Discregrid
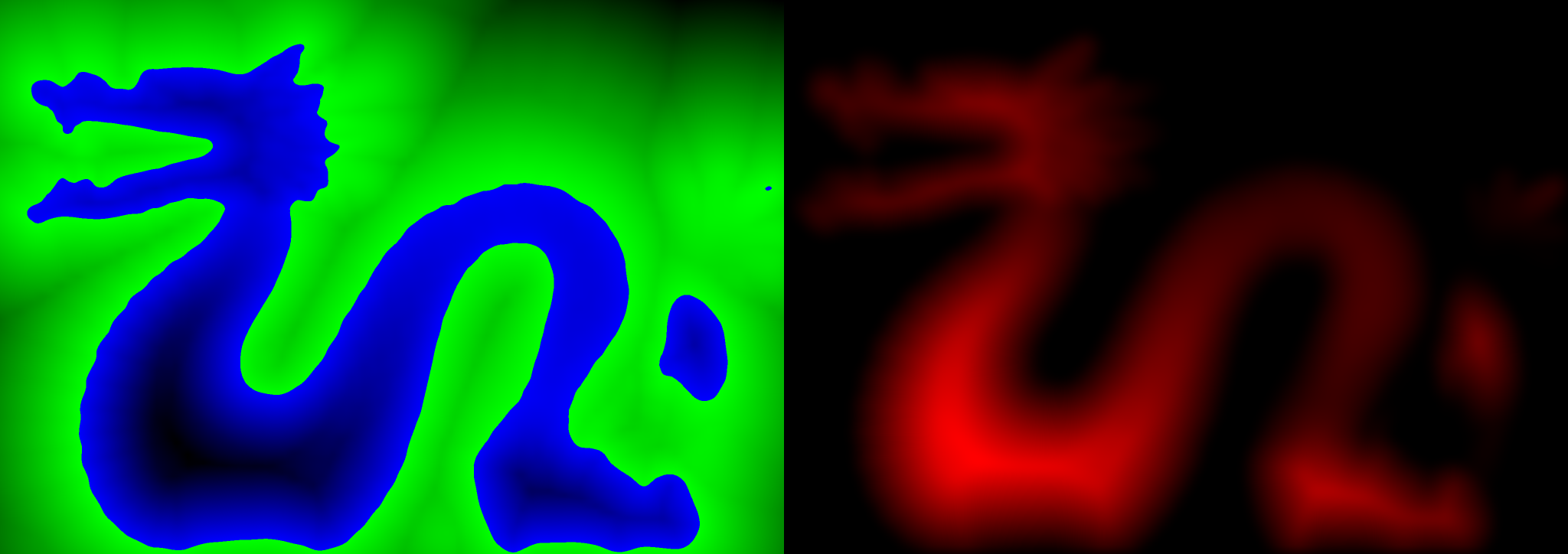
Discregrid is a static C++ library for the parallel discretization of (preferably smooth) functions on regular grids. The library generates a (cubic) polynomial discretization given a box-shaped domain, a grid resolution, and a function that maps a three-dimensional position in space to a real scalar value. Isoparametric cubic polynomials of Serendipity type for the cell-wise discretization are employed. The coefficient vector for the discrete polynomial basis is computed using regular sampling of the input function at the higher-order grid's nodes. The algorithm to generate the discretization is moreover fully parallelized using OpenMP and especially well-suited for the discretization of signed distance functions. The library moreover provides the functionality to serialize and deserialize the a generated discrete grid. Discregrid ships with TriangleMeshDistance to directly provide the capability to compute and discretize signed distance fields to triangle meshes.
Besides the library, the project includes three executable programs that serve the following purposes:
- GenerateSDF: Computes a discrete (cubic) signed distance field from a triangle mesh in OBJ format.
- DiscreteFieldToBitmap: Generates an image in bitmap format of a two-dimensional slice of a previously computed discretization.
- GenerateDensityMap: Generates a density map according to the approach presented in [KB17] from a previously generated discrete signed distance field using the widely adopted cubic spline kernel. The program can be easily extended to work with other kernel function by simply replacing the implementation in sph_kernel.hpp.
Author: Dan Koschier, License: MIT
Libraries using Discregrid
- PBD - A C++ library for physically-based simulation of rigid bodies, deformables, cloth and fluids using Position-Based Dynamics. Discregrid is used to compute discrete signed distance fields of rigid objects for collision handling purposes.
- SPlisHSPlasH - A C++ library for the physically-based simulation of fluids using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Discregrid is used to compute density maps according to my paper [KB17] for boundary handling.
Build Instructions
This project is based on CMake. Simply generate project, Makefiles, etc. using CMake and compile the project with the compiler of your choice. The code was tested with the following configurations:
- Windows 10 64-bit, CMake 3.8, Visual Studio 2017
- Debian 9 64-bit, CMake 3.8, GCC 6.3.
Usage
In order to use the library, the main header has to be included and the static library has to be compiled and linked against the client program. In this regard a find script for CMake is provided, i.e. FindDiscregrid.cmake. The main header can be included as follows:
#include <Discregrid/All>A base class for the data structure that generates and holds a discretization of a function f: R^3 -> R can be constructed as follows:
// Firstly, create a domain on which a discretization will be generated.
Eigen::AlignedBox3d domain;
// Then specify domain extents using e.g. domain.extend(...).
// Secondly, specify a grid resolution.
std::array<unsigned int, 3> resolution = {{10, 10, 10}}
// Finally, instantiate the grid.
Discregrid::CubicLagrangeDiscreteGrid discrete_grid(domain, resolution);Then, an arbitrary number of functions can be discretized on the initiated grid:
Discregrid::DiscreteGrid::ContinuousFunction func1 = ...;
Discregrid::DiscreteGrid::ContinuousFunction func2 = ...;
auto df_index1 = discrete_grid.addFunction(func1);
auto df_index2 = discrete_grid.addFunction(func2);Optionally, only coefficients at nodes fulfilling a certain predicate can be generated by specifying the predicate:
Discregrid::DiscreteGrid::ContinuousFunction func3 = ...;
auto df_index3 = discrete_grid.addFunction(func3, false, [&](Vector3d const& x)
{
...
// Return true if a certain criterion for the node location x is fulfilled, e.g.
return x.y() > 0.0;
});A value of a discrete field can be evaluated by interpolation. Additionally, the gradient at the given query point can be computed if desired.
auto val1 = sdf->interpolate(df_index1, {0.1, 0.2, 0.3});
Eigen::Vector3d grad2;
auto val2 = sdf->interpolate(df_index2, {0.3, 0.2, 0.1}, &grad2);If a discretization of the input function is only required in certain regions of the given domain, the discretization can be reduced resulting in a sparsely populated grid to save memory:
discrete_grid.reduce_field(df_index1, [](Eigen::Vector3d const& x, double v)
{
// E.g.
return x.x() < 0.0 && v > 0.0;
});Here x represents the location of sample point in the grid and v represents the sampled value of the input function. If the predicated function evaluates to true the sample point is kept but discarded otherwise.
Optionally, the data structure can be serialized and deserialized via
discrete_grid.save(filename);
discrete_grid.load(filename); // or
discrete_grid = Discregrid::CubicLagrangeDiscreteGrid(filename);References
- [KDBB17] D. Koschier, C. Deul, M. Brand and J. Bender, 2017. "An hp-Adaptive Discretization Algorithm for Signed Distance Field Generation", IEEE Transactions on Visualiztion and Computer Graphics 23, 10, 2208-2221.
- [KB17] D. Koschier and J. Bender, 2017. "Density Maps for Improved SPH Boundary Handling", ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 1-10.