))
// batch queries with scalars
liftQuery(List(1,2,3)).foreach(i => query[Person].filter(p => p.id == i).update(_.age -> 123))
// batch queries with additional lifts
liftQuery(people).foreach(p => query[Person].filter(p => p.age > lift(123)).contains(p.age)).updateValue(p))
// ...even with additional liftQuery clauses!
liftQuery(people).foreach(p => query[Person].filter(p => p.age > lift(123) && liftQuery(List(1,2,3)).contains(p.age)).updateValue(p))
// batch queries with `returning` clauses
liftQuery(vips).foreach(v => query[Person].insertValue(Person(v.first + v.last, v.age)).returning(_.id))Metas
QueryMeta, SchemaMeta, InsertMeta, and UpdateMeta are supported in ProtoQuill.
Please refer to meta-dsl in the Scala2-Quill documentation for more information.
Keep in mind that in ProtoQuill for these to generate compile-time queries, they need to be inline def.
Additionally, they can be defined using Scala 3 given syntax:
// SchemaMeta
inline given SchemaMeta[Person] = schemaMeta("PersonTable", name -> "nameRow")
// Insert Meta
inline given InsertMeta[Person] = insertMeta(_.id)
// Update Meta
inline given UpdateMeta[Person] = updateMeta(_.id)This also works with QueryMeta:
inline given QueryMeta[PersonName, String] =
queryMeta(
quote {
(q: Query[PersonName]) => q.map(p => p.name)
}
)((name: String) => PersonName(name))
val result = ctx.run(people)
// TODO Get SQLShareable Code
Since quotation of inline def code is optional, Quill expressions can share code with regular Scala constructs.
// case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
inline def onlyJoes(p: Person) = p.name == "Joe"
run( query[Person].filter(p => onlyJoes(p)) )
// TODO Get SQL
val people: List[Person] = ...
val joes = people.filter(p => onlyJoes(p))Advanced Example
Since Quill expressions can share code with regular Scala constructs, this can be generalized into higher-level constructs such as typeclasses.
// case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
trait Filterable[F[_]]:
extension [A](inline x: F[A])
inline def filter(inline f: A => Boolean): F[A]
extension [F[_]](inline people: F[Person])(using inline filterable: Filterable[F])
inline def onlyJoes = people.filter(p => p.name == "Joe")
class ListFilterable extends Filterable[List]:
extension [A](inline xs: List[A])
inline def filter(inline f: A => Boolean): List[A] = xs.filter(f)
class QueryFilterable extends Filterable[List]:
extension [A](inline xs: List[A])
inline def filter(inline f: A => Boolean): List[A] = xs.filter(f)
run( query[Person].onlyJoes )
// GET SQL
val people: List[Person] = ...
val joes = people.onlyJoesUsing this technique, a standard functor-hierarchy can be constructed that can be used for compile-time generation of Quill Queries. Have a look at the Typeclass-series examples for more inspiration.
Lifting and Lazy Lifting
Since Quill-Quotations define blocks of compile-time-inspectable code, adding variables whose value is only know during runtime typically requires lifting:
// NOTE: Be sure to import a context first!
// val ctx = new MirrorSqlContext(PostgresDialect, Literal); import ctx._
val runtimeValue = somethingFromSomewhere() // A value that we only know during runtime
inline def somePeople = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.name == lift(runtimeValue))
}
val results: List[Person] = run(somePeople)
// TODO Get SQLHowever, since Quotation in ProtoQuill is static, you can use lazyLift to lift a value without importing a context. The advantage of this is that you can lift things before what context to use.
import io.getquill._
val name = ...
inline def q = quote { query[Person].filter(p => p.name == lift(name)) }
// Now we can use this quotation in multiple contexts
{
val ctx = new PostgresJdbcContext(Literal, "ctx")
val results = ctx.run(q)
// TODO Get SQL
}
{
val ctx = new H2JdbcContext(Literal, "ctx")
val results = ctx.run(q)
// TODO Get SQL
}Note however that for lazy-lifts to work, for a query, all of it's parts need to be inline def. That is to say, Dynamic Queries do not work with lazyLift.
How it Works
Internally, the lift-method will use the mechanisms of the underlying database-layer (e.g. JDBC) to lift the runtimeValue ultimately swapping it into the "?" location using some kind of prepared statement. This is typically handled by the encoders.
/* Note that is an approximate example! Not actual Quill code. */
trait Encoders:
implicit val stringEncoder: Encoder[String] =
JdbcEncoder(sqlType, (index: Int, value: String, row: PrepareRow) => {
row.setString(index, value)
row
})
class MyDatabaseContext(...) with Encoders
def lift(value: T)(using Encoder[T]) = ...Note that the above is only a conceptual model of how
liftworks. In reality it needs to be implemented using Scala 3 Macros in order to function properly.
This means that in order to do lifting we must first import a context.
// Must do this:
val ctx = new MyDatabaseContext()
import ctx._
// Before Doing this:
inline def somePeople = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.name == lift(runtimeValue))
}Unlike lift, lazyLift does not require a encoder to be imported at the call-site because it delays summoning the encoder until the run function.
inline def somePeople = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.name == lazyLift(runtimeValue))
}
// Need to import a context only for the `run` function.
val ctx = new MyDatabaseContext()
import ctx._
val result: List[Person] = run(somePeople) // summons Encoder[String] hereConceptually, lazyLift can be thought of like this:
// Return some kind of information that can be evaluated later when an encoder is summoned
def lift(value: T) = (encoder: Encoder[T]) => encoder.encode(t)
class MyDatabaseContext:
def run(q: Quoted[Query[T]]) =
val statement = prepareStatement(q)
val t = q.lifts(0)
statement.prepare(1, summon[Encoder[T]].encode(t)) // Summon the actual encoder at the `run` site.Again, please note that this is not the actual Quill code, this is just a conceptual model of how it works.
Filtering Tables by Key/Values
On typical use-case that ProtoQuill can do (which has been difficult in the past) is to filter a query based on an arbitrary group of column/value pairs. This is typically done with Http-Based systems where URL-parameters &key=value are decoded as a map. In ProtoQuill, the filterByKeys addresses this use-case.
val values: Map[String, String] = Map("firstName" -> "Joe", "age" -> "22")
// filterByKeys uses lift so you need a context to use it
val ctx = new MirrorContext(Literal, PostgresDialect)
import ctx._
inline def q = quote {
query[Person].filterByKeys(values)
}
run(q)
// SELECT p.firstName, p.lastName, p.age
// FROM Person p
// WHERE
// (p.firstName = ? OR ? IS NULL) AND
// (p.lastName = ? OR ? IS NULL) AND
// (p.age = ? OR ? IS NULL) AND
// trueThe way that this works is that in each ? slot, the corresponding column is looked up from the map.
// SELECT p.firstName, p.lastName, p.age
// FROM Person p
// WHERE
// (p.firstName = { values("firstName") } OR { values("firstName") } IS NULL) AND
// (p.lastName = { values("lastName") } OR { values("lastName") } IS NULL) AND
// (p.age = { values("age") } OR { values("age") } IS NULL) AND
// true
Co-Product Rows
Co-Product are supported using Enums and sealed traits. Keep in mind that for now, only static-global enums are supported and any sealed traits that are used must be sealed in a separate object in order to work. Otherwise a sum-type mirror of them will not be found. In ORM-terms, Quill uses a "Table Per Class-Hierarchy" model of co-product polymorhism in which data for all co-products must be encodeable within a simple row.
Note: As a possible avenue of exploration, this approach can be combined with QueryMeta to relax the requirement of having a single table for all coproducts since QueryMeta can be used to produce a set of joins under the facade of being a single table.
To use co-product rows do the following:
- Create the Coproduct
object StaticEnumExample { enum Shape(val id: Int): case Square(override val id: Int, width: Int, height: Int) extends Shape(id) case Circle(override val id: Int, radius: Int) extends Shape(id) }
Note: Currently all Enums used for Co-Product rows need to be in a static namespace (i.e. in an Object). This is due a Dotty/Scala3 issue.
- Create an object called a row-typer which will take a Database row and figure out how what element of the coproduct to decode into.
given RowTyper[Shape] with def apply(row: Row) = row.apply[String]("type") match case "square" => classTag[Shape.Square] case "circle" => classTag[Shape.Circle]
- Create and run your query:
inline def q = quote { query[Shape].filter(s => s.id == 18) } val result: List[Shape] = ctx.run(q)
Custom Parsing
The Parser API has been refined considerably in ProtoQuill Beta2 and it is now in a ready state.
Reason for This
In Quill you can define methods (including extension methods) that return quoted sections. This is typically used for user-defined logic:
import io.getquill._
object MyBusinessLogic:
extension (inline i: Int)
inline def **(exponent: Int) = quote { sql"power($i, $exponent)" }
def main(args: Array[String]) =
import MyBusinessLogic._
run( query[Person].map(p => p.age ** 2 )
// SELECT power(p.age, 2) FROM Person pHowever, it is entirely possible that you might also want to use these Business-Logic constructs in regular Scala code:
object MyBusinessLogicNonQuill: // Need to define a different object that does non-quill logic
extension (inline i: Int)
inline def **(exponent: Int) = Math.pow(i, exponent)
val ageSquared = person.age ** 2This is cumbersome because multiple objects need to be defined for the two implementations that this power-method (i.e. **) needs to be.
For this reason, ProtoQuill supports an easy extension syntax for custom parsing. It works like this:
Syntax
- First, define your business logic and methods as usual:
object MyBusinessLogic: // Be sure that Nothing is inline here! extension (i: Int) def **(exponent: Int) = Math.pow(i, exponent)
- Then define a parser to handle this construct:
Note that these to steps need to be done in a separate compilation unit. That typically means that you need to make a separate SBT project with this logic that is compiled before the rest of your application code.
import io.getquill.parser._ import io.getquill.ast.{ Ast, Infix } import io.getquill.quat.Quat case class CustomOperationsParser(root: Parser[Ast] = Parser.empty)(override implicit val qctx: Quotes) extends Parser.Clause[Ast] { import quotes.reflect._ import CustomOps._ def reparent(newRoot: Parser[Ast]) = this.copy(root = newRoot) def delegate: PartialFunction[Expr[_], Ast] = case '{ ($i: Int)**($j: Int) } => Infix( List("power(", " ,", ")"), List(astParse(i), astParse(j)), true, Quat.Value) } object CustomParser extends ParserLibrary: import Parser._ override def operationsParser(using qctx: Quotes) = Series.of(new OperationsParser, new CustomOperationsParser)
- Now in your application code, you can use the custom parser after defing it as a given (or implicit)
given myParser: CustomParser.type = CustomParser import MyBusinessLogic._ case class Person(name: String, age: Int) inline def q = quote { query[Person].map(p => p.age ** 2) } // SELECT power(p.age ,2) FROM Person p
Migration Notes
- Most Scala2-Quill code should either work in ProtoQuill directly or require minimal changes in order to work.
However, since ProtoQuill compile-time queries rely on
inline def, these queries must be changed from this:To this:case class Person(name: String, age: Int) val people = quote { query[Person] } val joes = quote { people.filter(p => p.name == "Joe") } run(joes) // Dynamic Query Detected
case class Person(name: String, age: Int) inline def people = quote { query[Person] } inline def joes = quote { people.filter(p => p.name == "Joe") } run(joes) // SELECT p.name, p.age FROM Person p WHERE p.name = 'Joe'
- If you have not implemented
io.getquill._or are importing components one by one, you will need to add this import. Unlike in Scala2-Quill where methods such asquery,quote, etc... come from your context (e.g. inval ctx = new PostgresJdbcContext(...); import ctx._), in ProtoQuill these methods come from the Dsl object which is exported toio.getquill. If you want to import the minimal amount of components, you will at least needio.getquill.quoteandio.getquill.query. - TBD: Warnings will occur when there are encoders for some type T but not decoders for it. This is due to possible Quat issues.
- TBD: The
Embeddedconstruct is not strictly required in some cases (review cases, Embedded[T] summon is also supported).
Extensions
ProtoQuill supports standard Dotty extensions. An inline extension will yield a compile-time query.
case class Person(first: String, last: String)
extension (inline p: Person) // make sure this variable is `inline`
inline def fullName = p.first + " " + p.last
run( query[Person].map(p => p.fullName) )
// SELECT p.name || ' ' || p.age FROM Person pIn Scala2-Quill, this kind of extension was supported by a hacky use of implicit classes:
implicit class PersonExpt(p: Person)
def fullName = p.first + " " + p.last
run( query[Person].map(p => p.fullName) )
// SELECT p.name || ' ' || p.age FROM Person p
This latter kind of extension mechanism is not yet supported and ProtoQuill but will likely be eventually supported for backwards-compatibility reasons. The Queries in which it is used will inherently become Dynamic.
Rationale for Inline
For a basic reasoning of why Inline was chosen (instead of Refined-Types on val expressions) have a look at the video: Quill, Dotty, And The Awesome Power of 'Inline'. A more thorough explination is TBD.
Caliban Integration
Experimental Caliban integration is provided by the quill-caliban module. This makes it relatively easy to setup a Caliban GraphQL endpoint where you can filter by any column returned from a Quill query as well as include/exclude any column, and these exclusions are pushed down to the database (In Spark-speak, these are called filter-pushdown, predicate-pushdown respectively). In order to setup the Caliban integration, do the following:
// Import Quill
import io.getquill._
// Import the Caliban integration
import io.getquill.CalibanIntegration._
// Given some simple schema
case class PersonT(id: Int, first: String, last: String, age: Int)
case class AddressT(ownerId: Int, street: String)
case class PersonAddress(id: Int, first: String, last: String, age: Int, street: Option[String])
// Create a query and add .filterColumns and .filterByKeys to the end
inline def peopleAndAddresses(inline columns: List[String], inline filters: Map[String, String]) =
quote {
// Given a query...
query[Person].leftJoin(query[Address]).on((p, a) => p.id == a.ownerId)
.map((p, a) => PersonAddress(p.id, p.first, p.last, p.age, a.map(_.street)))
// Add these to the end
.filterColumns(columns)
.filterByKeys(filters)
}
// Create a data-source that will pass along the column include/exclude and filter information
object DataService:
def personAddress(columns: List[String], filters: Map[String, String]) =
run(q(columns, filters)).provide(Has(myDataSource))
// Assume this returns:
// List(
// PersonAddress(1, "One", "A", 44, Some("123 St")),
// PersonAddress(2, "Two", "B", 55, Some("123 St")),
// PersonAddress(3, "Three", "C", 66, None),
// )
// Create your Caliban Endpoint
case class Queries(
personAddress: Field => (ProductArgs[PersonAddress] => Task[List[PersonAddress]])
)
// Implement the endpoint
val endpoint =
graphQL(
RootResolver(
Queries(
personAddress =>
(productArgs =>
DataService.personAddress(
quillColumns(personAddress) /* From CalibanIntegration module*/,
productArgs.keyValues
)
)
)
)
).interpreter
// Test-run the endpoint like this! (make sure not use the 'query' variable or it will collide with Quill!):
val calibanQuery =
"""
{
# Filter by any field in PersonAddress here including first, last, age, street! (or any combination of filters!)
personAddressFlat(first: "Joe") {
# Include/Exclude any fields from PersonAddress here!
id
last
street
}
}"""
val output =
zio.Runtime.default.unsafeRun(for {
interpreter <- api.interpreter
result <- interpreter.execute(calibanQuery)
} yield (result)
)
// The following data will be returned:
output.data.toString == """{"personAddress":[{"id":1,"first":"One","last":"A","street":"123 St"}]}"""You can also plug in this Caliban endpoint into ZIO-Http
object CalibanExample extends zio.App:
val myApp = for {
_ <- Dao.resetDatabase()
interpreter <- endpoints
_ <- Server.start(
port = 8088,
http = Http.route { case _ -> Root / "api" / "graphql" =>
ZHttpAdapter.makeHttpService(interpreter)
}
)
.forever
} yield ()
override def run(args: List[String]): ZIO[ZEnv, Nothing, ExitCode] =
myApp.exitCode
end CalibanExampleHave a look at the Quill-Caliban Examples here and the Quill-Caliban tests here.
How it works
When the .filterColumns(columns) and the .filterByKeys(filters) methods are called, the following query (that results from the Person<->Address table join):
SELECT
p.id, p.first, p.last, p.age, a.street
FROM
Person p
LEFT JOIN Address a ON p.id = a.ownerId...becomes this:
SELECT
CASE WHEN ? THEN p.id ELSE null END,
CASE WHEN ? THEN p.first ELSE null END,
CASE WHEN ? THEN p.last ELSE null END,
CASE WHEN ? THEN p.age ELSE null END,
CASE WHEN ? THEN a.street ELSE null END
FROM
Person p
LEFT JOIN Address a ON p.id = a.ownerId
WHERE
(cast(CASE WHEN ? THEN p.id ELSE null END as VARCHAR) = ? OR ? IS NULL)
AND (CASE WHEN ? THEN p.first ELSE null END = ? OR ? IS NULL)
AND (CASE WHEN ? THEN p.last ELSE null END = ? OR ? IS NULL)
AND (cast(CASE WHEN ? THEN p.age ELSE null END as VARCHAR) = ? OR ? IS NULL)
AND (CASE WHEN ? THEN a.street ELSE null END = ? OR ? IS NULL)In each question mark in the SELECT and WHERE clauses, the appropriate field is selected from the columns list and filters map.
Here is roughly how that looks:
SELECT
CASE WHEN ${columns.contains("id")} THEN p.id ELSE null END,
CASE WHEN ${columns.contains("first")} THEN p.first ELSE null END,
CASE WHEN ${columns.contains("last")} THEN p.last ELSE null END,
CASE WHEN ${columns.contains("age")} THEN p.age ELSE null END,
CASE WHEN ${columns.contains("street")} THEN a.street ELSE null END
FROM
Person p
LEFT JOIN Address a ON p.id = a.ownerId
WHERE
(cast(CASE WHEN ${filters.contains("id")} THEN p.id ELSE null END as VARCHAR) = ${filters("id").orNull} OR ${${filters("id").orNull}} IS NULL)
AND (CASE WHEN ${filters.contains("first")} THEN p.first ELSE null END = ${filters("first").orNull} OR ${${filters("first").orNull}} IS NULL)
AND (CASE WHEN ${filters.contains("last")} THEN p.last ELSE null END = ${filters("last").orNull} OR ${${filters("last").orNull}} IS NULL)
AND (cast(CASE WHEN ${filters.contains("age")} THEN p.age ELSE null END as VARCHAR) = ${filters("age").orNull} OR ${${filters("age").orNull}} IS NULL)
AND (CASE WHEN ${filters.contains("street")} THEN a.street ELSE null END = ${filters("street").orNull} OR ${${filters("street").orNull}} IS NULL)The important thing to understand is that the SQL optimizer can see into these CASE WHEN (condition) clauses when condition is a static variable and then know whether the actual column on the right-hand side of the Query actually needs to be used. In Database-Speak, we would call this SARGable.
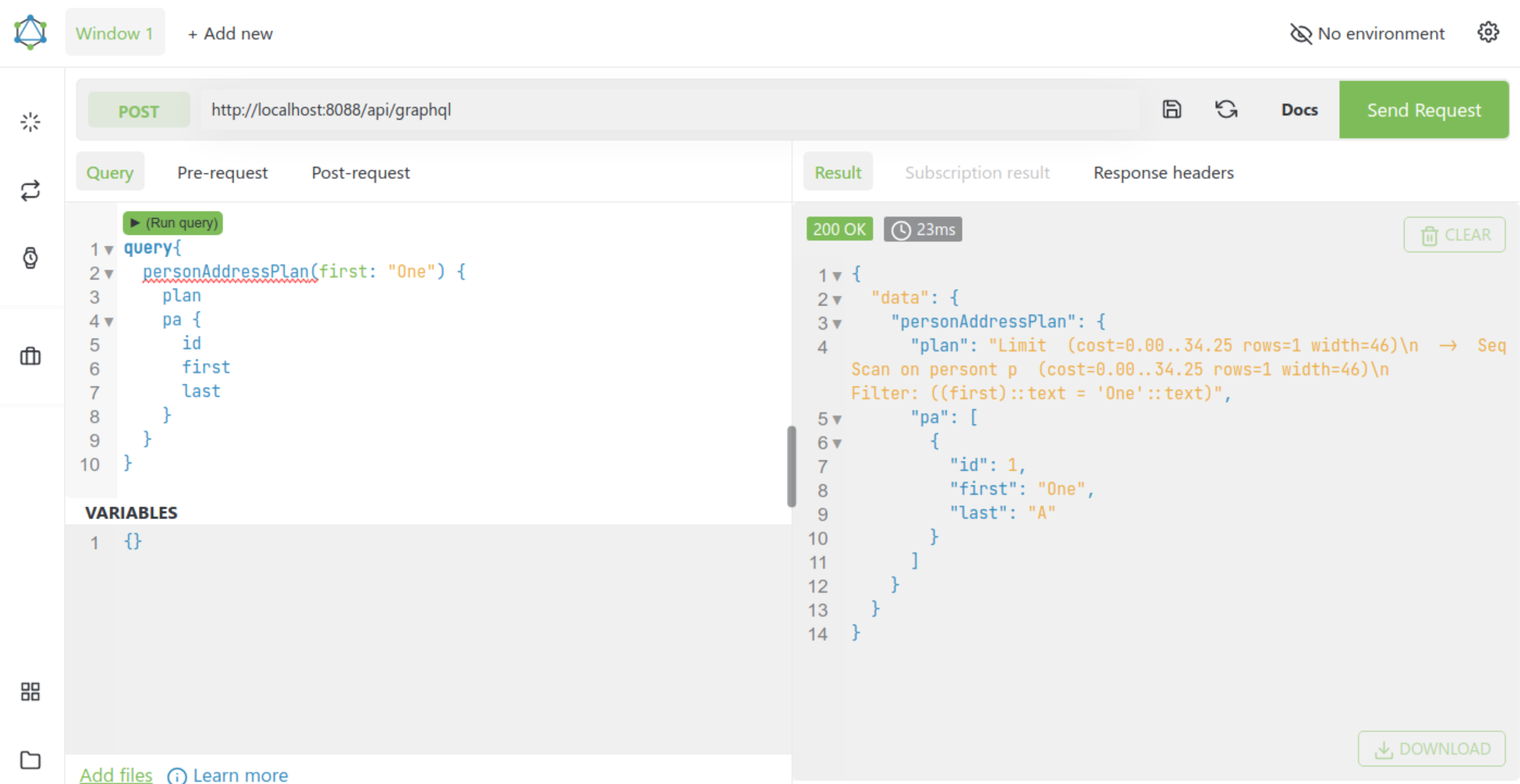
Don't take my word for it though, have a look at the examples under quill-caliban here. For example run the CalibanExample.scala and execute the following GraphQL query:
query{
personAddressPlan(first: "One") {
plan
pa {
id
street
first
last
# Exclude the street column
}
}
}
In the response you will not only the results but the Query plan as well. Note that in this particular case our Query-Planner knows that:
- We are using the filter "One" on the Person.first column.
- Since the only column we care about from the Address table is Address.street and our Query doesn't even want that column (and because in our case Person<->Address is a one-to-one relationship, that means that the table Address doesn't even need to be scanned!
As the writer of Caliban puts it... "From the front-end down to the DB, you only pay for what you ask!"
Interesting Ideas
- Implement a
lazyFilterByKeysmethod using the same logic as filterByKeys but using lazy lifts. in order to be able to use this kind of functionality with out having to import a context. - Implement a
filterByLikeswhich is the same asfilterByKeysbut useslikeinstead of==. then can also implement alazyFilterByLikes. - Write a
query.filter(p => p.firstName.inSet("foo", lift(bar), "baz"))using theListFlicer. this could either translate intoWHERE firstName == 'foo' OR firstName == ? OR firstName == 'baz'orWHERE firstName in ('foo', ?, 'baz'). - Combine MapFlicer and ListFilcer to allow up to N maps to filter each field up to N times
this would be very useful with
likein order to check that a field matches multiple patterns e.g. `... FROM Person p WHERE p.firstName like 'j%' AND p.firstName like '%e' i.e. find all people whose name starts with 'j' and ends with 'e'.